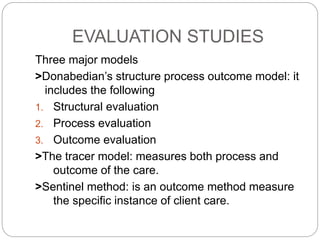
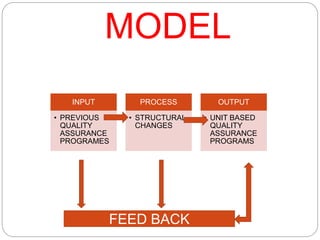
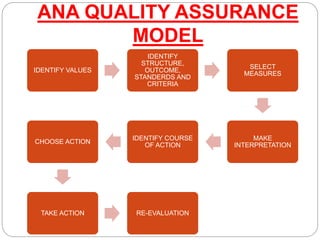
This document discusses quality assurance in healthcare and the role of nurses. It defines quality and quality assurance, and outlines some models for quality assurance programs. Key points include:
- Quality assurance aims to systematically review, analyze, and evaluate compliance with standards to ensure quality of care.
- Components of quality healthcare include professionalism, efficient resource use, low patient risk, patient satisfaction, and positive health outcomes.
- Nurses play an important role in quality assurance through participation in quality improvement teams, monitoring care effectiveness, innovation, patient safety initiatives, education, and research.
- Common models for quality assurance programs include the system model, ANA model, JCAHO model, and ISO model. These aim