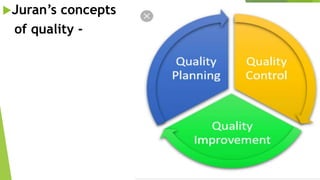
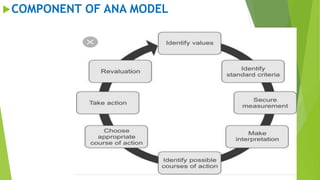
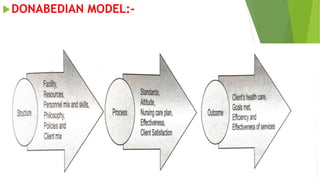
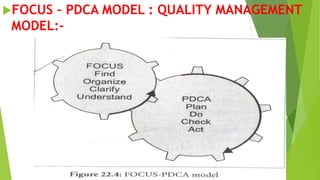
This document provides an overview of quality assurance in nursing. It discusses the historical perspective of quality assurance dating back to Florence Nightingale establishing early nursing standards. Common models of quality assurance are described, including the American Nurses' Association model and Donabedian model which evaluate quality through structure, process and outcomes. Key aspects of total quality management are outlined such as customer focus, continuous improvement, and employee involvement. The purposes of quality assurance in nursing are ensuring high quality care, meeting customer needs, and improving efficiency.