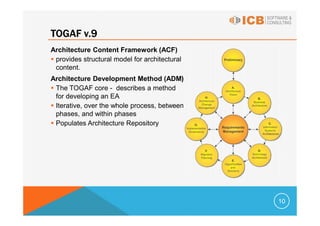
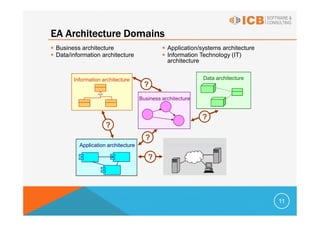
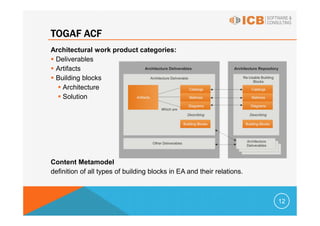
Enterprise architecture (EA) addresses problems caused by increasing IT system complexity and poor business alignment. EA frameworks provide guidance for developing an organization-specific architecture that embodies best practices and ensures all domains are adequately addressed. The most commonly used EA frameworks are the Zachman Framework, TOGAF, FEA, and Gartner Methodology. TOGAF provides both a framework for architectural content and an iterative architecture development method (ADM) comprised of phases to develop the EA. EA benefits include more efficient IT operations, reduced investment risk, and return on investment through greater flexibility, reduced complexity, and faster delivery.