The document discusses training and development in organizations. It defines training as helping employees acquire basic skills for their job functions, while development deals with activities to expose employees to additional duties and positions. Reasons for training and development include remaining relevant in business, creating replacements, enhancing abilities, and ensuring resources for expansion. The purpose is to increase productivity, job satisfaction, and efficiency while decreasing supervision needs.
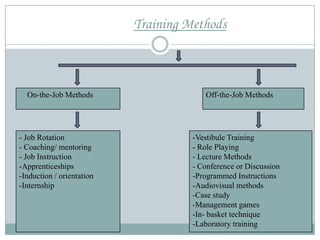
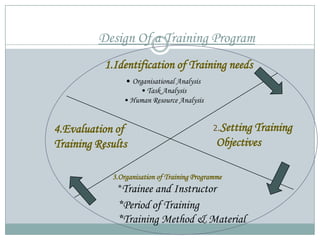
The training process involves assessing needs, setting objectives, selecting trainees and methods, and evaluating. Methods include on-the-job by supervisors and off-the-job by internal or external instructors. Effectiveness is measured by trainee reaction, learning, and improved job behavior post-training. Legal issues around training include inadequate