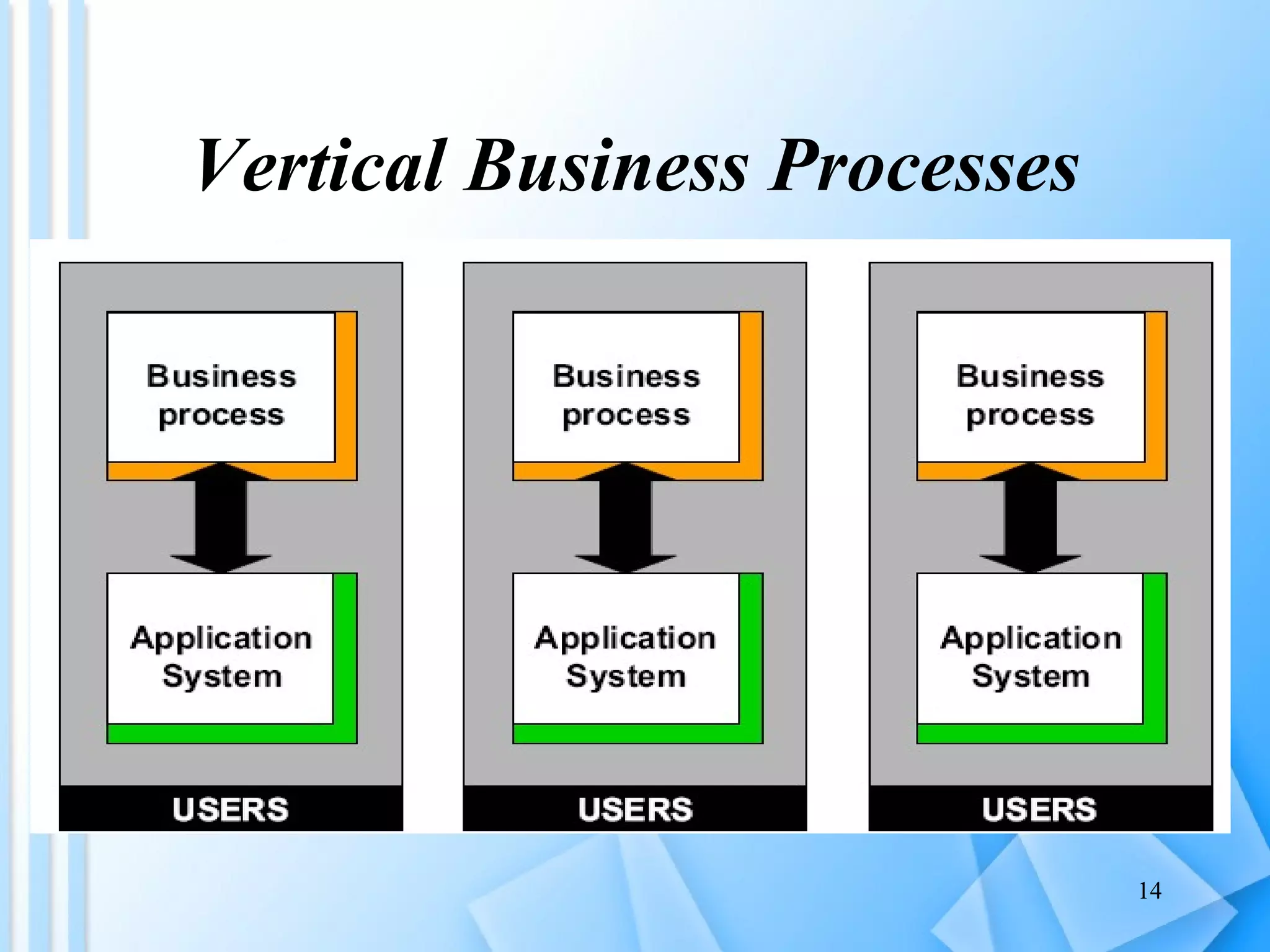
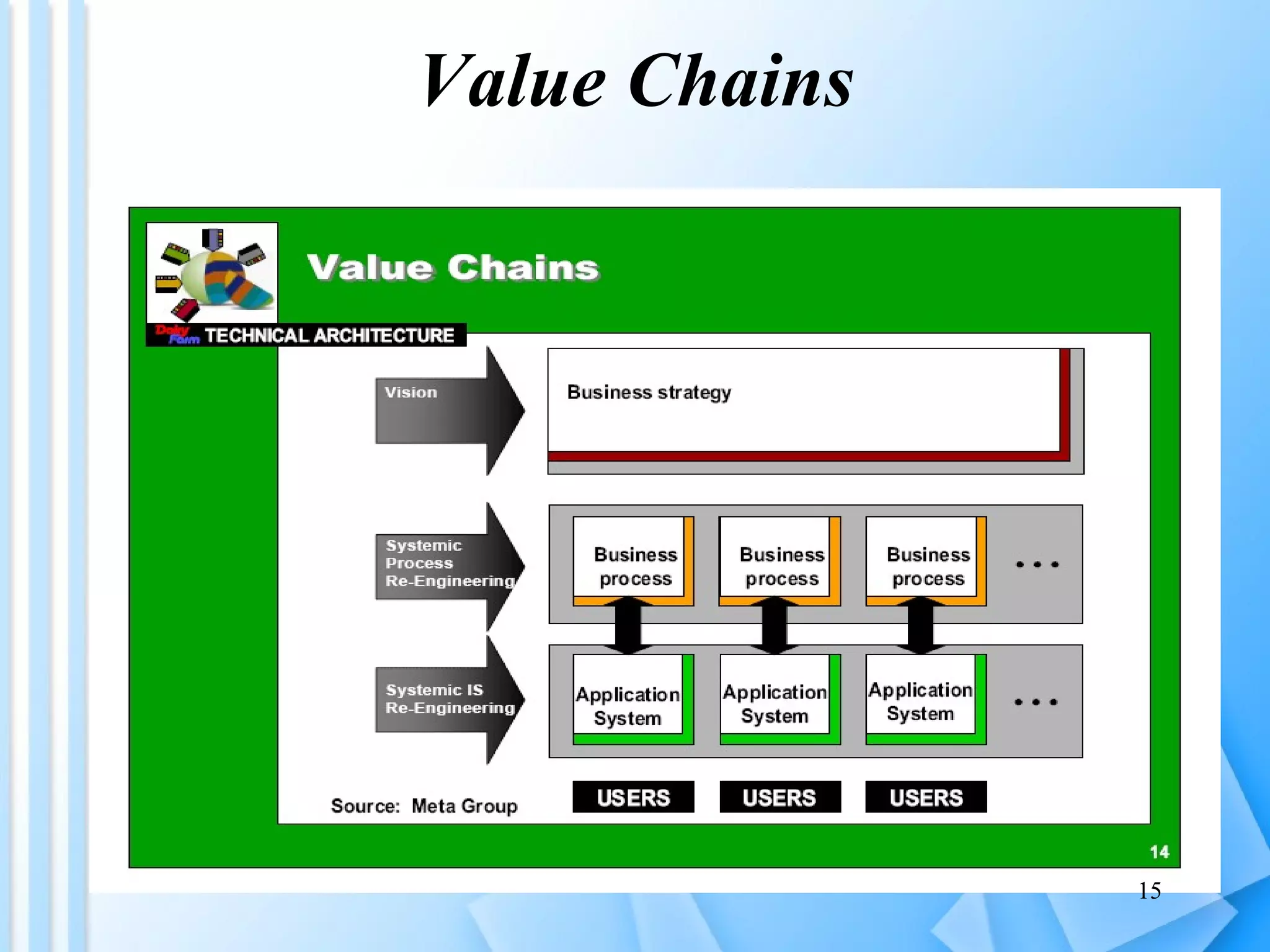
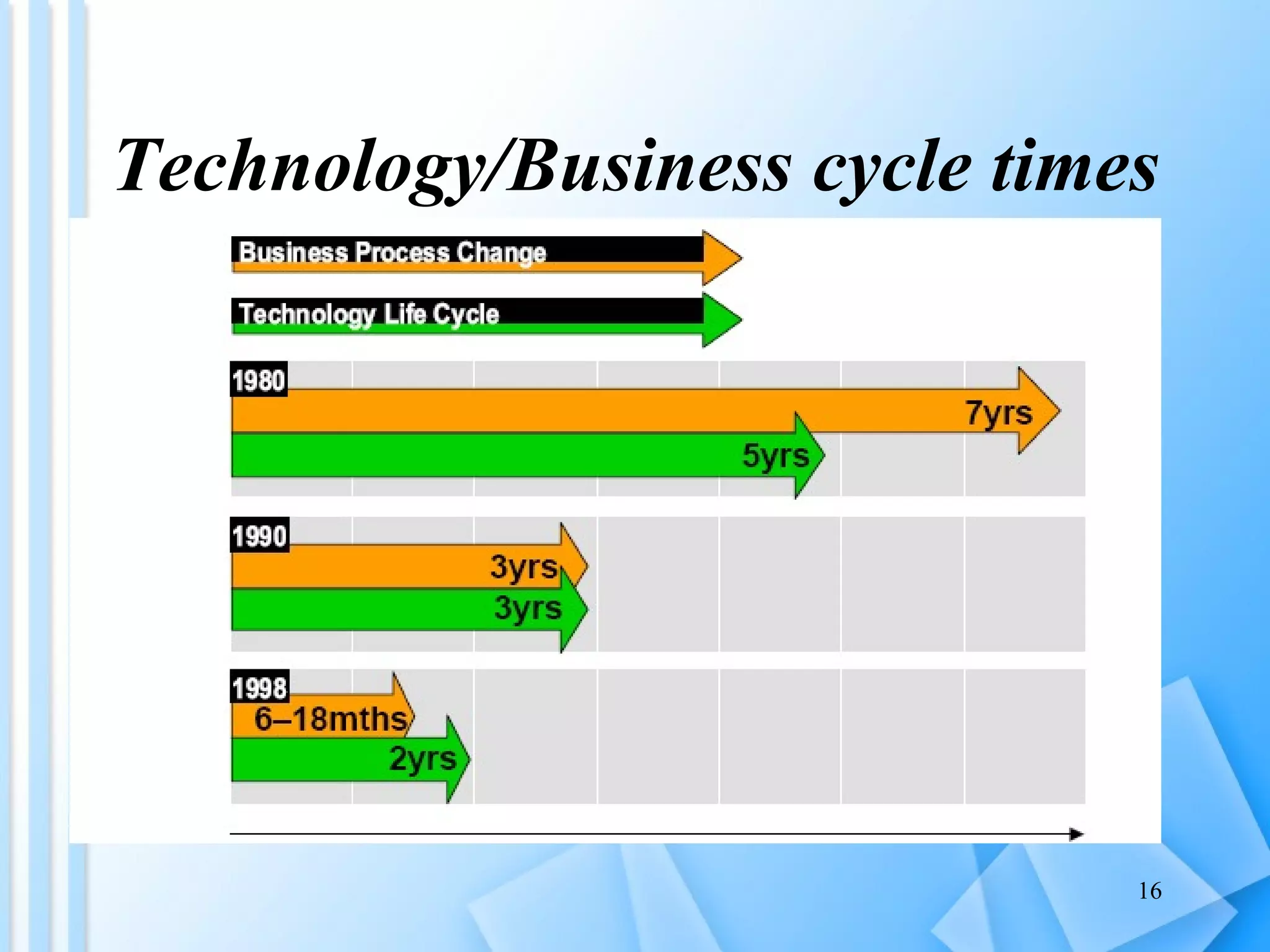
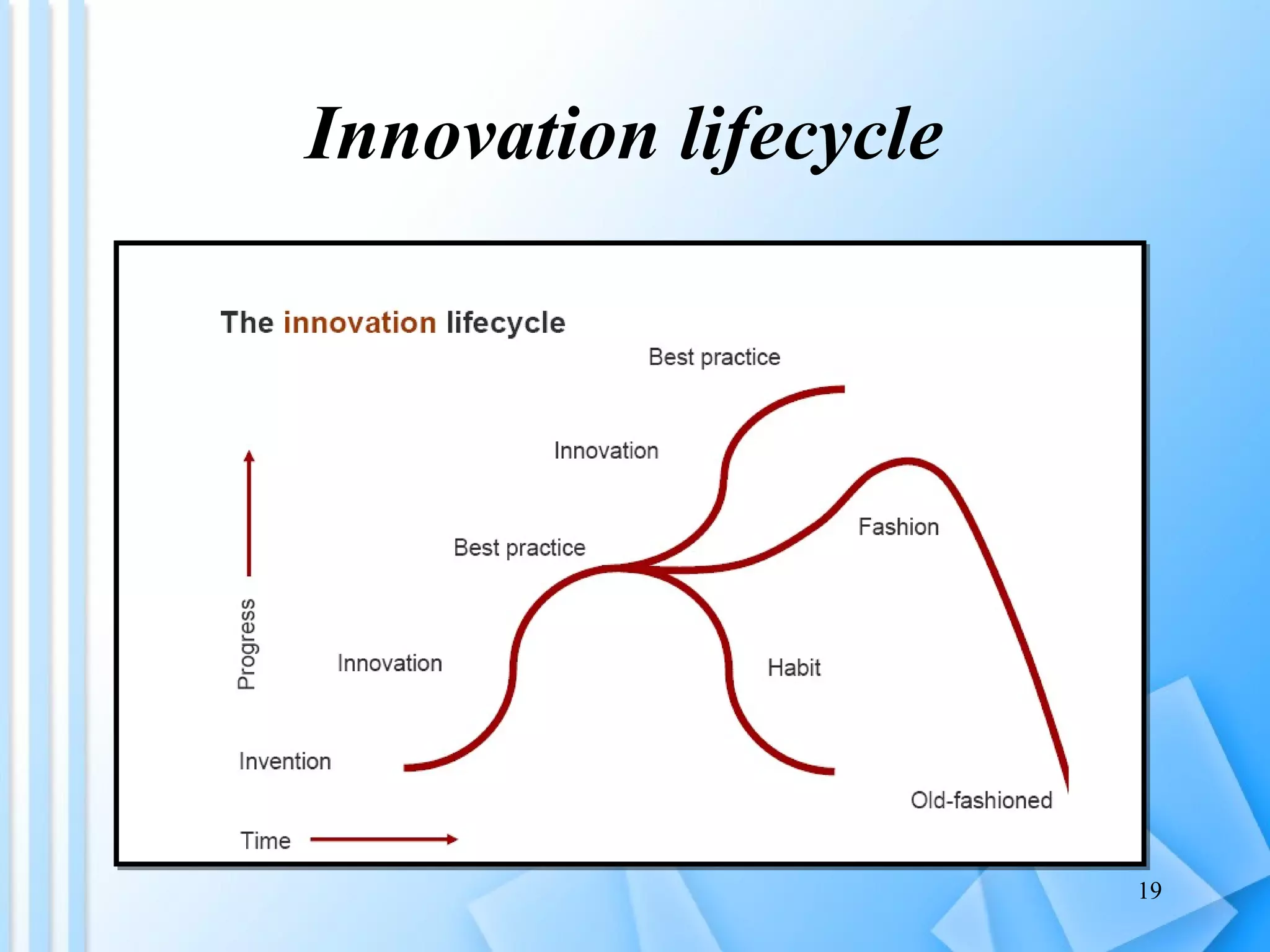
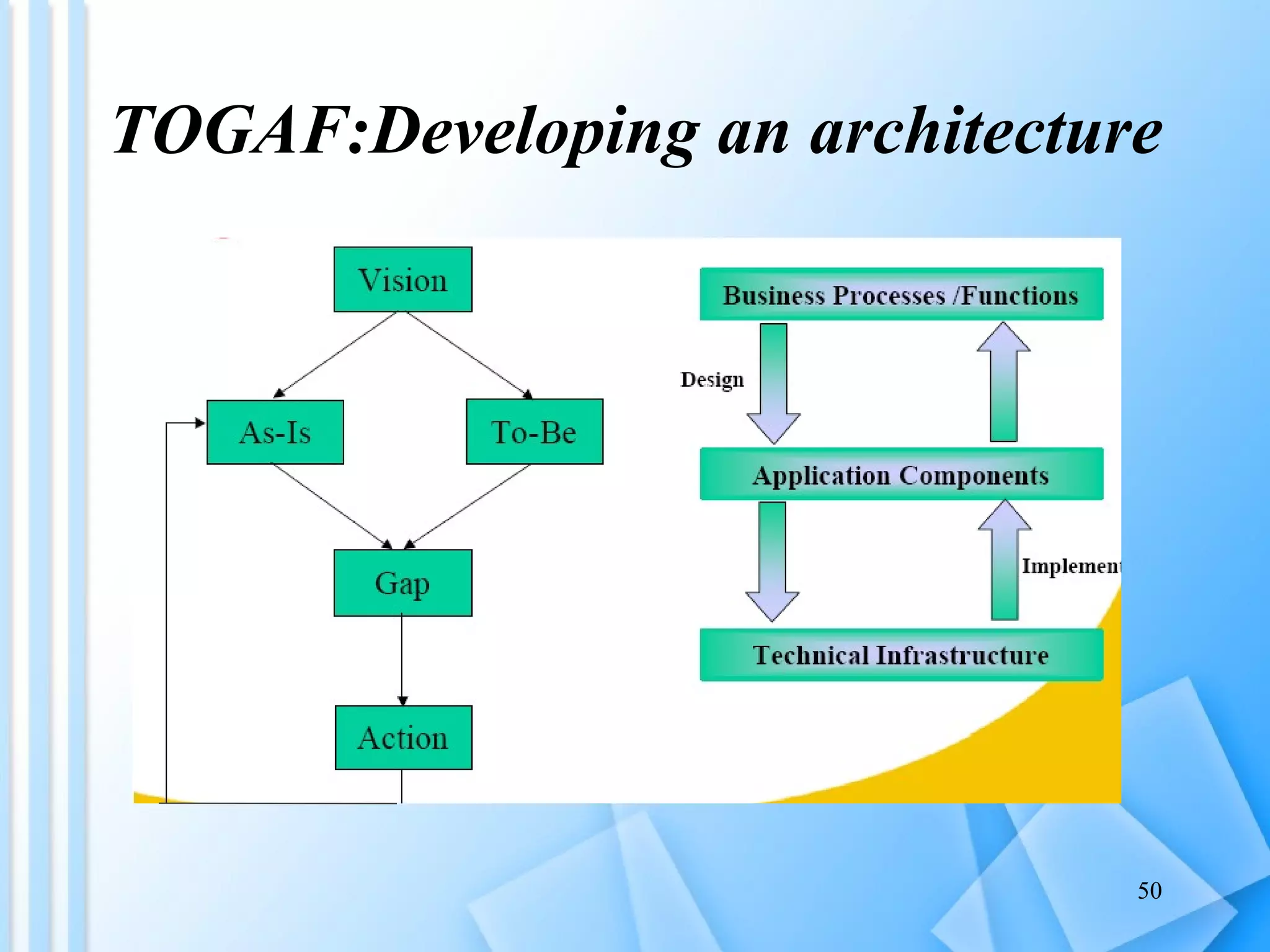
