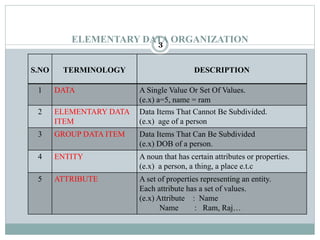
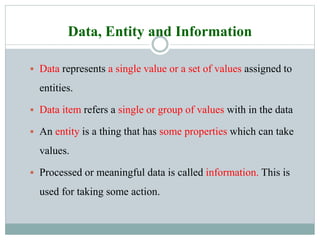
1. The document discusses elementary data organization and data structures. It defines key terms like data, entity, attribute, field, record, and file.
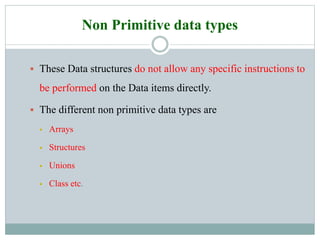
2. Different data types are described including primitive types like integer and float, and non-primitive types like arrays and structures.
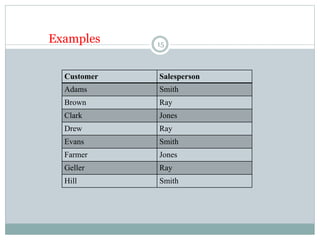
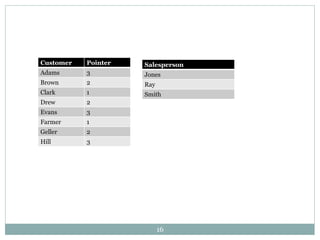
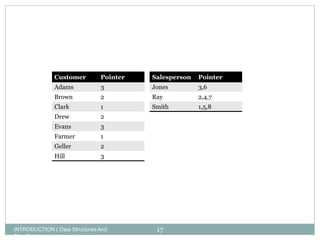
3. Data structures are defined as arrangements of data in memory or storage. Common structures include arrays, linked lists, queues, and trees. Algorithms are used to manipulate data within these structures.
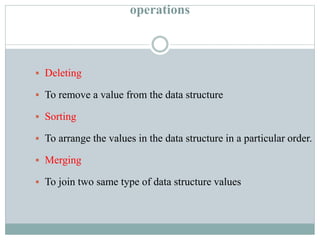
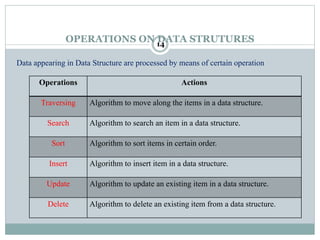
4. Common operations on data structures are discussed, including traversing, searching, inserting, deleting, sorting, and merging.