Transport involves the movement of people, animals, and goods from one location to another. There are various modes of transport including road, rail, water, air, cable, pipeline, and space. Transport plays an important role in trade by enabling the production and distribution of goods and services. It facilitates production by moving raw materials to production sites and distribution by delivering finished goods to consumers.
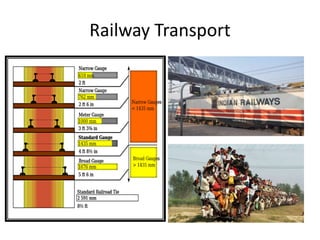
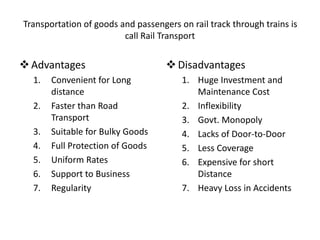
The document then discusses the traditional and modern means of various modes of transport like walking, bullock carts, bicycles, trains, ships, airplanes, and pipelines. It provides details on the advantages and disadvantages of different forms of transport like road, rail, water and air. Road transport is suitable for short distances but uneconom