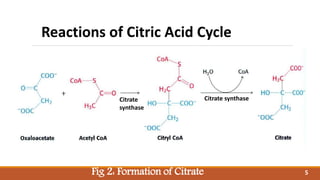
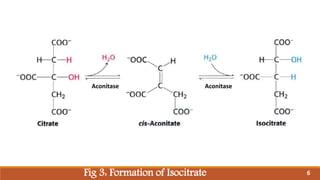
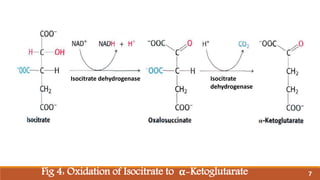
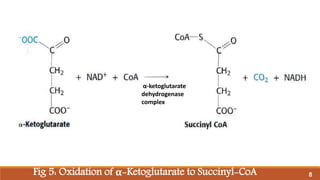
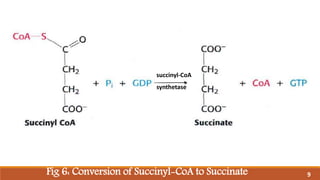
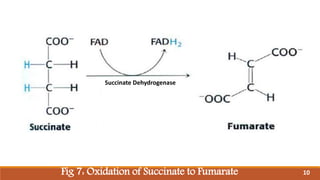
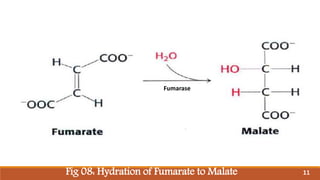
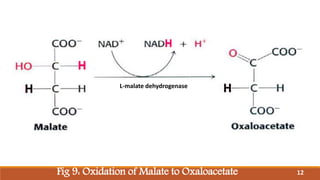
The document summarizes the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle or TCA cycle), which is a series of chemical reactions in the mitochondria that breaks down food molecules into carbon dioxide. It discusses how the cycle was discovered by Sir Hans Krebs, and outlines the key reactions where acetyl-CoA is oxidized, releasing carbon dioxide and producing reduced cofactors that are used to generate ATP. The citric acid cycle is an important amphibolic pathway that generates important biosynthetic intermediates and allows anaplerotic reactions to replenish cycle intermediates.