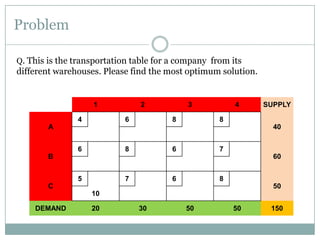
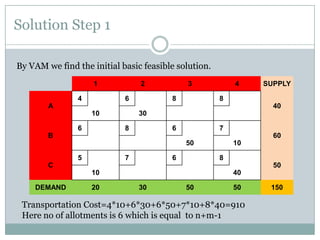
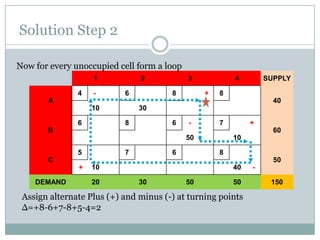
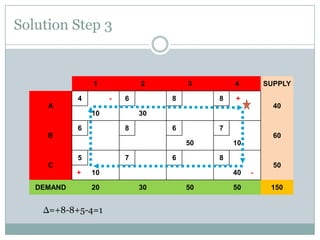
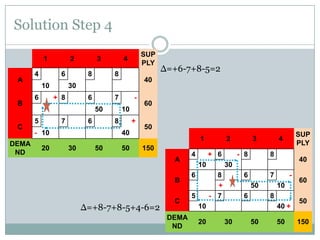
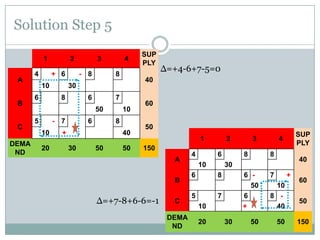
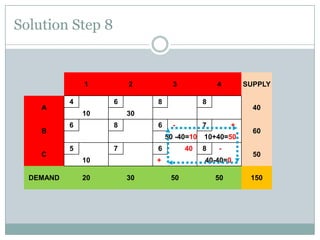
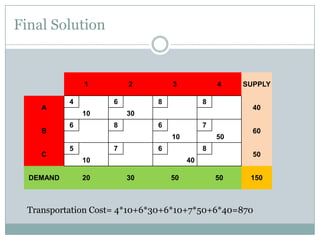
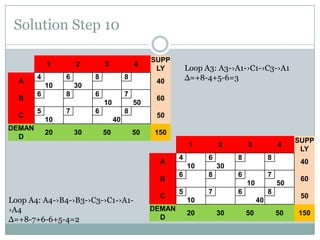
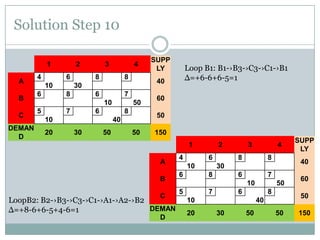
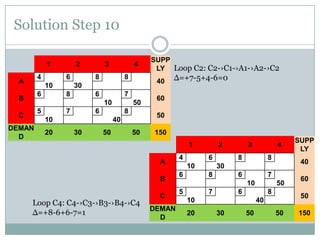
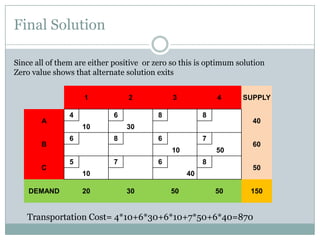
The stepping stone method is used to find the optimal feasible solution to a transportation problem after an initial basic feasible solution is found. It involves systematically checking each unused cell to see if shipping one additional unit to that cell would lower total transportation costs. This is done by forming closed loops around the cell and calculating the net change in cost. If a cell is found that lowers costs, units are reallocated until no further improvements can be made. The document provides an example problem that is solved step-by-step using this method, ultimately arriving at a lower optimal transportation cost than the initial basic feasible solution.