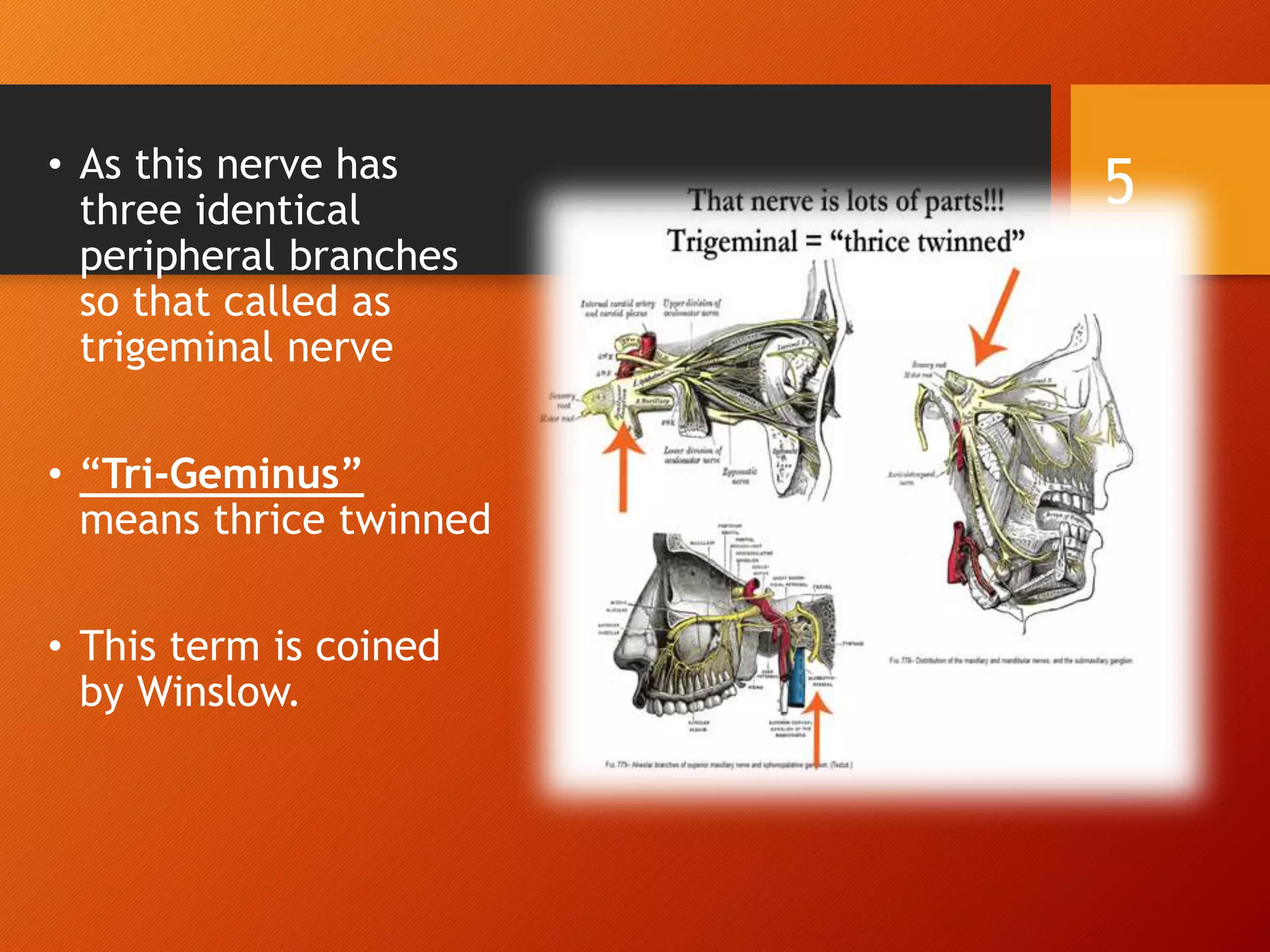
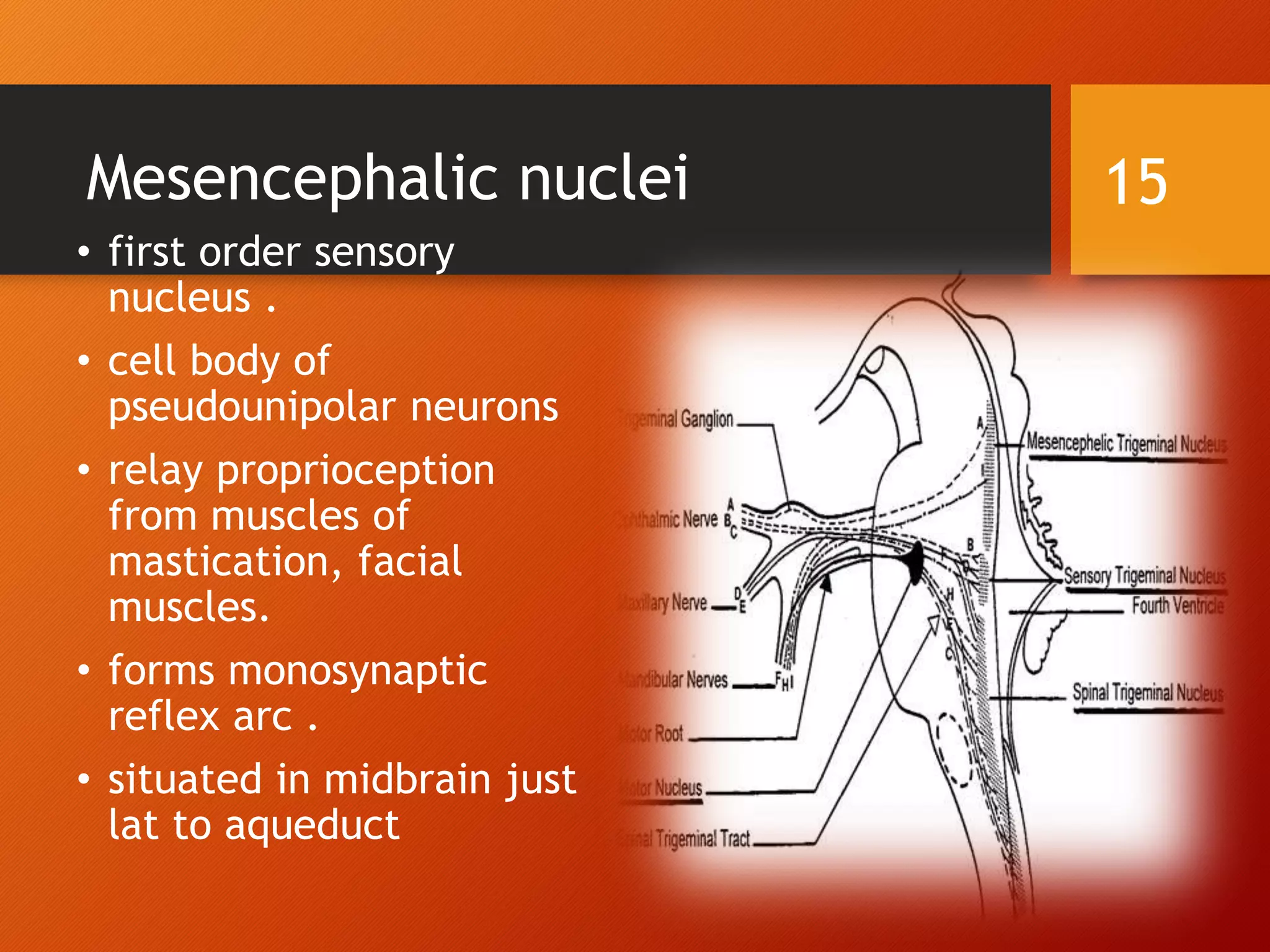
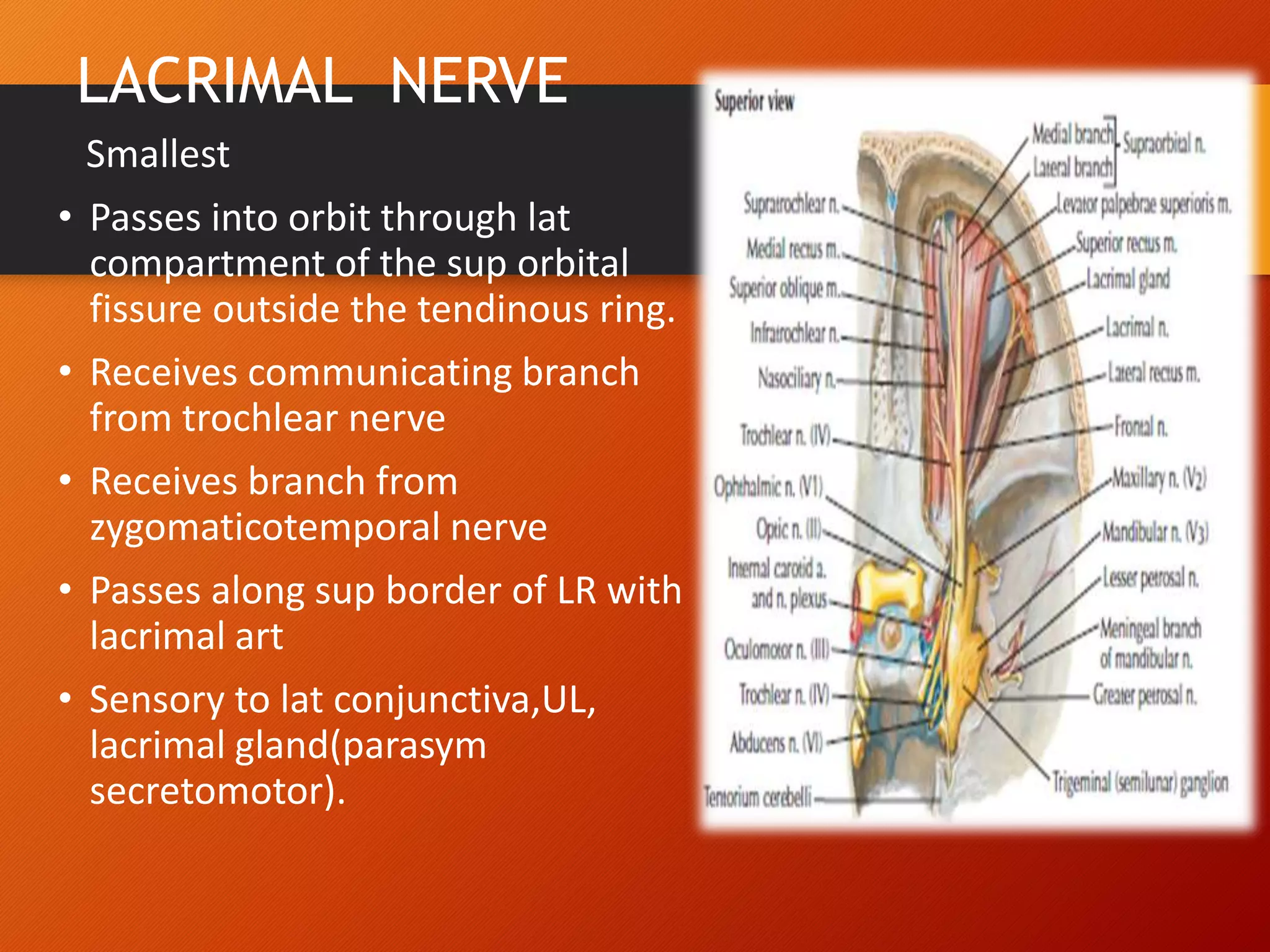
