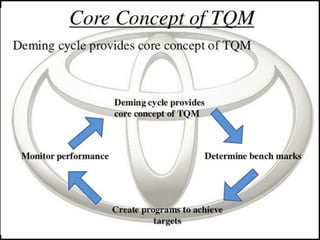
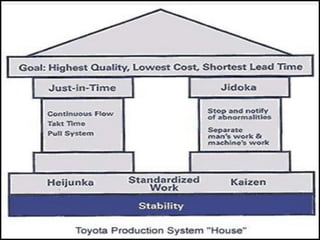
This document discusses the implementation of total quality management (TQM) in manufacturing industries, using Toyota as a reference example. It defines TQM as ensuring quality in all activities and processes through continuous improvement and employee commitment. The key aspects of Toyota's approach discussed are applying the Deming cycle of plan-do-check-act, emphasizing customer satisfaction, empowering employees in quality control, implementing tools like SMED (single minute exchange of die) to reduce setup times, and following the four principles of the Toyota Production System for continuous process improvement.