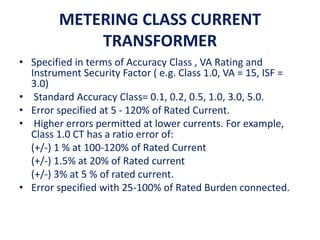
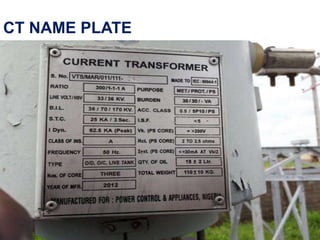
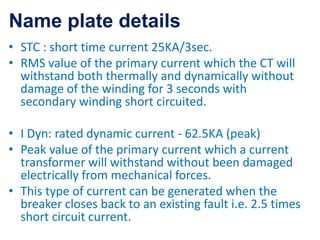
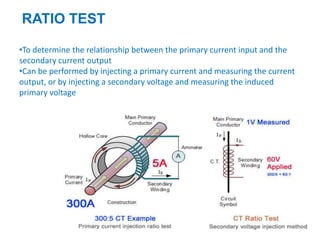
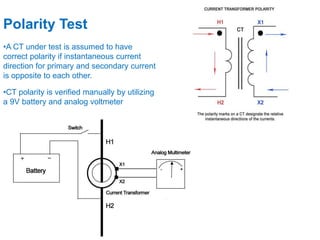
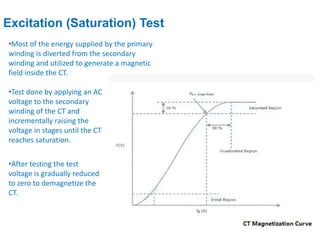
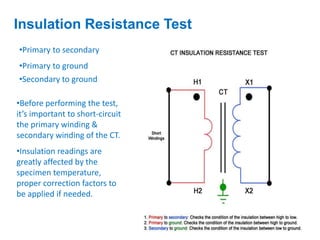
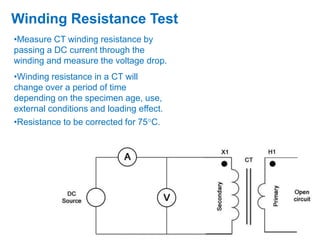
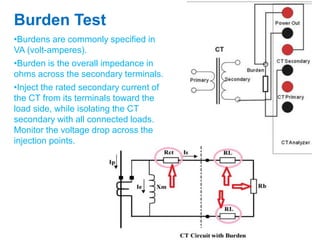
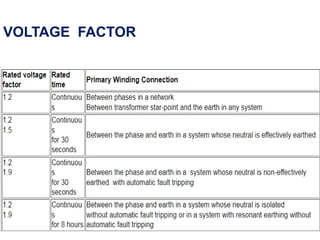
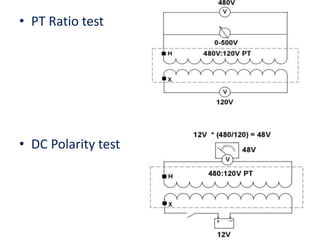
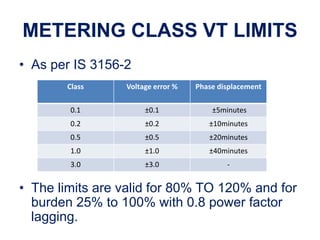
Instrument transformers, including current and voltage transformers, produce a scaled down replica of primary system quantities (current or voltage) for measurement and protection applications. Current transformers are specified based on their accuracy class, VA burden, and limit or accuracy factor, while voltage transformers are specified based on their voltage and phase angle errors. Both current and voltage transformers undergo various tests to evaluate their performance and ensure proper operation, such as ratio, polarity, excitation, insulation resistance, and winding resistance tests.