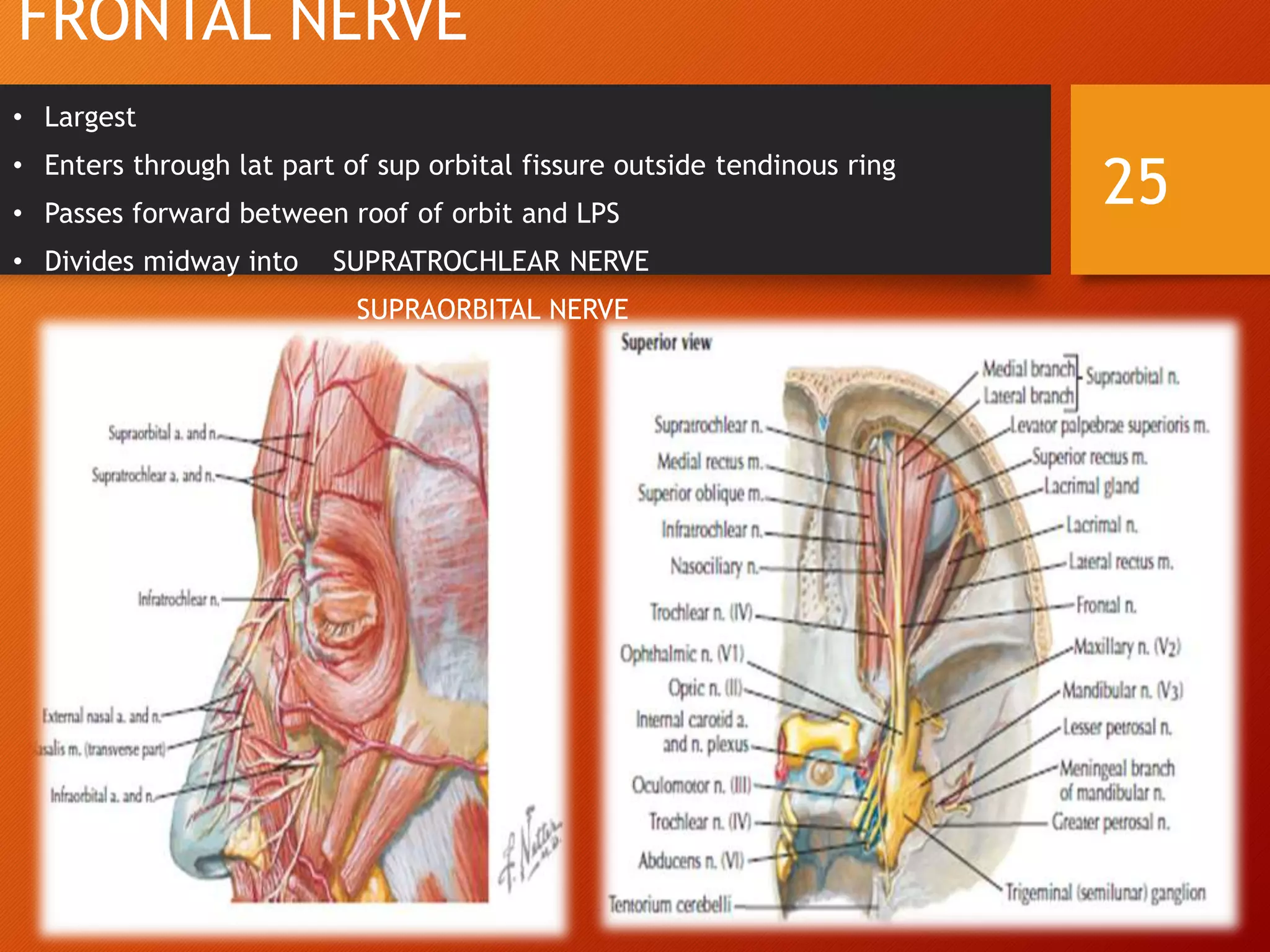
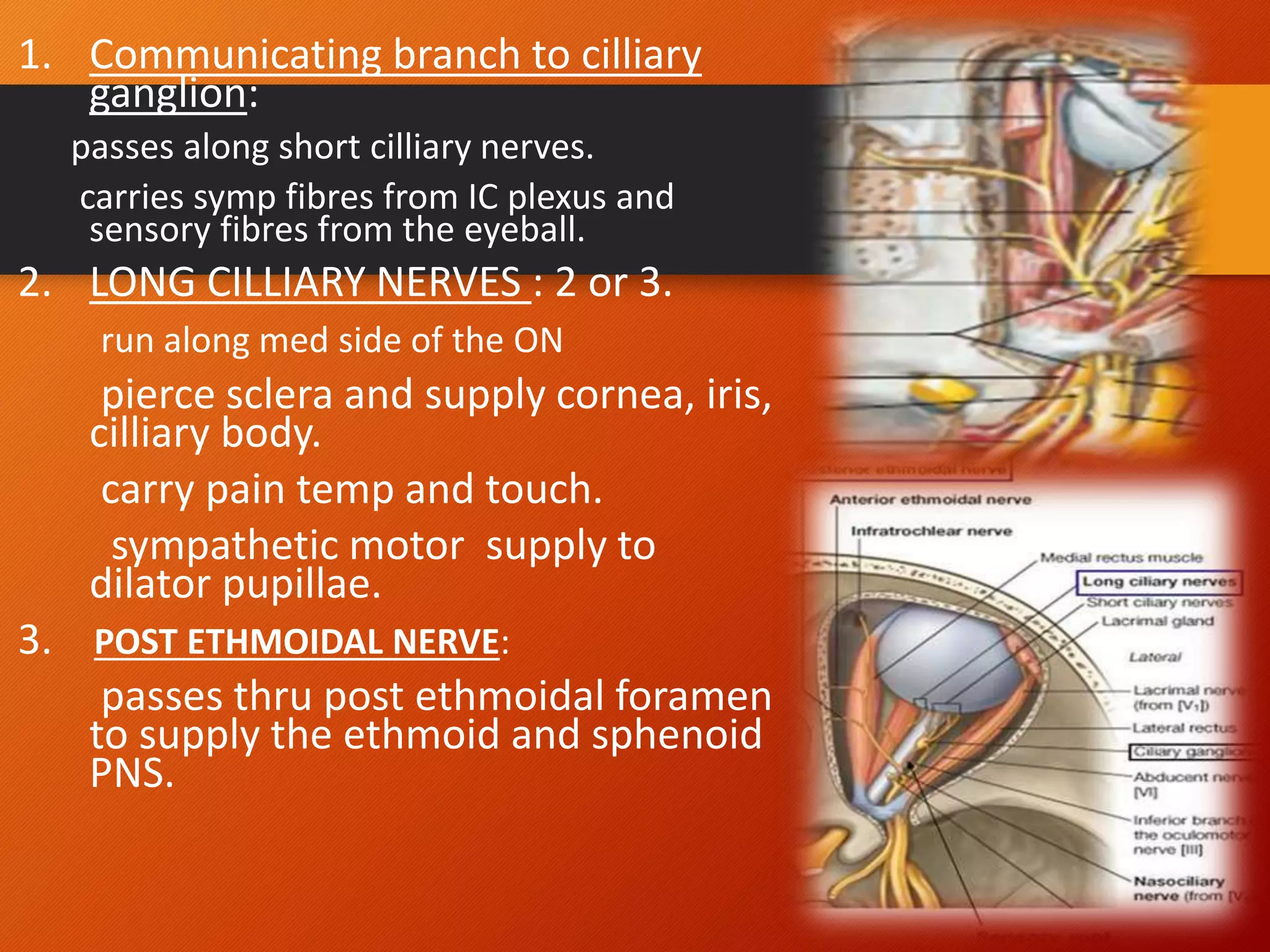
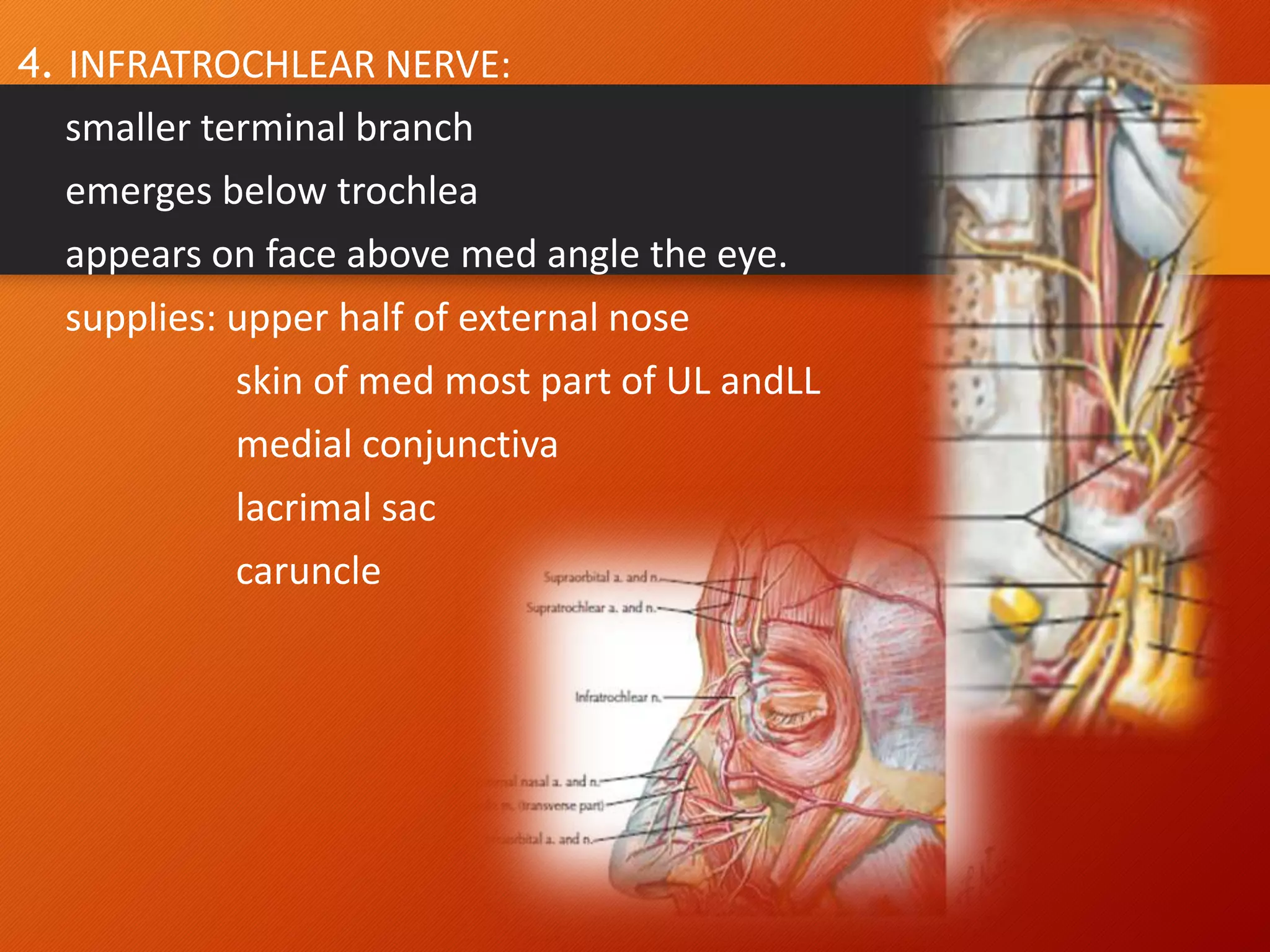
