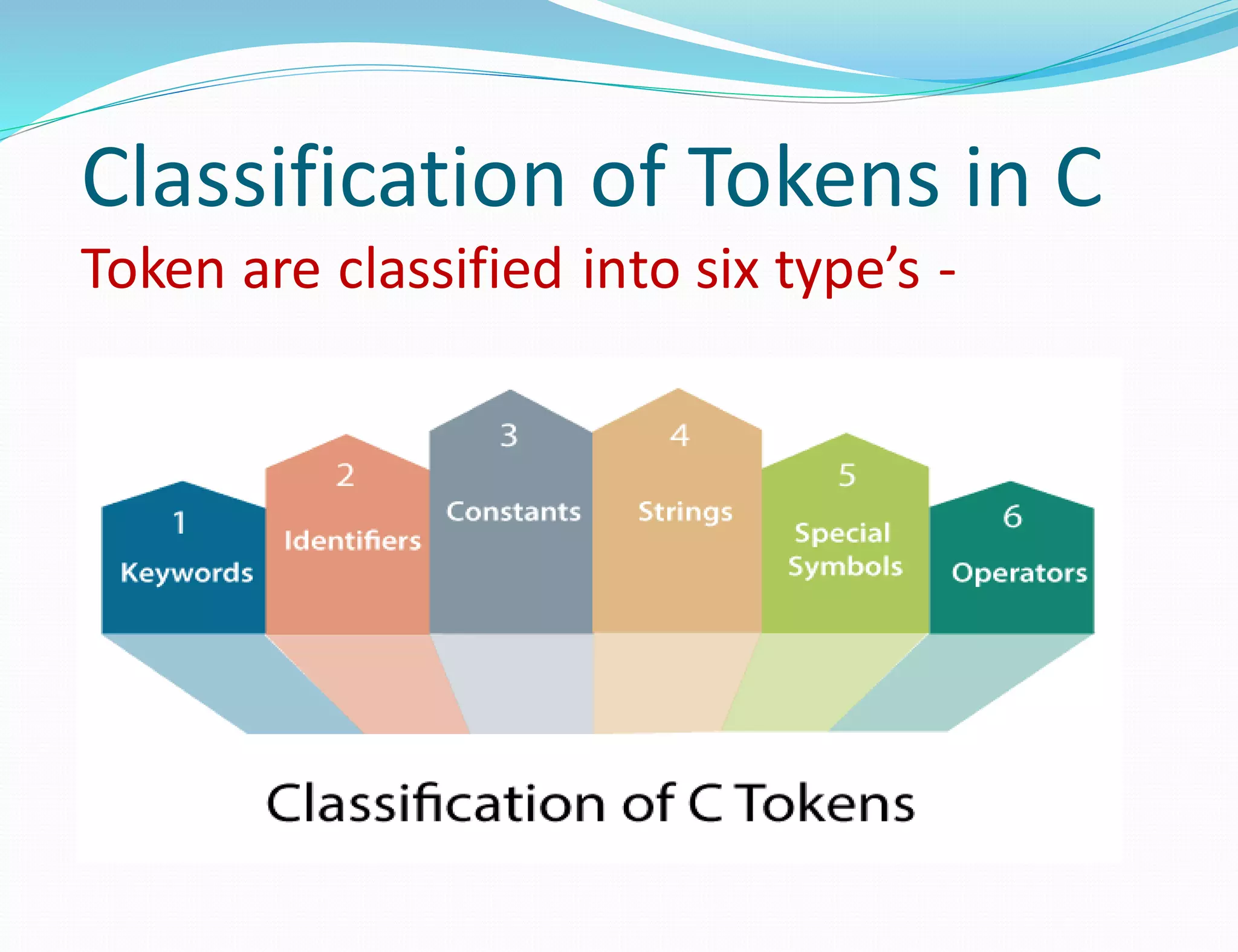
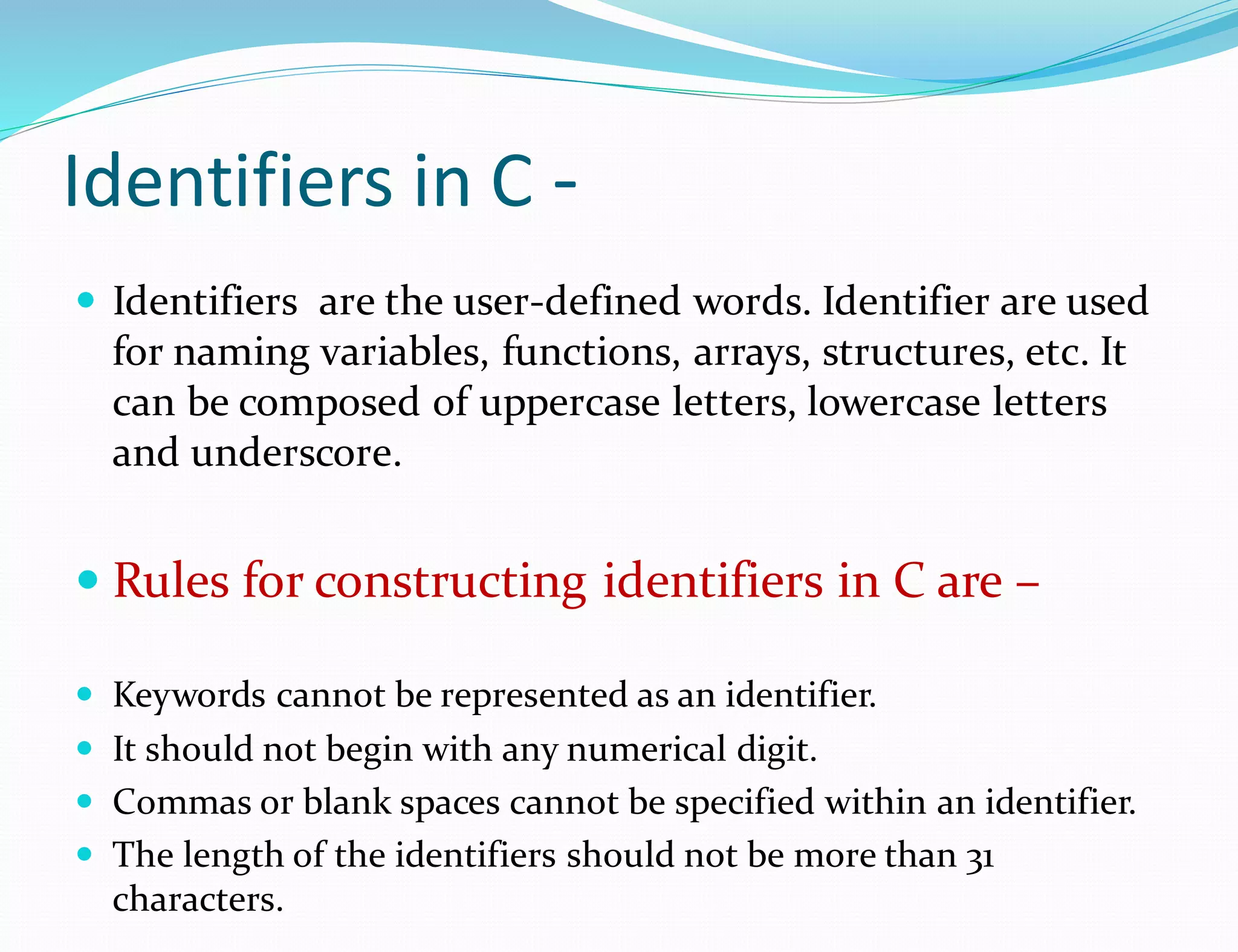
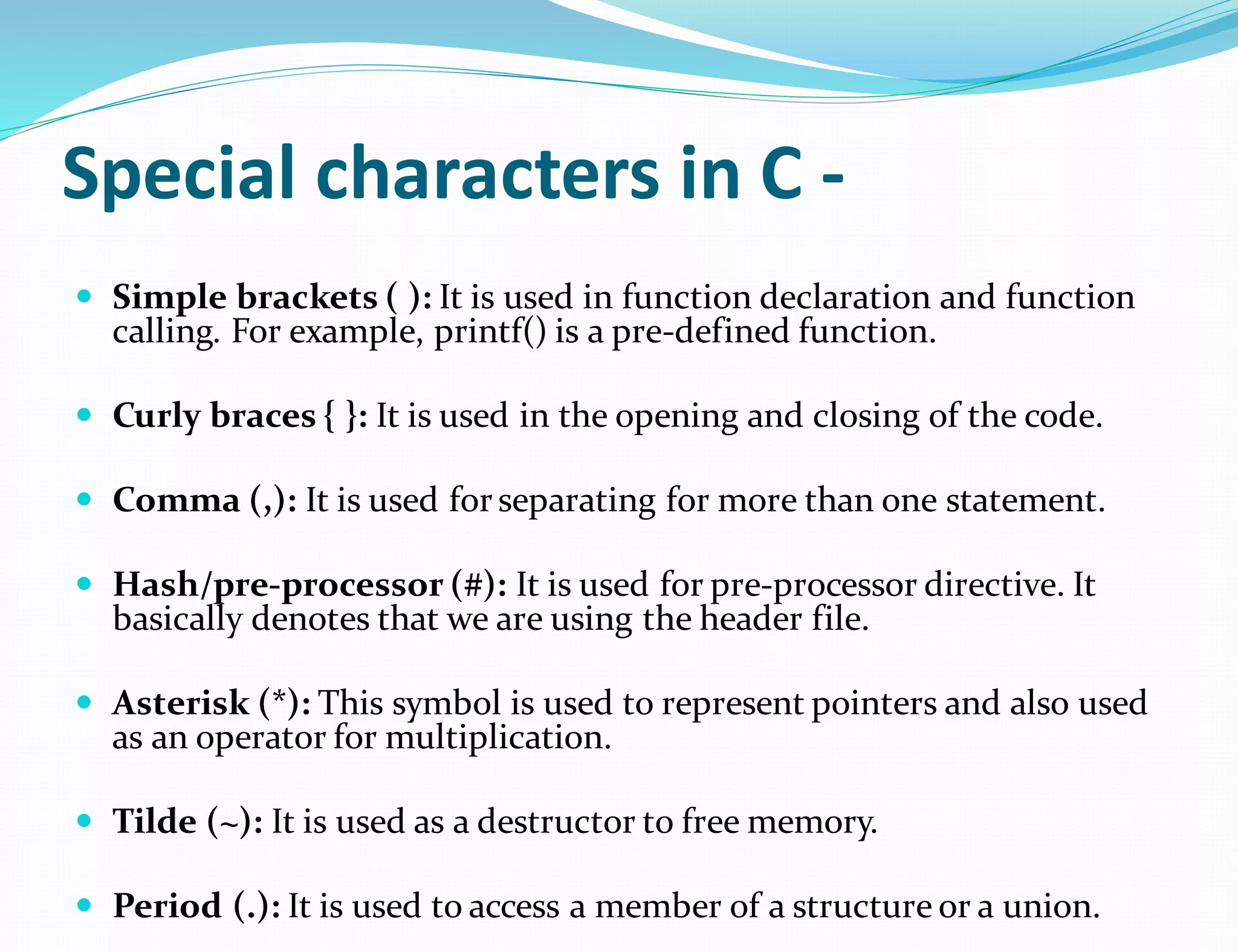
This document discusses the different types of tokens in the C programming language. It identifies six main types of tokens: keywords, identifiers, special characters, constants, operators, and punctuators. Keywords are reserved words with predefined functionality. Identifiers are user-defined names for variables, functions, etc. Special characters include brackets, braces, periods, and asterisks. Constants represent fixed values that cannot change, and include integer, floating-point, octal, and hexadecimal constants. Operators perform operations like arithmetic, and punctuators aid the syntax of the language.