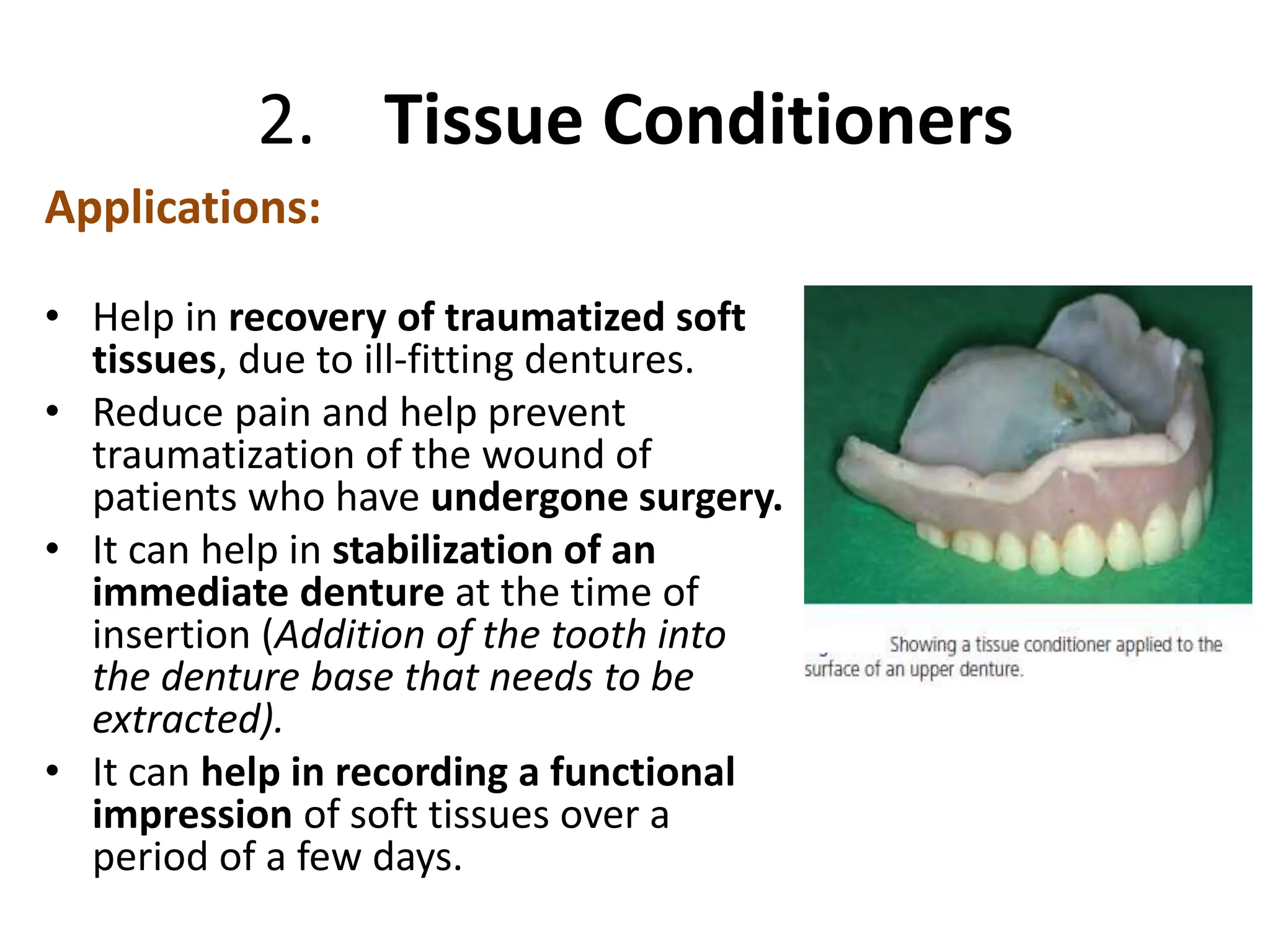
The document discusses denture lining materials, categorizing them into three main groups: hard reline materials, tissue conditioners, and soft lining materials. It highlights the indications, contraindications, properties, and manipulation techniques associated with each type, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it covers the importance of proper material selection and care in maintaining the functionality and comfort of dentures.