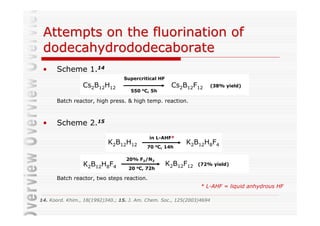
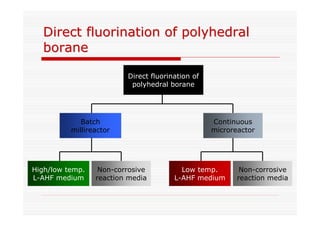
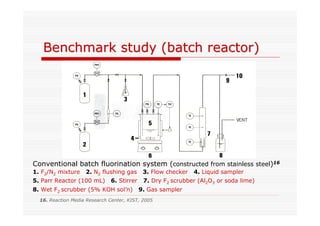
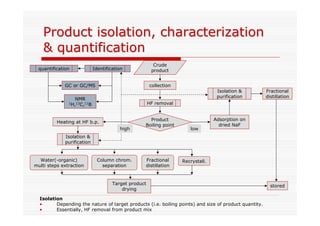
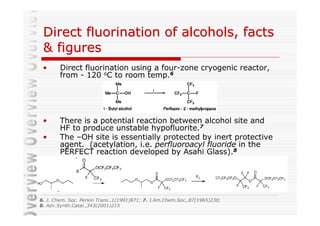
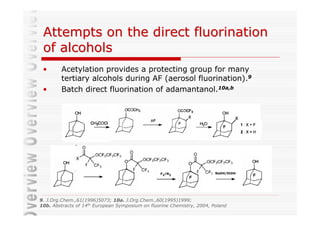
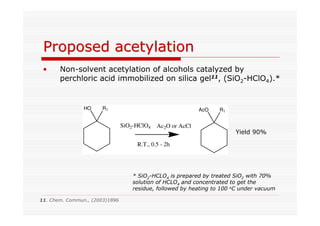
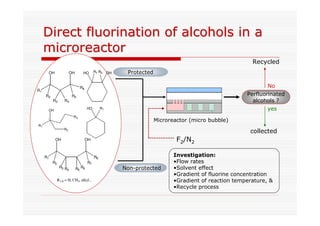
The document discusses direct fluorination reactions in microreactors. It proposes acetylating alcohols prior to fluorination to protect the alcohol group. The fluorination would take place in a microreactor using a gas-liquid system with elemental fluorine and nitrogen. Previous attempts at direct fluorination of alcohols and polyhedral boranes in batch reactors are described. The document outlines characterization techniques that could be used to analyze products from the proposed microreactor fluorination experiments.



![Synthesis of
dodecahydrododecaborate
Scheme 1.12
• Na[B3H8] in diglyme, reflux under nitrogen until colorless, then
diglyme
NaBH4 + I2 Na[B3H8] + NaI + H2
Reflux 100 oC
under N2
Scheme 2.13
• Na[B3H8] treated with concentrated (CH3)3NHCl in water and
cooled to R.T. The solid is separated, dried, and recrystallized
from water-ethyl alcohol to give (Me3NH)2B12H12.
diglyme
NaB3H8 + [HNMe3]Cl [HNMe3]2B12H12 + NaCl
100 oC, under N2
12. Yingyong Huaxue, Chem. Abstr., 15(1998)111.; 13. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 85(1963)3885](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microreactor-fluorination-freiburg-111009231609-phpapp01/85/Microreactor-fluorination-freiburg-8-320.jpg)