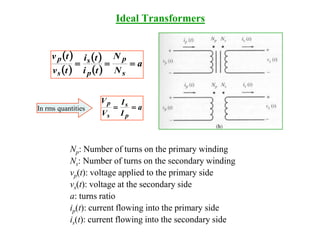
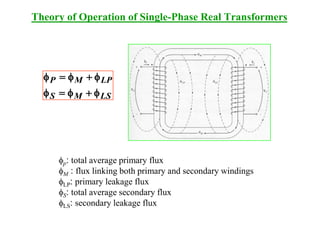
A transformer is a device that changes alternating current (ac) electric power at one voltage level to ac power at another voltage level through magnetic induction. It consists of two or more coils wound around a core and linked by a magnetic field. An ideal transformer has no losses and the power input equals the power output. Real transformers have losses due to winding resistance, core losses, and leakage fluxes. The performance of real transformers can be modeled using an equivalent circuit with parameters determined from open-circuit and short-circuit tests. Transformer voltage regulation and efficiency are important performance metrics.




























![PU System
Per unit system, a system of dimensionless parameters, is used for
computational convenience and for readily comparing the performance
of a set of transformers or a set of electrical machines.
PU Value
Actual Quantity
Base Quantity
Where ‘actual quantity’ is a value in volts, amperes, ohms, etc.
[VA]base and [V]base are chosen first.
I base
VA base
V base
Pbase Qbase S base VA base V baseI base
2
2
V base V base V base
Rbase X base Z base
I base S base VA base
I
Ybase base
V base
Z
PU
Z
ohm
Z base
VAbase pri VAbase sec
V base pri
turns ratio
V base sec](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transformers-140211093339-phpapp02/85/Transformers-31-320.jpg)
