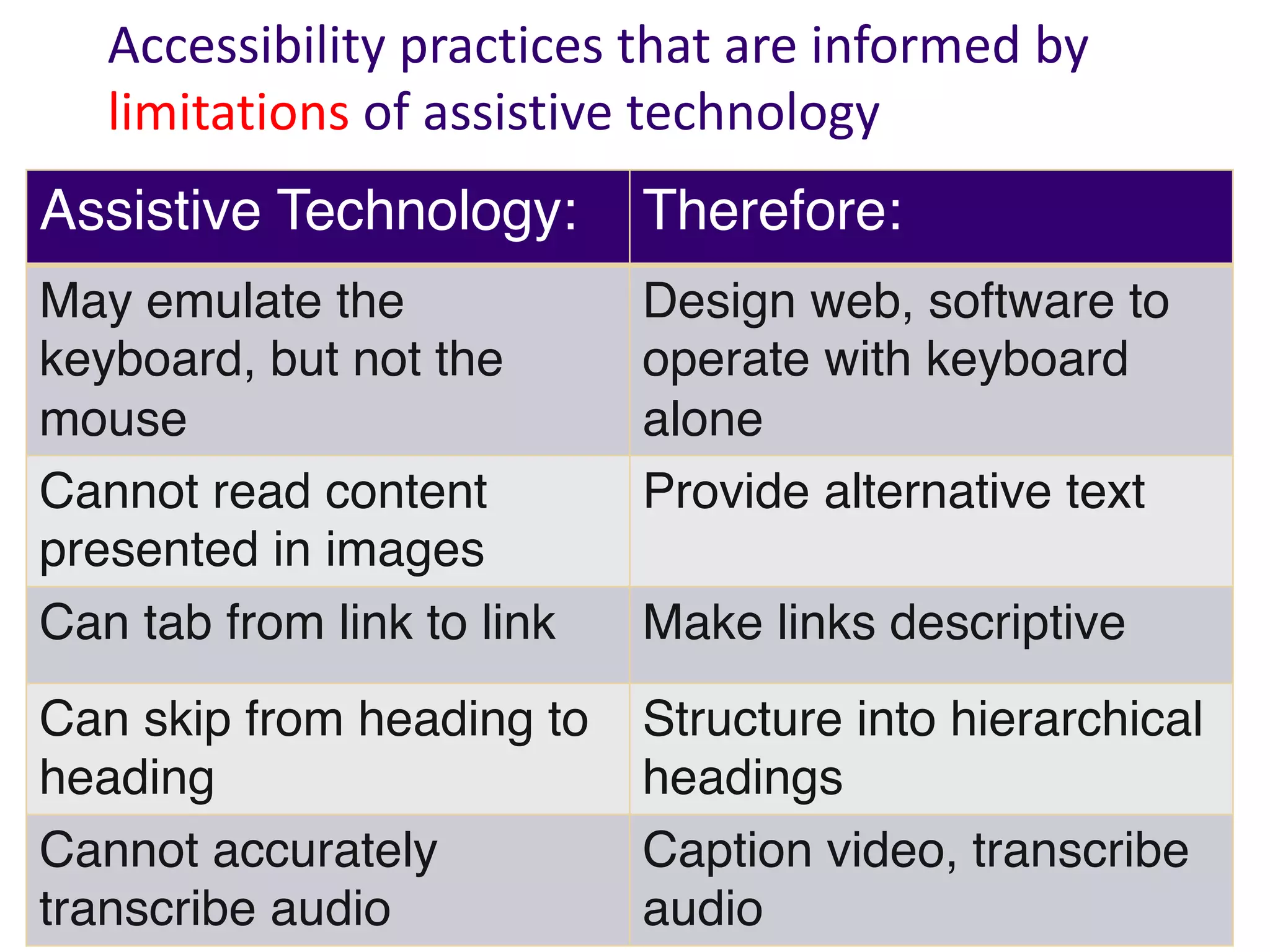
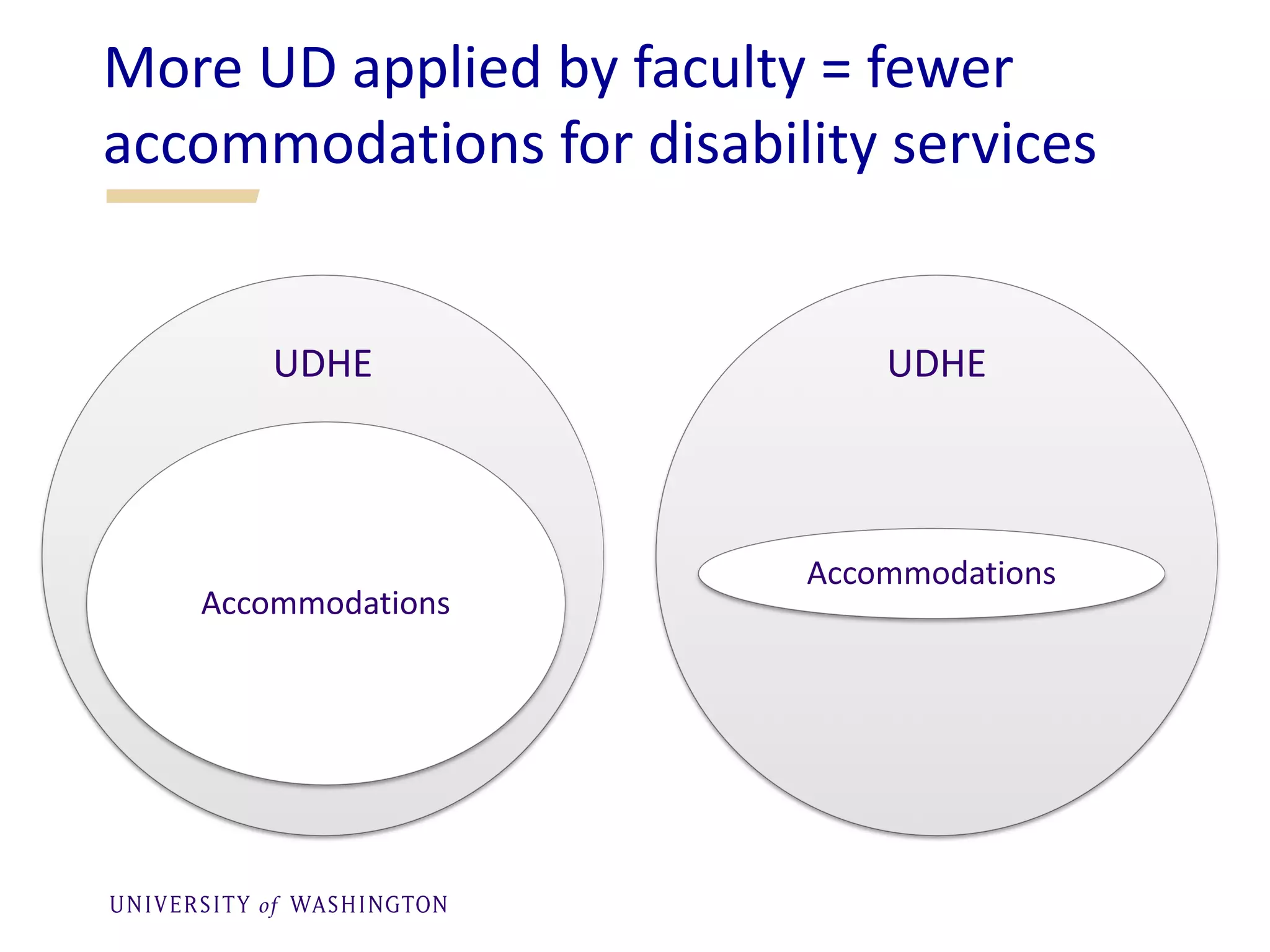
The document provides tips for online learning instructors on accessibility, emphasizing the importance of universal design to ensure all students, including those with disabilities, can access and engage with course materials equally. It outlines legal obligations for accessibility and offers practical strategies such as using clear layouts, alternative text for images, and captioned videos. The author advocates for proactive design principles that benefit all learners, promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion in educational environments.