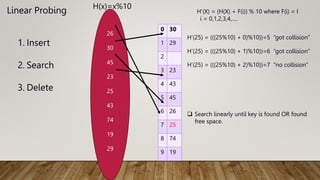
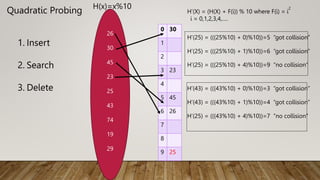
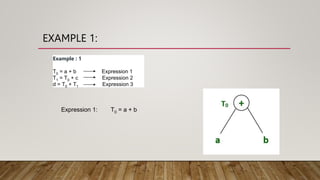
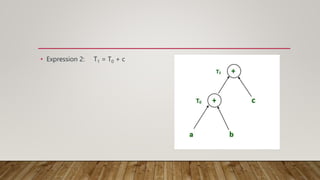
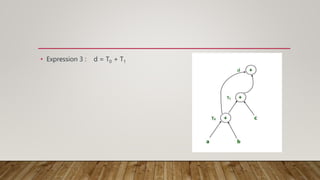
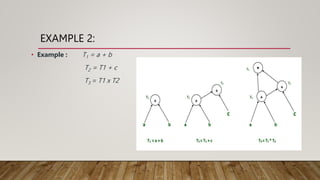
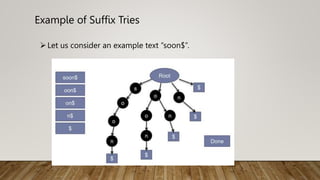
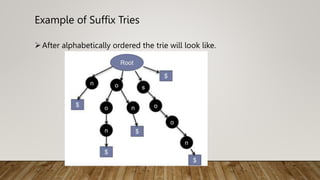
Directed acyclic graph (DAG) is used to represent the flow of values between basic blocks of code. A DAG is a directed graph with no cycles. It is generated during intermediate code generation. DAGs determine common subexpressions and the flow of names and computed values between blocks of code. An algorithm is described to construct a DAG by creating nodes for operands and adding edges between nodes and operator nodes. Examples show how expressions are represented by a DAG. The complexity of a DAG depends on its width and depth. Applications of DAGs include determining common subexpressions, names used in blocks, and which statements' values may be used outside blocks.






























![Hash Function (contd.)
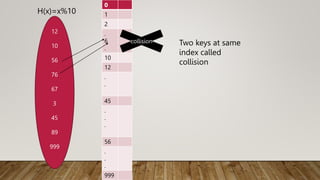
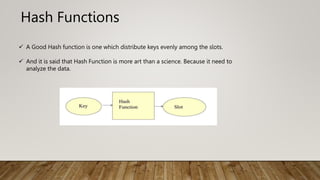
The Mapping of keys to indices of a hash table is called a hash function.
The Hash Function is usually the composition of two maps.
Hash code map
Keys Integer
Compression map
Integer A[o…….m-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dagtriehashing-240105125210-bfad05ce/85/presentation-on-important-DAG-TRIE-Hashing-pptx-51-320.jpg)