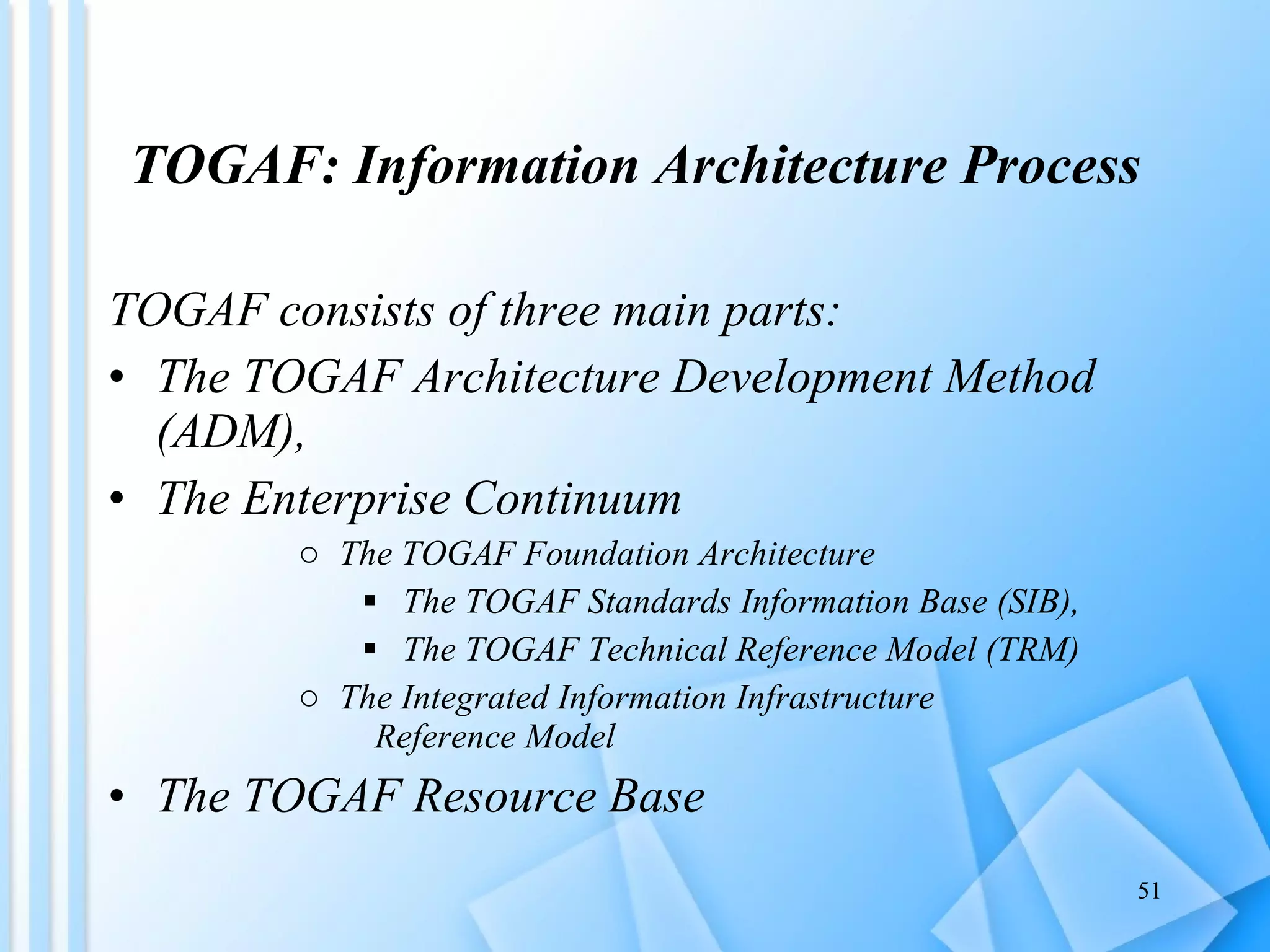
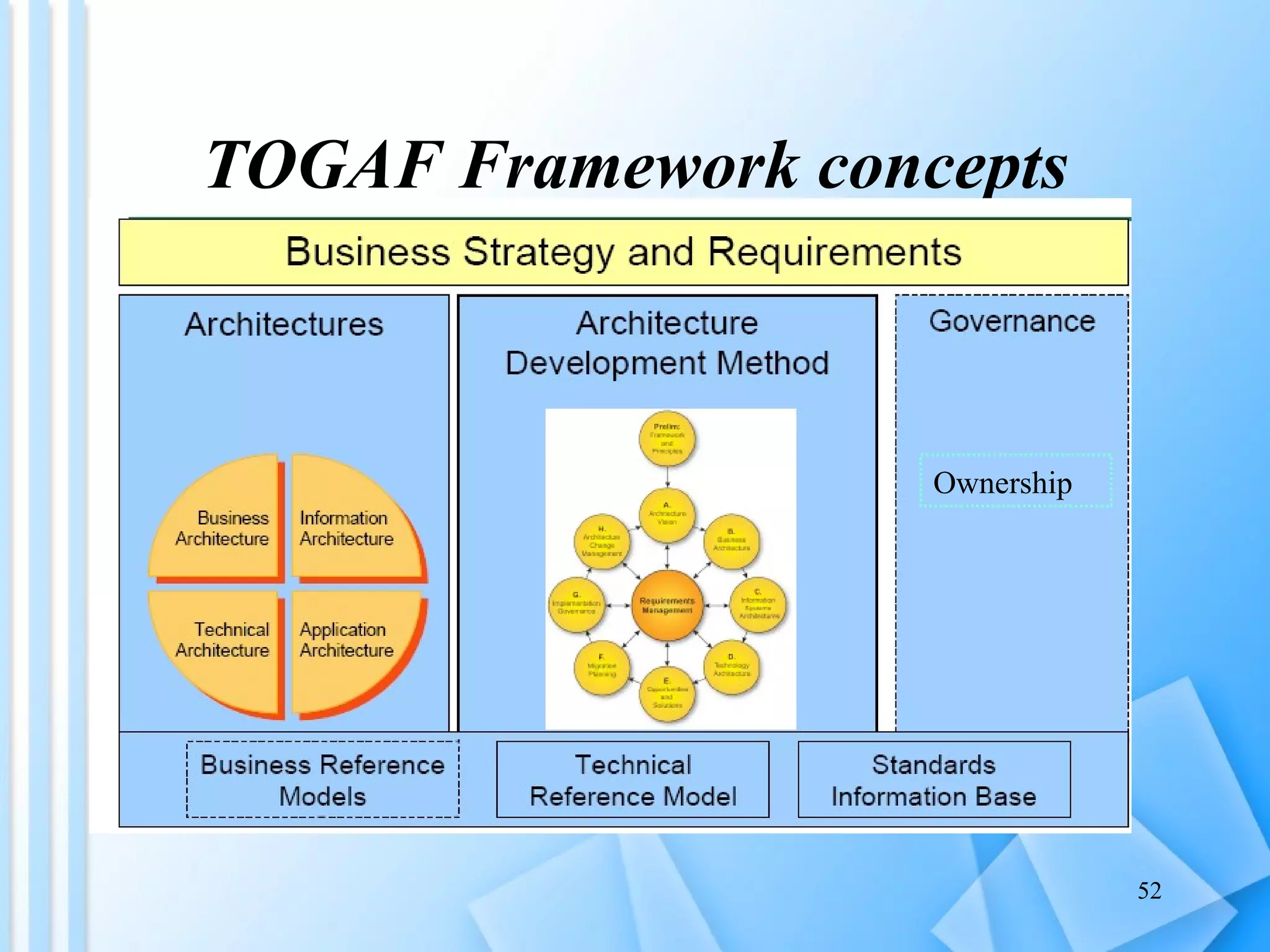
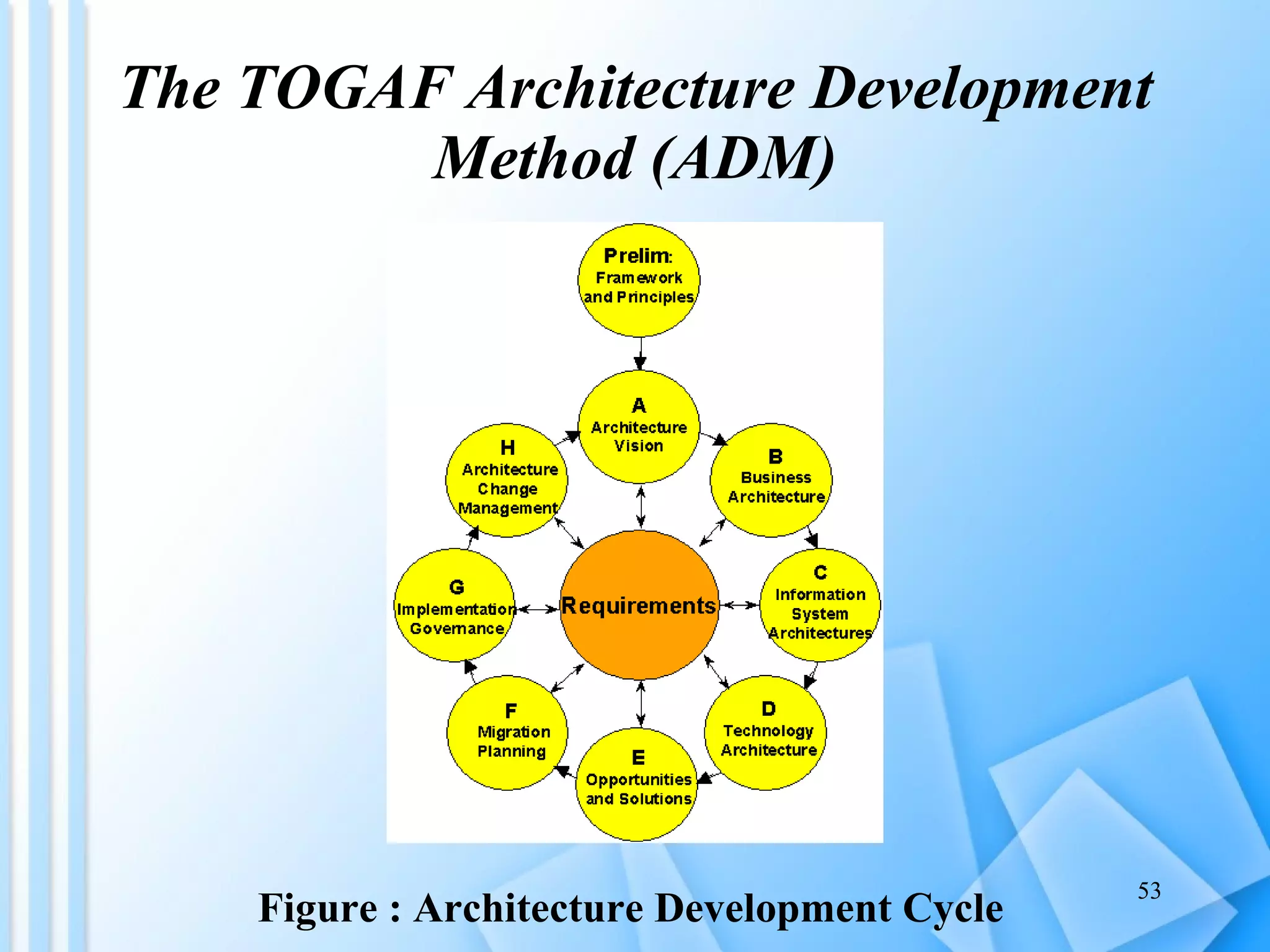
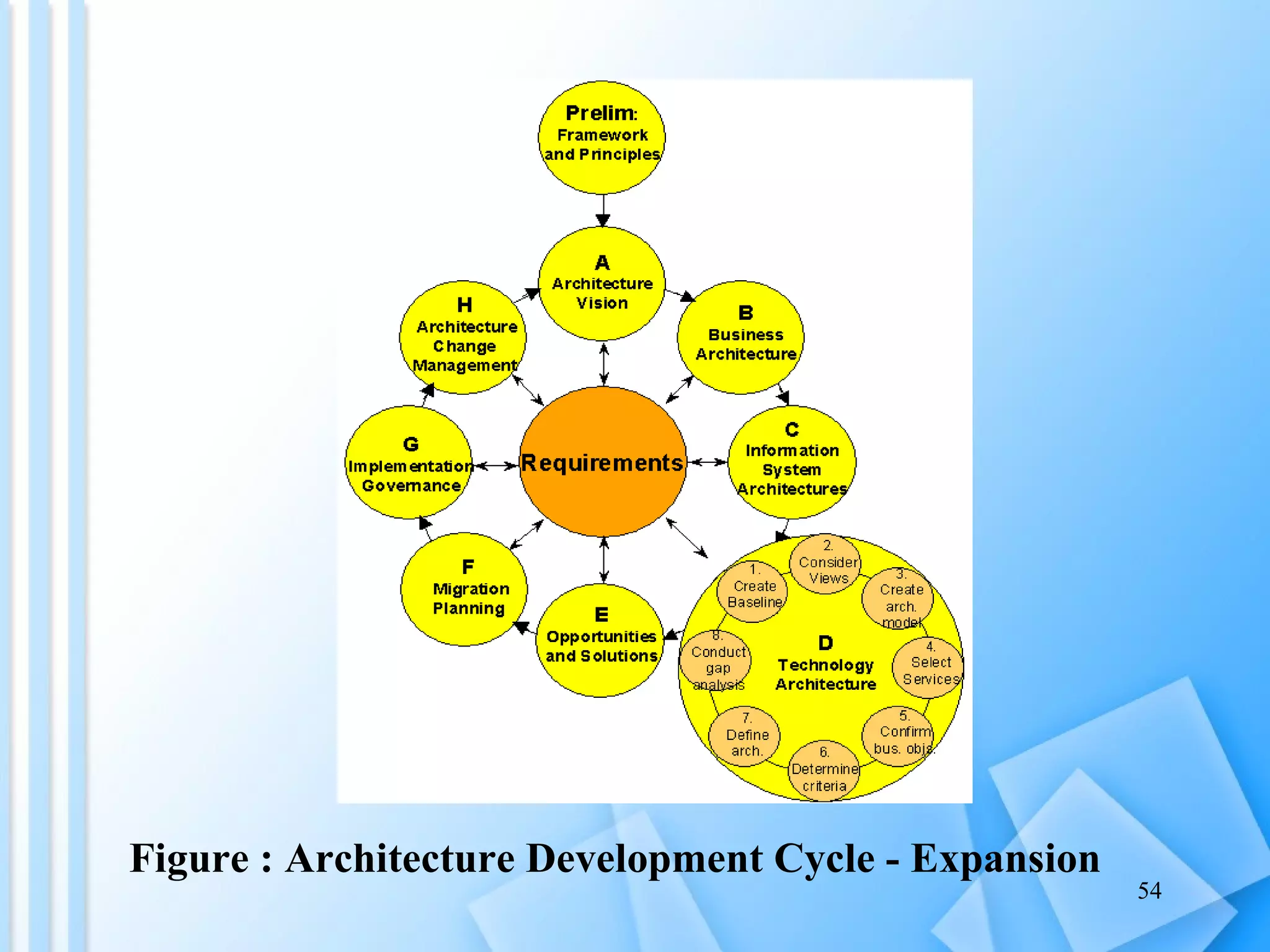
