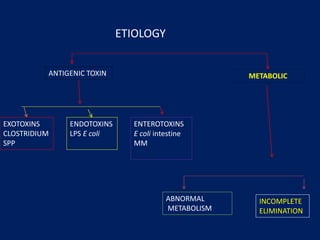
- Toxemia is caused by widespread activation of the host defense system in response to toxins produced by bacteria or tissue injury. Endotoxemia specifically refers to toxemia caused by lipopolysaccharide components of gram-negative bacteria in the blood.
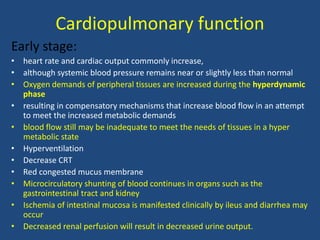
- Endotoxemia can cause abnormalities in multiple body systems including cardiopulmonary, hematologic, gastrointestinal, and others. This can progress to endotoxic shock with severe hypotension.
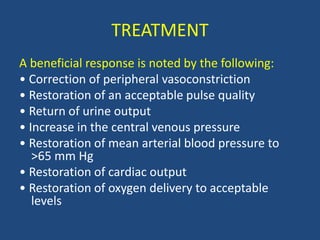
- Treatment of endotoxemia focuses on removing infection sources, antibiotics with gram-negative coverage, aggressive fluid therapy, and inhibiting inflammatory pathways. Despite treatment, endotoxemia carries a high fatality rate.