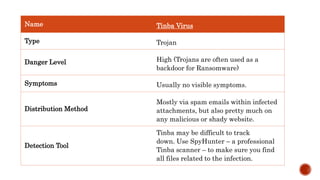
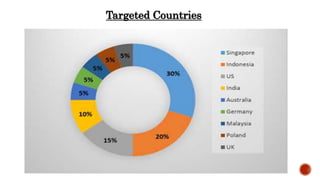
The Tinba virus is a trojan that targets financial institution websites. It is a modified version of older banker trojans and Zeus trojan that is much smaller, at only 20KB, making it difficult to detect. It operates using packet sniffing to launch man-in-the-browser attacks or create fake login pages to steal users' sensitive banking login and account information. Tinba was first discovered in 2012 and has since infected over two dozen major US banks by extracting site formatting to mimic legitimate login pages or intercepting keystrokes during encrypted sessions. Prevention involves being careful of what is downloaded and visited online to avoid malware infections.