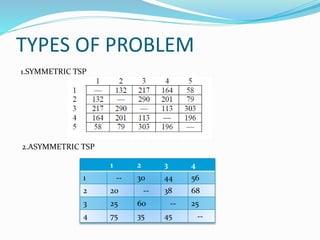
The document discusses the travelling salesman problem (TSP). TSP involves finding the shortest possible route for a salesman to visit each city in a set and return to their starting point. The problem was first studied in the 1800s and became increasingly popular in scientific circles in the 1950s-60s. TSP is an NP-complete optimization problem with many real-world applications like delivery routing. Exact methods to solve TSP take too long, so heuristic methods provide good but not necessarily optimal solutions more quickly. The objective is to minimize the total distance traveled between cities, and TSP problems can be symmetric or asymmetric depending on whether distances between cities are the same in both directions.