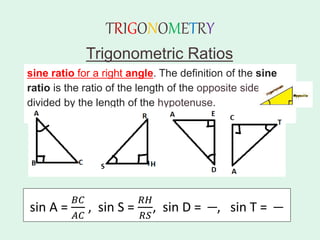
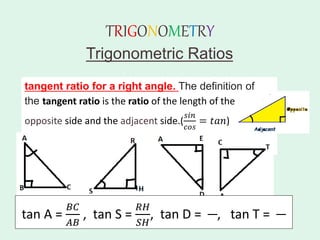
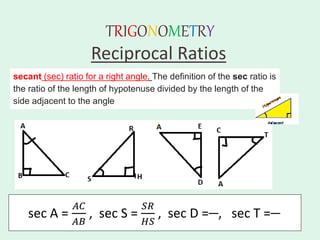
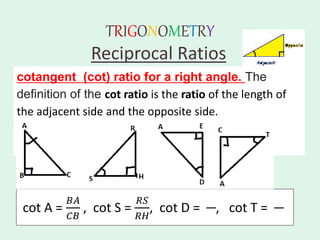
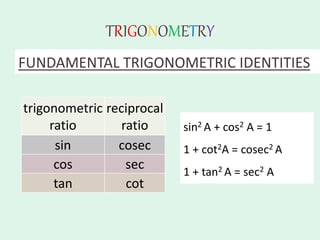
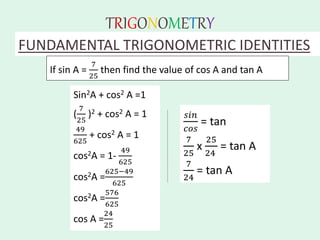
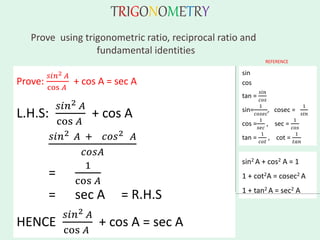
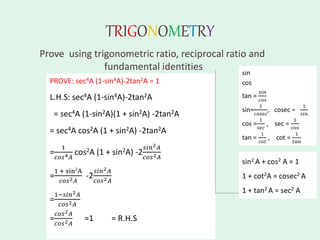
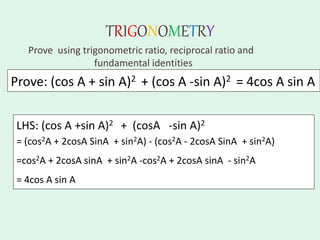
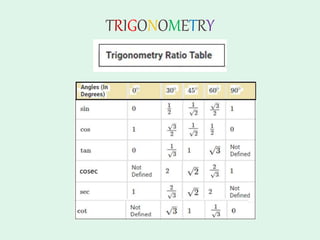
The document discusses trigonometry, covering essential concepts such as the six trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent, alongside their definitions related to right-angled triangles. It also presents fundamental identities and formulas for calculating relations among these ratios, providing examples and proofs for various trigonometric identities. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for understanding trigonometric functions and their applications.