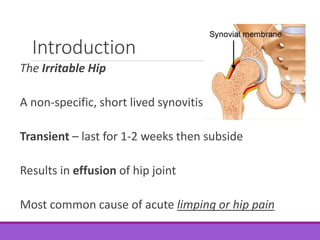
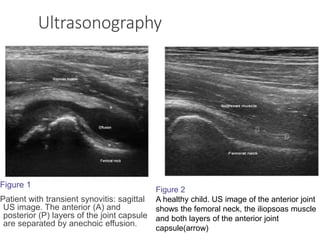
The document discusses irritable hip syndrome, characterized by transient synovitis leading to hip pain and limping, typically lasting 1-2 weeks. Diagnosis is primarily clinical, supported by imaging and blood tests to rule out serious conditions. Management includes symptomatic care, rest, and monitoring, with a generally good prognosis despite potential for recurrence.