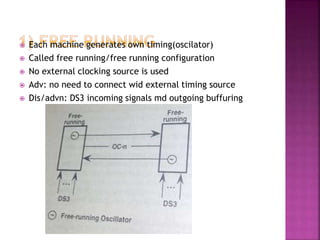
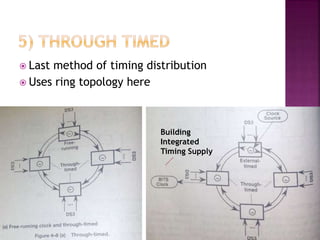
This document discusses timing and synchronization in digital communication systems. It explains that digital signals are transmitted as pulses or clocks, and receivers must detect these signals accurately by synchronizing to the transmitter's clock. Five methods of clock exchange are described to achieve synchronization between machines: free running, line-timed, loop-timed, external, and through-timed. Maintaining accurate synchronization is important to avoid errors that can reduce throughput or cause audible clicks in signals like voice and video.