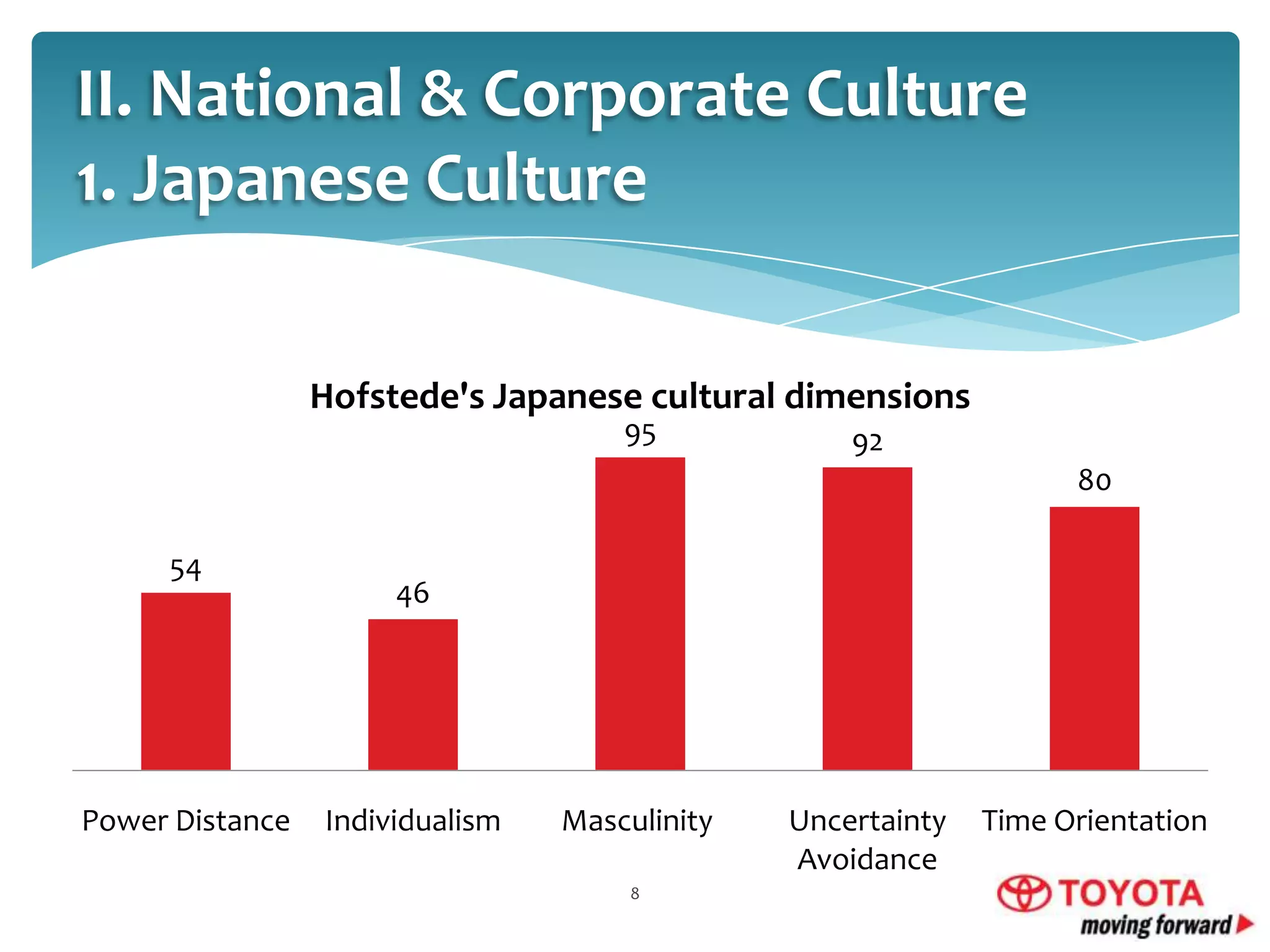
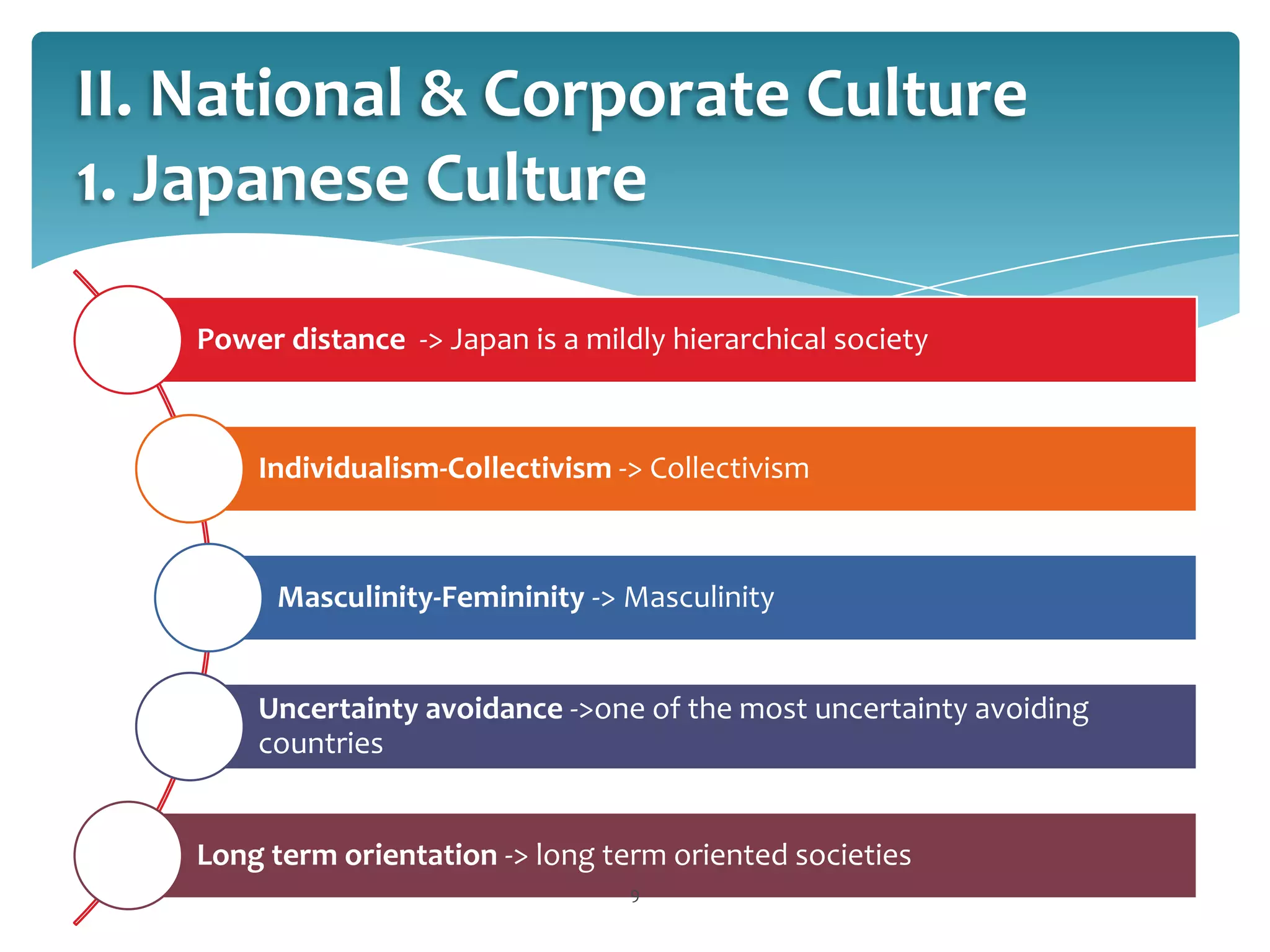
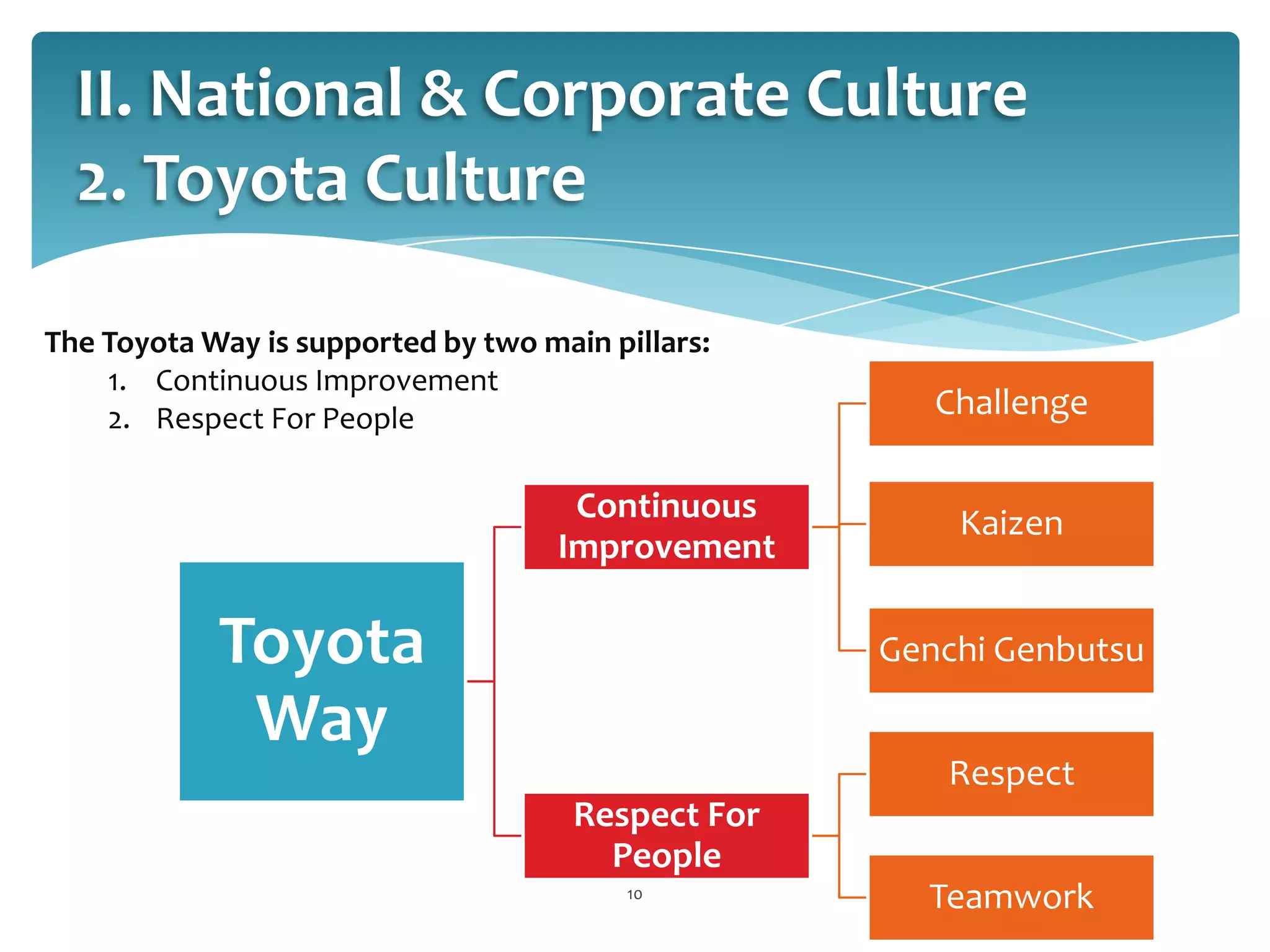
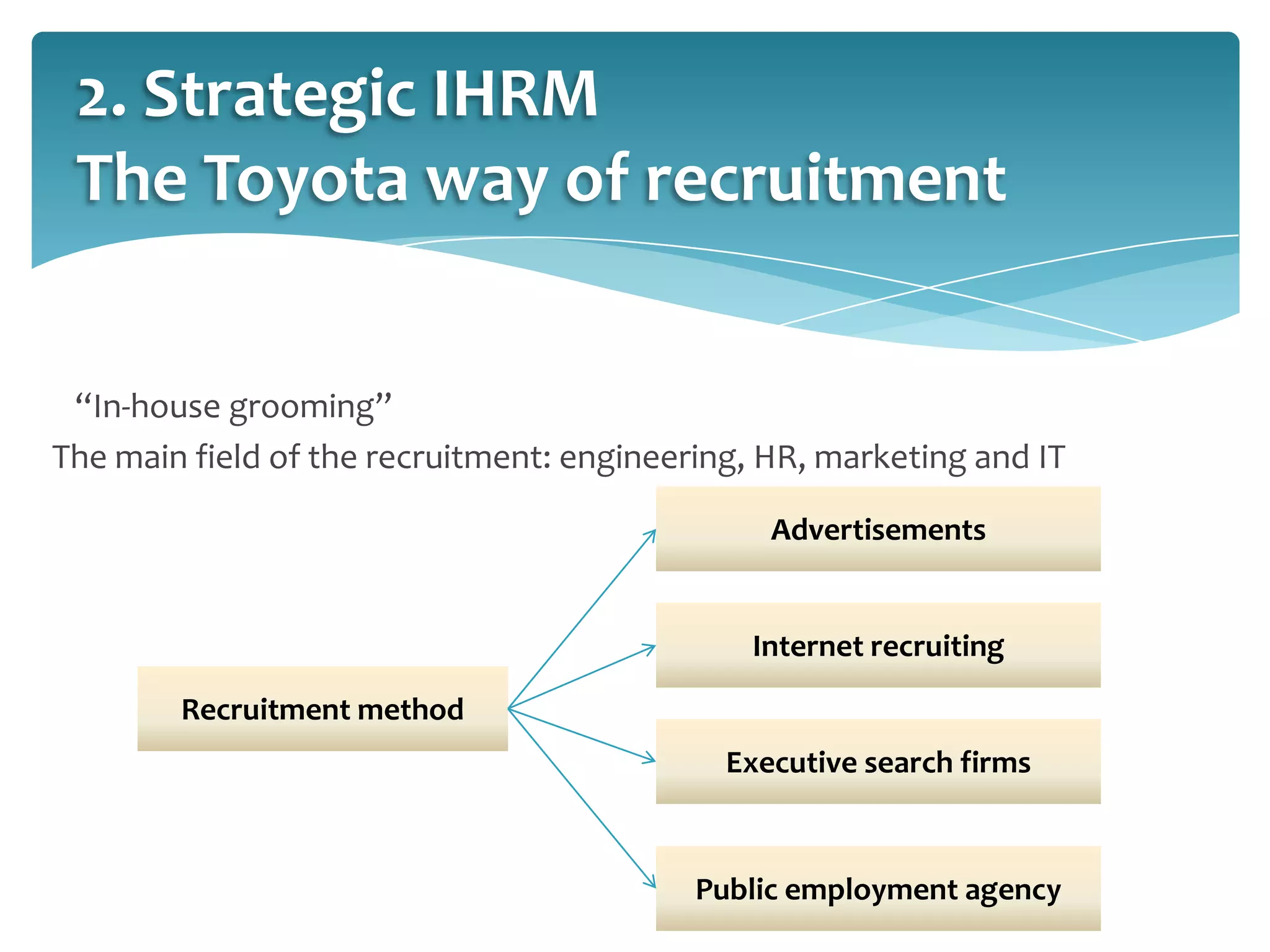
This document provides an overview of Toyota Motor Corporation's international human resource management practices. It discusses Toyota's origins in Japan and decision to globalize. Toyota pursues a geocentric business strategy, standardizing some practices while adapting others locally. Toyota culture is based on continuous improvement and respect for people. Toyota recruits using in-house grooming and screens candidates rigorously based on fit with Toyota values. It uses both parent country nationals and host country nationals, supporting expatriates. Toyota provides structured training and development and performance management to enhance employee productivity.