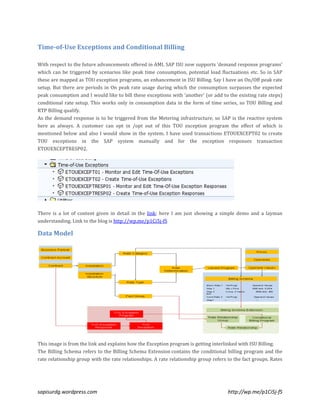
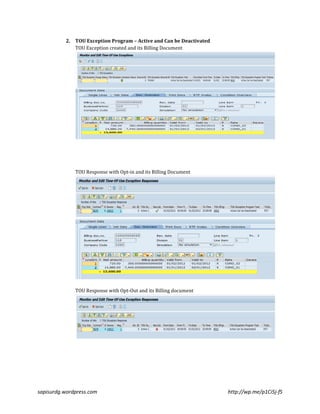
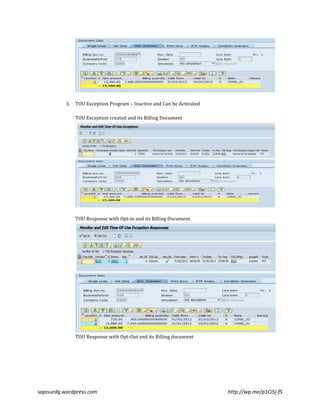
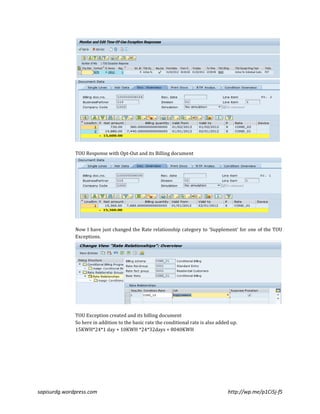
The document outlines the features of SAP's time-of-use (TOU) exception programs, which allow for conditional billing based on demand response scenarios, peak consumption, and load fluctuations. It explains how these programs integrate with ISU billing, describing the setup, activation categories, and billing processes for different scenarios including opt-in and opt-out responses. The author provides a simplified demo along with links to additional detailed content for further understanding.