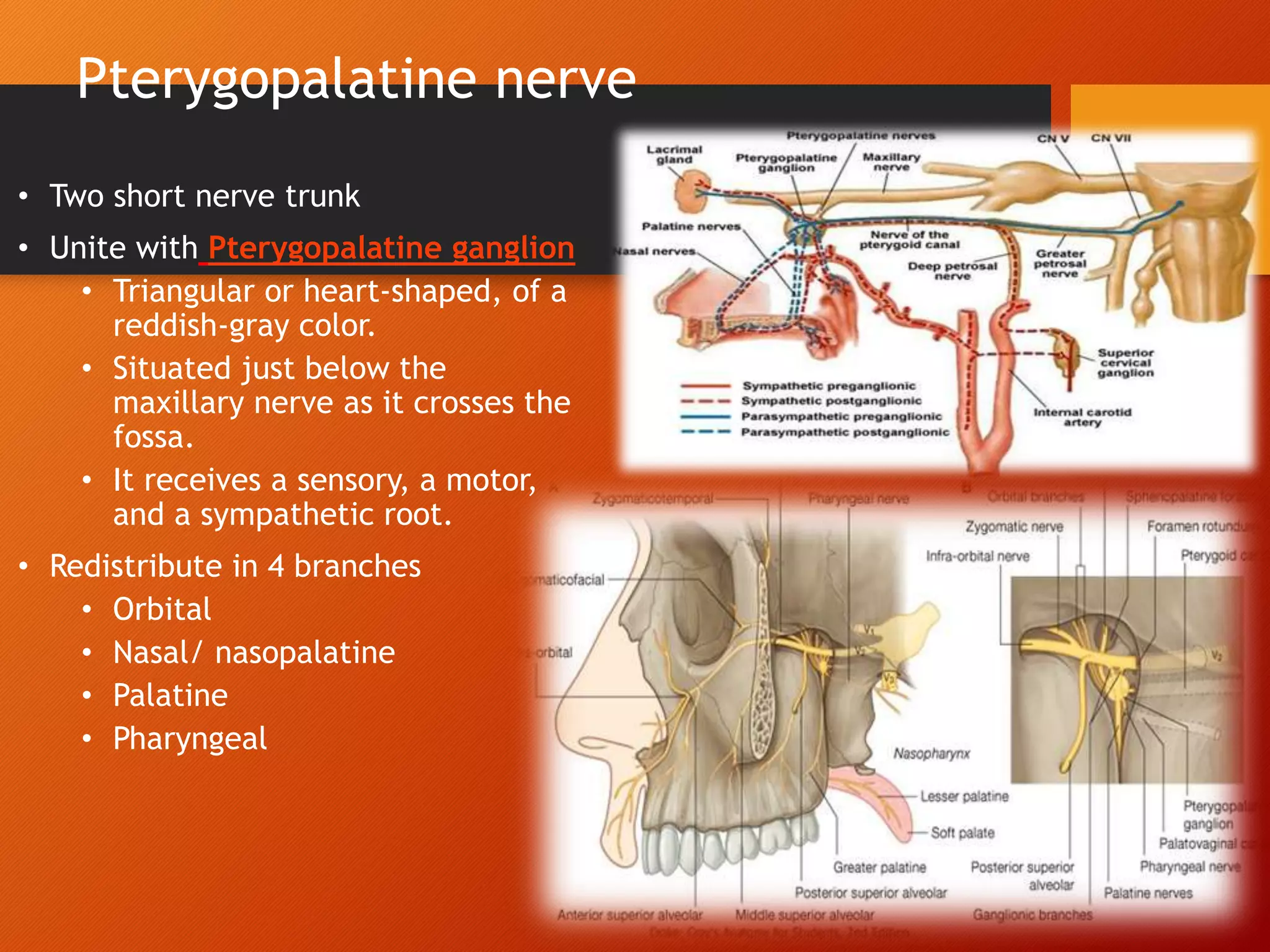
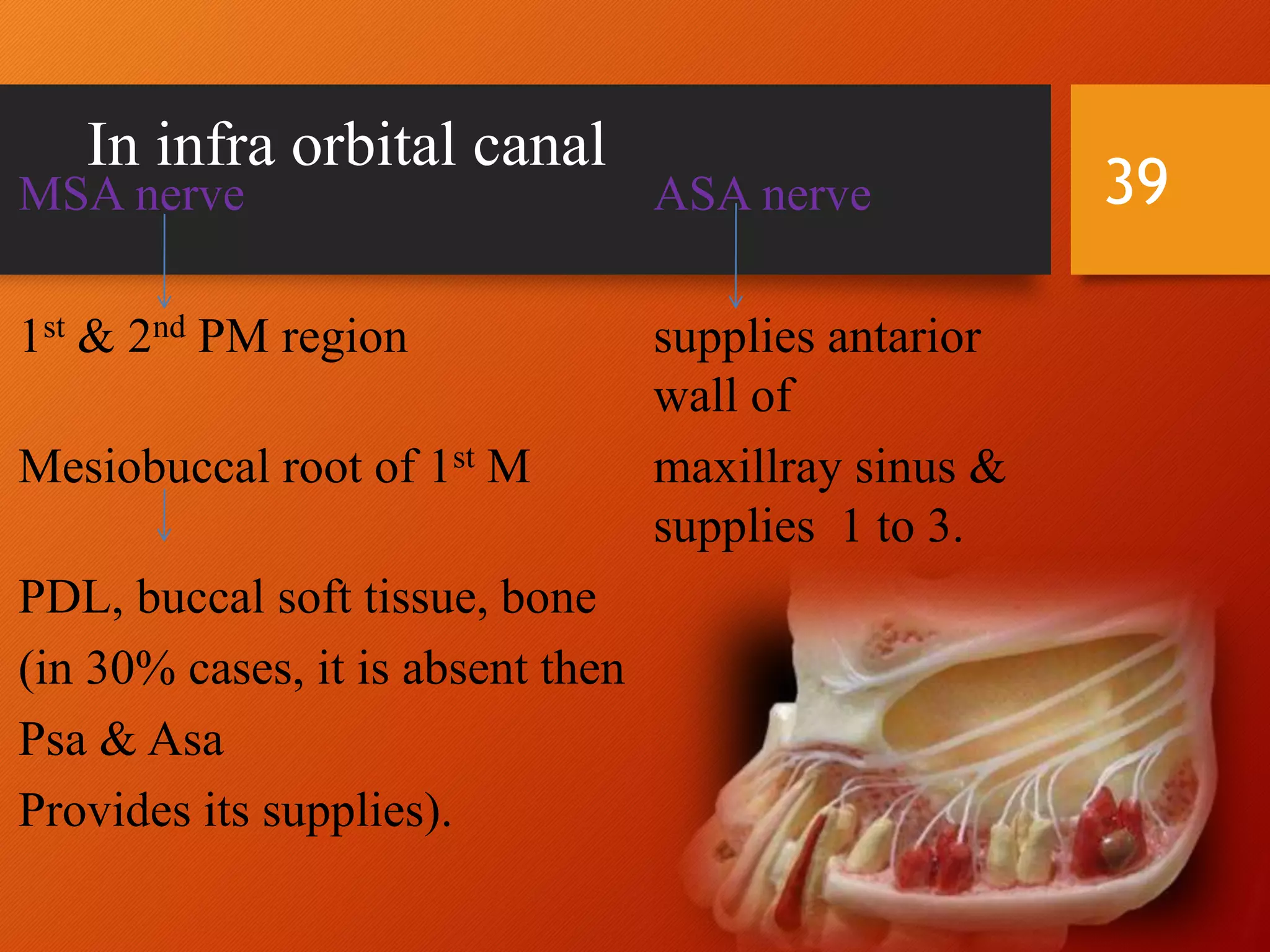
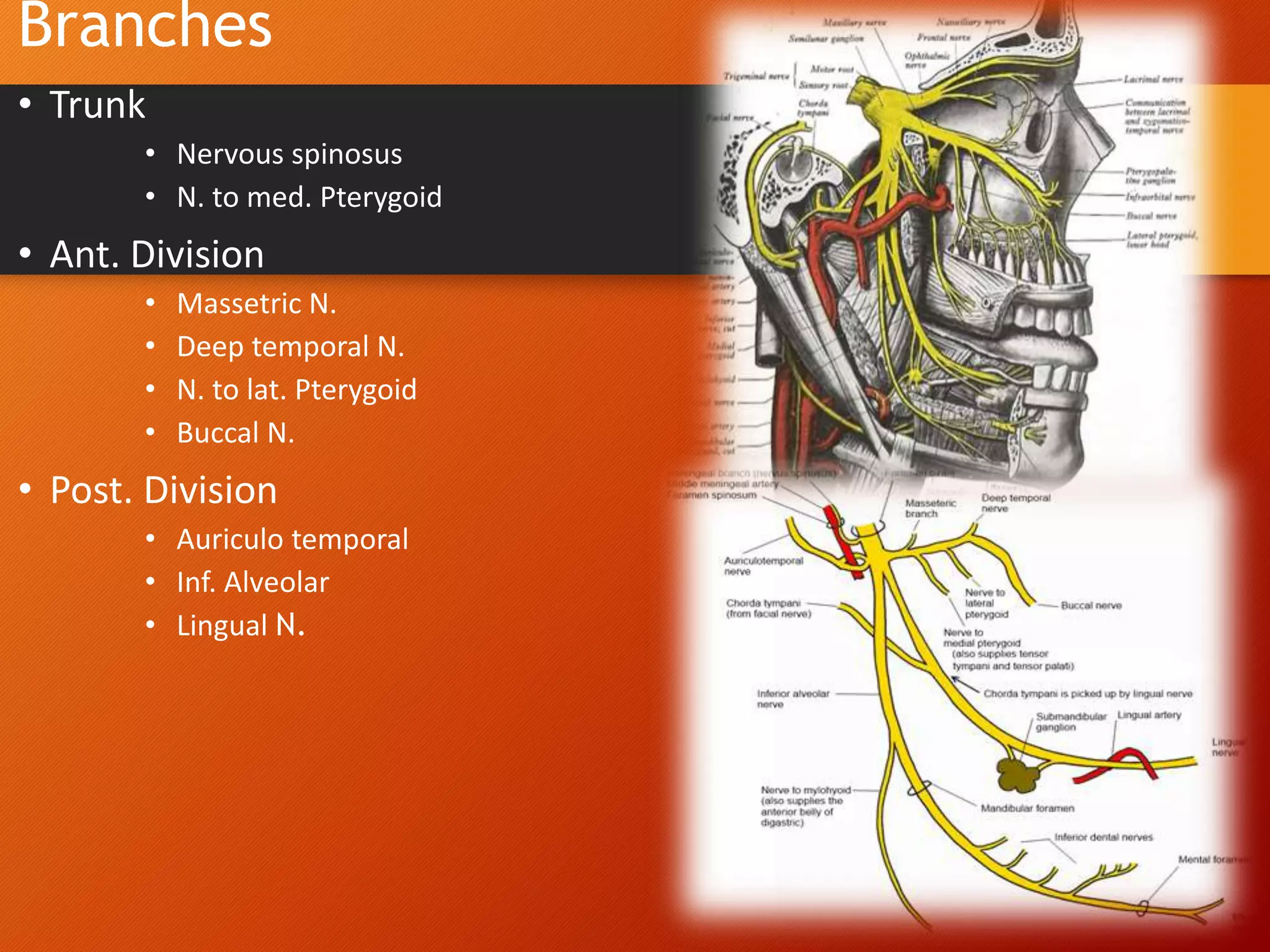
