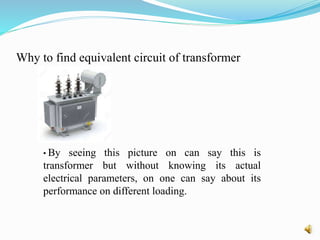
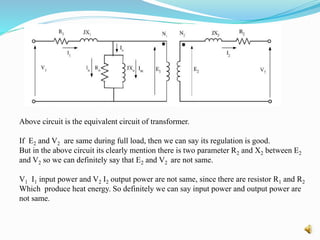
This document discusses the equivalent circuit model of transformers. It explains that an equivalent circuit is needed to analyze a transformer's performance under different loading conditions like regulation and efficiency. The equivalent circuit models the transformer's windings using resistors and inductors obtained from open and short circuit tests. This allows analyzing the transformer using circuit analysis to find values like no-load and full-load voltages, losses, and regulation percentage under different load conditions like lagging, leading, or unity power factor. The key point is that the equivalent circuit is required to evaluate a real transformer's performance for various load scenarios.