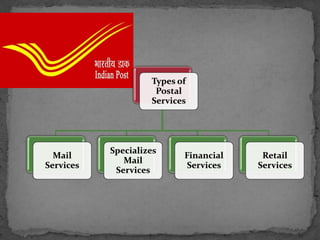
The document defines communication and describes its key components: sender, message, encoding, channel, receiver, decoding, and feedback. It then discusses various traditional and modern means of communication, focusing on mail/postal services and their types (mail services, specialized services, financial services, retail services). Telephone and wireless communication methods are also summarized, including mobile communication, broadband, and Indian satellites.