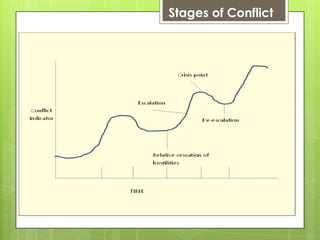
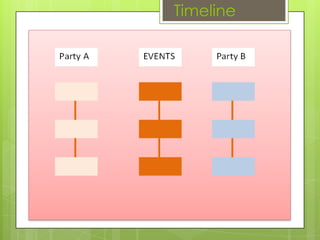
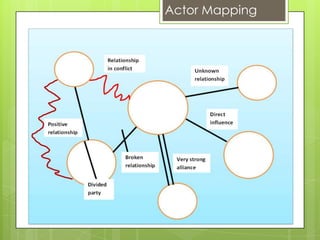
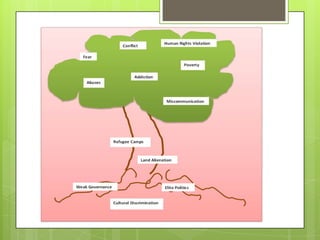
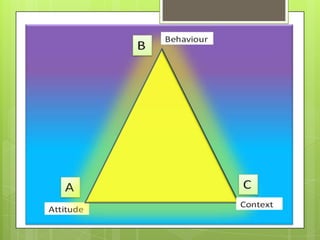
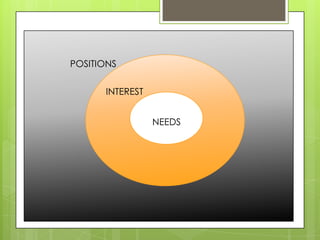
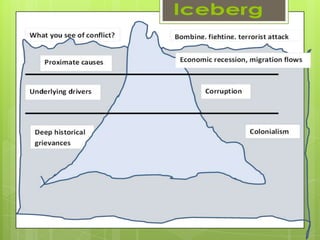
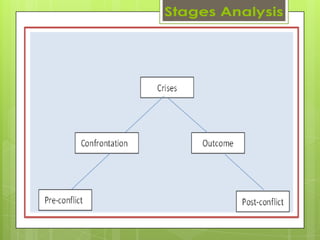
This document outlines various tools that can be used for conflict analysis, including stages of conflict, timelines, actor mapping, conflict trees, and the ABC triangle. It describes how each tool can be used for both analyzing different aspects of a conflict as well as identifying opportunities for intervention. The overall purpose of conflict analysis is to better understand the context, parties, causes, and dynamics of a conflict in order to help prevent escalation and adopt conflict-sensitive practices.