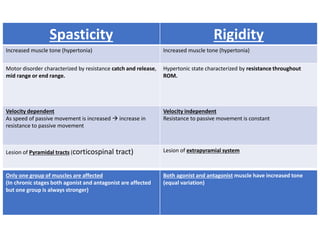
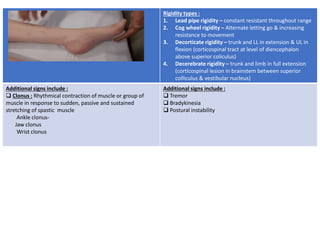
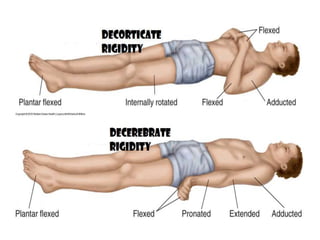
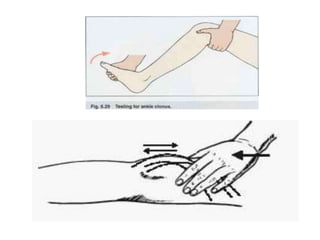
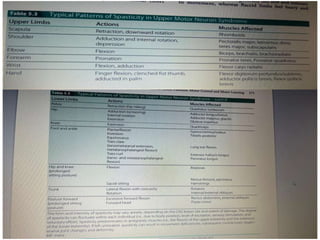
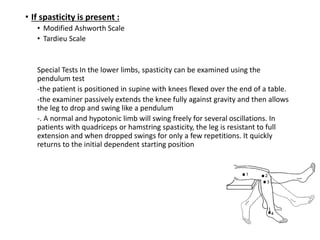
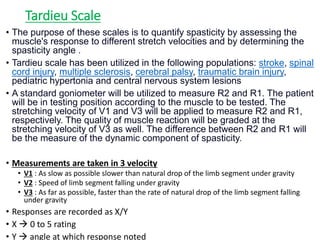
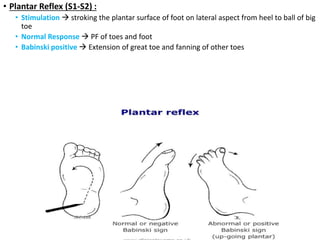
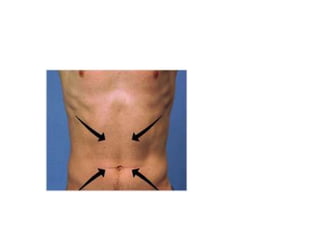
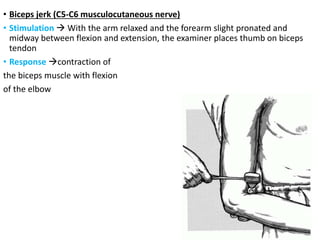
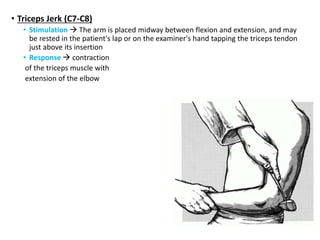
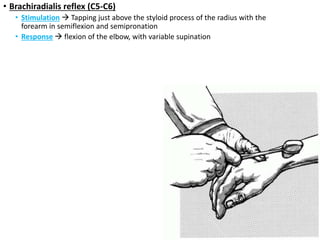
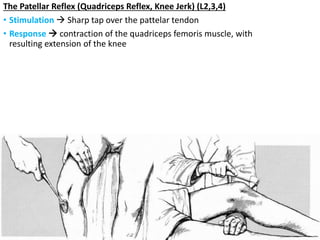
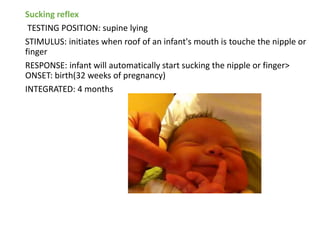
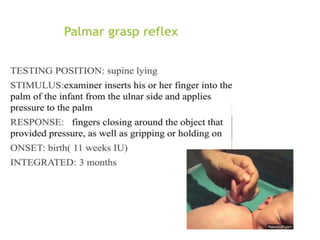
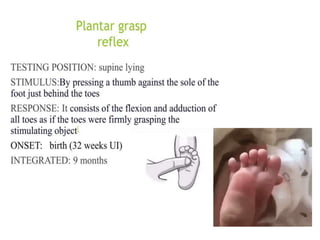
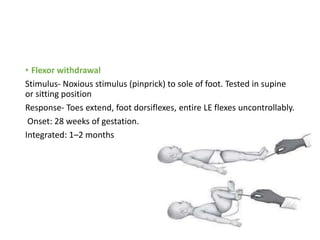
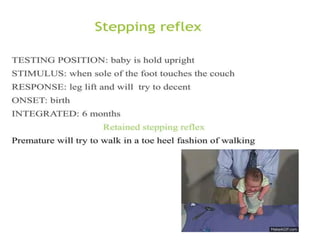
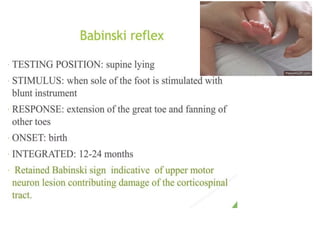
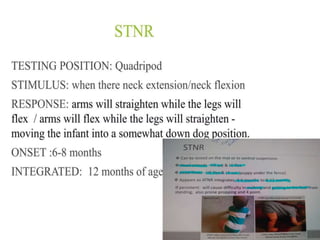
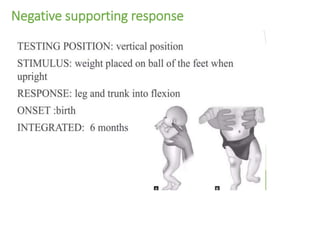
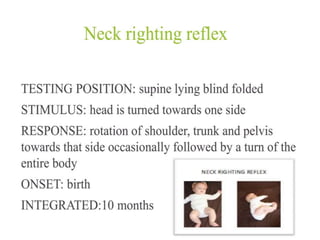
This document provides information about performing a motor examination, including assessing muscle tone, reflexes, and strength. It describes how to evaluate tone through passive movement testing, defines types of abnormal tone like spasticity and rigidity, and compares conditions. Reflex testing techniques are outlined for superficial reflexes like plantar and abdominal reflexes as well as deep tendon reflexes at sites like the biceps, triceps, knee and ankle. Clinical scales for grading tone and reflexes are also presented.