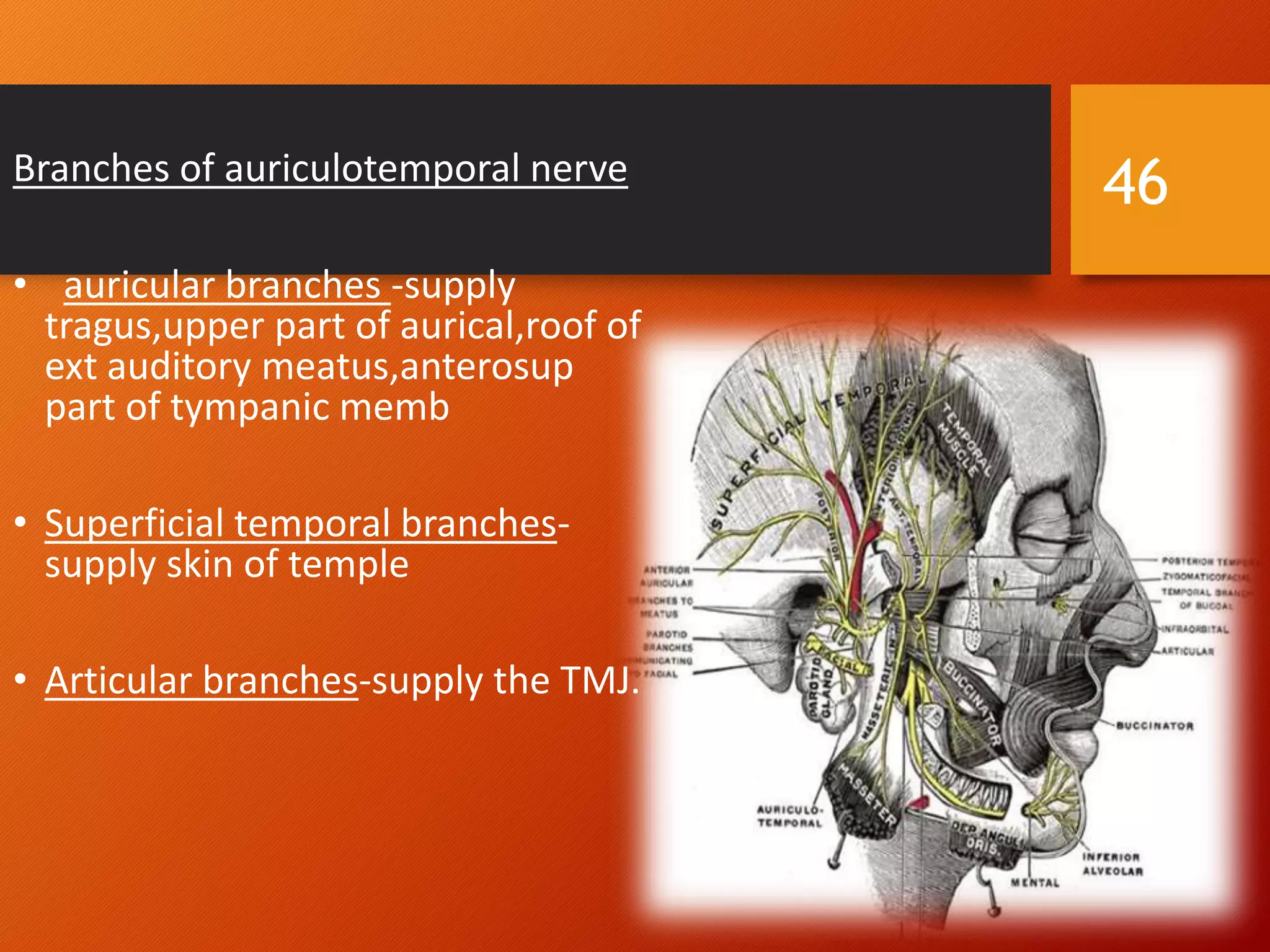
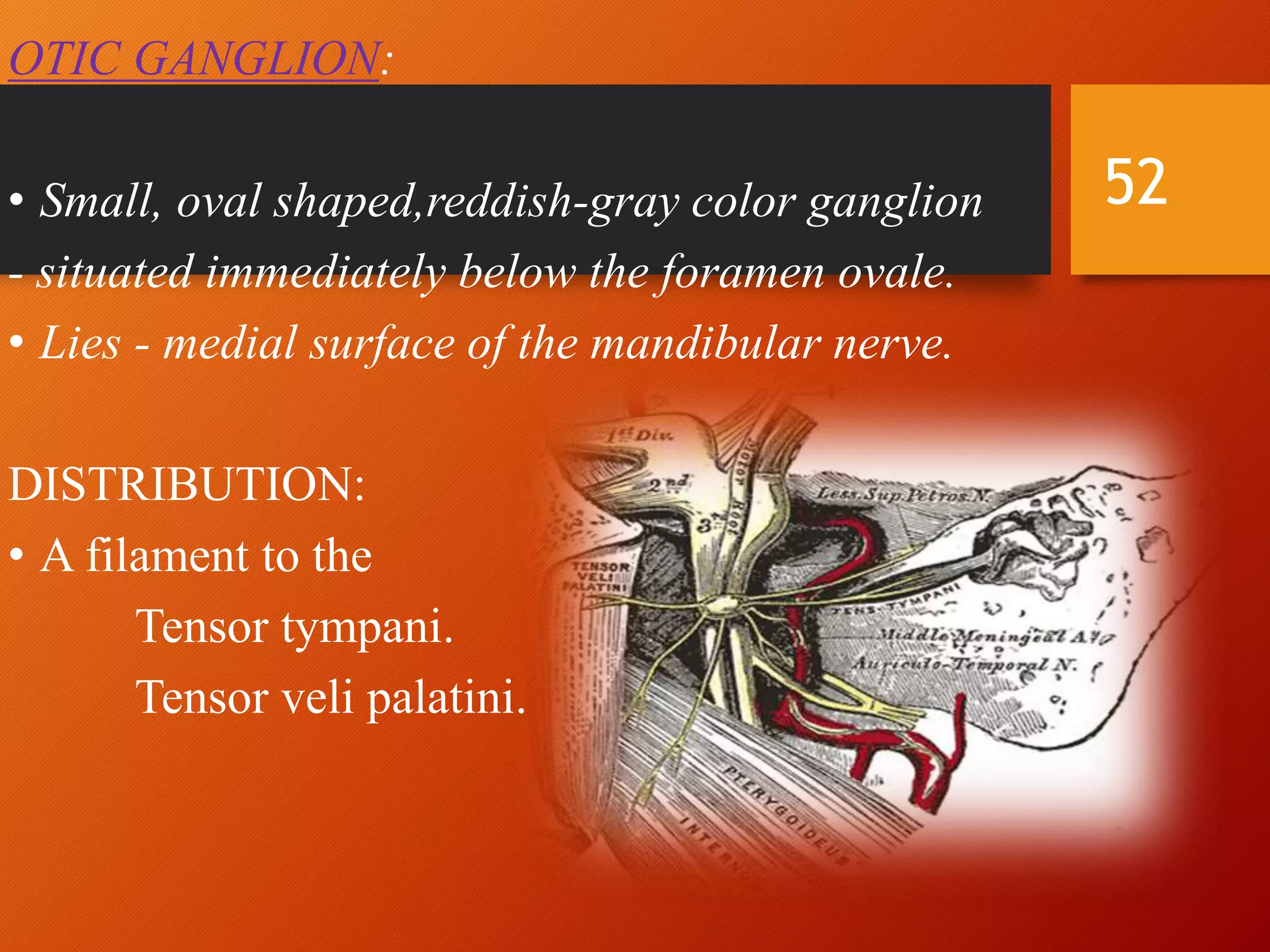
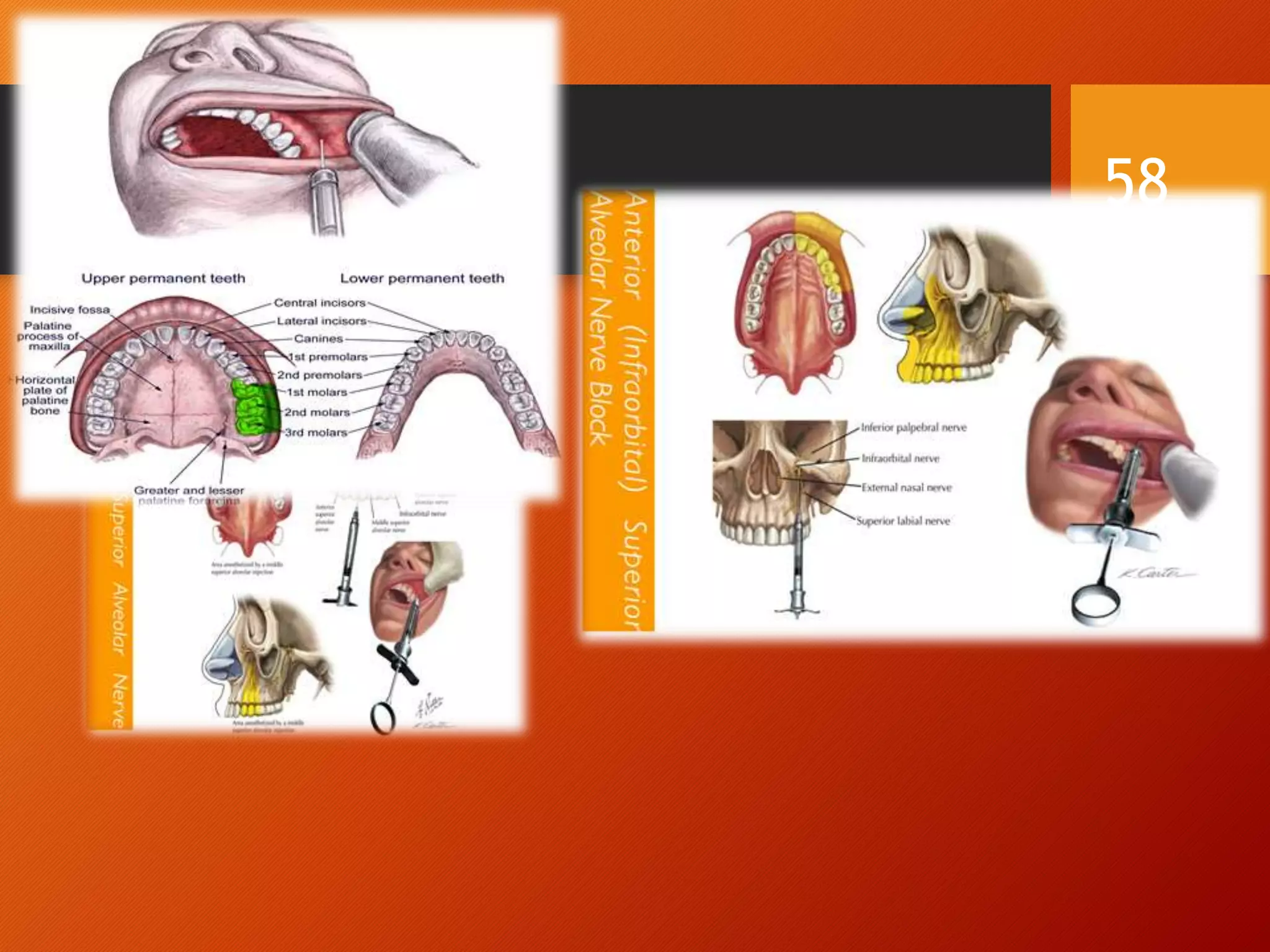
The trigeminal nerve, the 5th cranial nerve, is the largest cranial nerve and serves as the main sensory nerve for the face and head, consisting of three branches: ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. It has both sensory and motor fibers and plays a pivotal role in sensory innervation, proprioception, and motor functions related to mastication. Clinical implications of trigeminal nerve lesions include pain syndromes like trigeminal neuralgia, sensory loss in facial regions, and complications from surgical interventions.