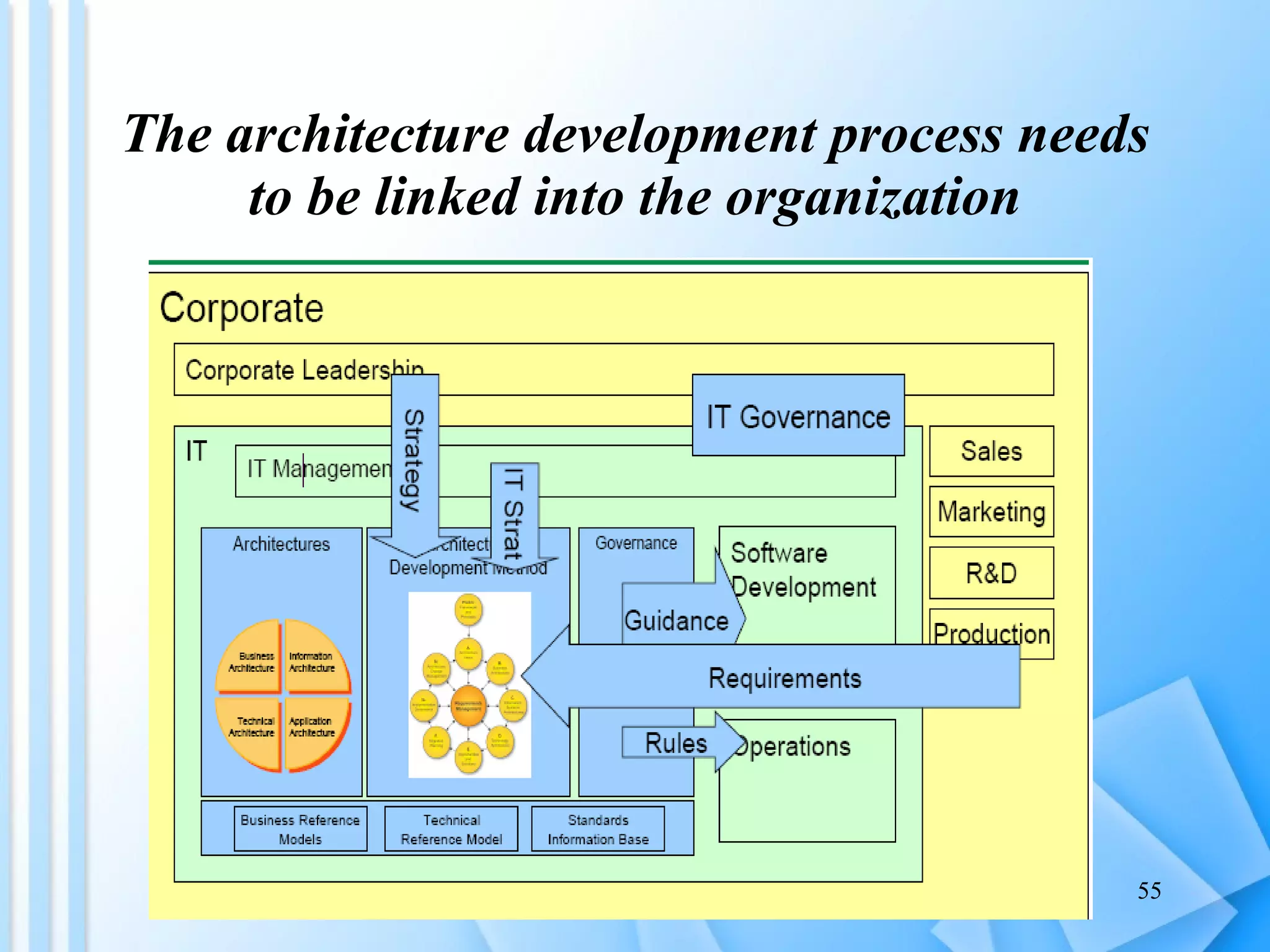
The document discusses information architecture as an emerging 21st century profession. It provides an overview of information architecture, including definitions, key challenges in designing complex information systems, and the roles and skills of information architects. It also describes the TOGAF framework for developing enterprise architecture, which provides a standard process and common language for designing, planning and implementing an enterprise information architecture.
![Information Architecture: An emerging 21 st century profession By : Dr. A.K. Ramani Prof. & Head SCSIT, DAVV, Indore(M.P.), India [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conferencekualalumpur-100516065158-phpapp01/75/Information-Architecture-Profession-1-2048.jpg)






















































![Wrap Up Contact information: Dr. A.K Ramani Prof. & Head SCSIT,DAVV(Indore) email: [email_address] Thank you and Good Luck….](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conferencekualalumpur-100516065158-phpapp01/75/Information-Architecture-Profession-75-2048.jpg)