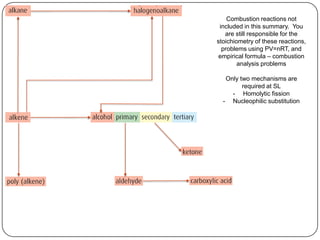
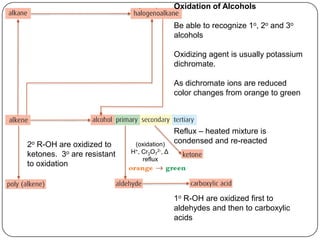
This document summarizes key organic chemistry reactions for IB Chemistry at both the SL and HL levels. It outlines addition, substitution, elimination, oxidation, reduction, condensation, and polymerization reactions. Specific mechanisms that must be known include homolytic fission, SN1 and SN2 nucleophilic substitution, and elimination reactions. Condensation reactions forming esters and amides are also included.


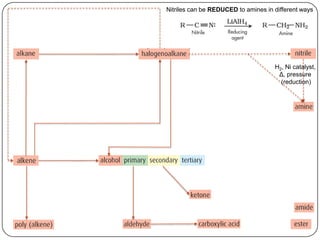
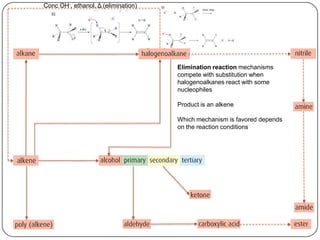
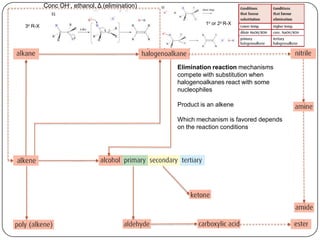
![Conc OH-, ethanol, Δ (elimination)
1o or 2o R-X
3o R-X
Homolytic fission, UV light (substitution) KCN
SN1 H2, Ni catalyst,
NaOH, Δ (substitution)
Δ, pressure
H2, Ni catalyst, Δ (addition)
3o R-X
(reduction)
SN2
1o R-X
(addition)
X2 or HX, Δ
(condensation)
with R-COOH
(addition)
H2O, [H2SO4], Δ
polymerization
addition
(oxidation)
H+,Cr2O72-, Δ
reflux
(condensation)
with R-OH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic1020-reactionsummaryandreview-130203223244-phpapp01/85/Topic-10-20-reaction-summary-and-review-3-320.jpg)


![Homolytic fission, UV light
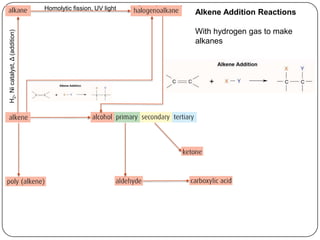
Alkene Addition Reactions
With hydrogen gas to make
H2, Ni catalyst, Δ (addition)
alkanes
With halogens or HX’s to make
halogenoalkanes (R-X)
(addition)
X2 or HX, Δ
With water to make alcohols
(R-OH)
(addition)
H2O, [H2SO4], Δ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic1020-reactionsummaryandreview-130203223244-phpapp01/85/Topic-10-20-reaction-summary-and-review-9-320.jpg)
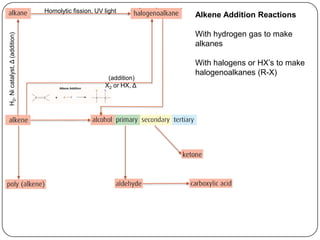
![Homolytic fission, UV light
Alkene Addition Reactions
With hydrogen gas to make
H2, Ni catalyst, Δ (addition)
alkanes
With halogens or HX’s to make
halogenoalkanes (R-X)
(addition)
X2 or HX, Δ
With water to make alcohols
(R-OH)
(addition)
H2O, [H2SO4], Δ
Monomer subunits combine to
polymerization
make polymers
addition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic1020-reactionsummaryandreview-130203223244-phpapp01/85/Topic-10-20-reaction-summary-and-review-10-320.jpg)
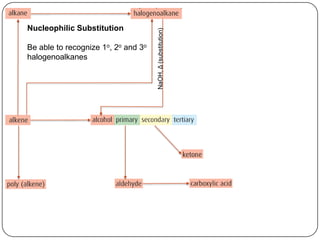
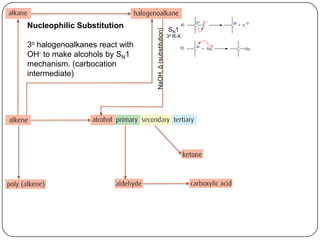

![Homolytic fission, UV light
SN1
NaOH, Δ (substitution)
H2, Ni catalyst, Δ (addition)
3o R-X
SN2
1o R-X
(addition)
X2 or HX, Δ
(addition)
H2O, [H2SO4], Δ
polymerization
addition
(oxidation)
H+,Cr2O72-, Δ
reflux](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic1020-reactionsummaryandreview-130203223244-phpapp01/85/Topic-10-20-reaction-summary-and-review-15-320.jpg)

![Conc OH-, ethanol, Δ (elimination)
1o or 2o R-X
3o R-X
Homolytic fission, UV light (substitution) KCN
SN1 H2, Ni catalyst,
NaOH, Δ (substitution)
Δ, pressure
H2, Ni catalyst, Δ (addition)
3o R-X
(reduction)
SN2
1o R-X
(addition)
X2 or HX, Δ
(condensation)
with R-COOH
(addition)
H2O, [H2SO4], Δ
polymerization
addition
(oxidation)
H+,Cr2O72-, Δ
reflux
(condensation)
with R-OH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic1020-reactionsummaryandreview-130203223244-phpapp01/85/Topic-10-20-reaction-summary-and-review-17-320.jpg)
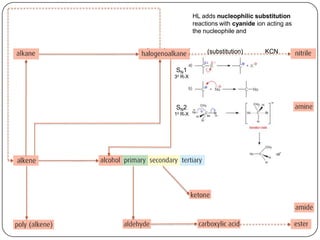
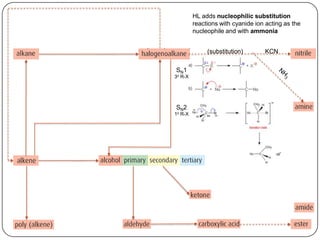


![Conc OH-, ethanol, Δ (elimination)
1o or 2o R-X
3o R-X
Homolytic fission, UV light (substitution) KCN
SN1 H2, Ni catalyst,
NaOH, Δ (substitution)
Δ, pressure
H2, Ni catalyst, Δ (addition)
3o R-X
(reduction)
SN2
1o R-X
(addition)
X2 or HX, Δ
(condensation)
with R-COOH
(addition)
H2O, [H2SO4], Δ
polymerization
addition
(oxidation)
H+,Cr2O72-, Δ
reflux
(condensation)
with R-OH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic1020-reactionsummaryandreview-130203223244-phpapp01/85/Topic-10-20-reaction-summary-and-review-25-320.jpg)