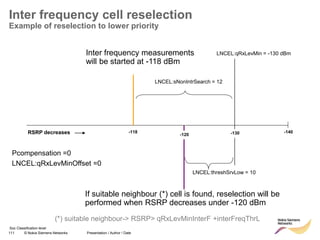
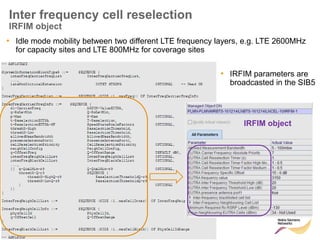
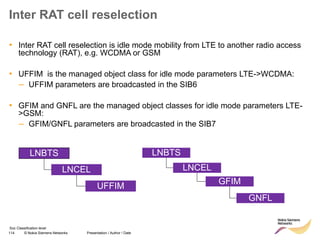
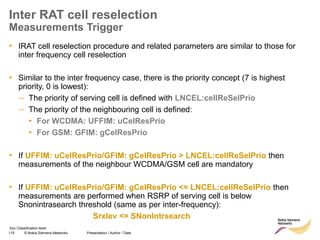
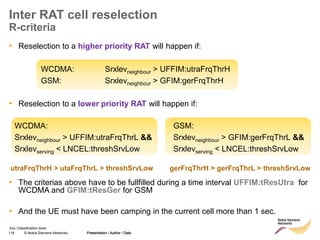
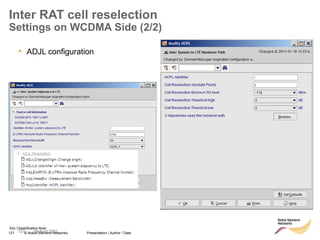
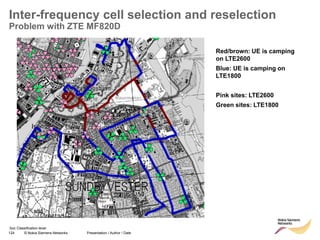
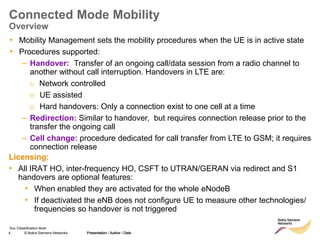
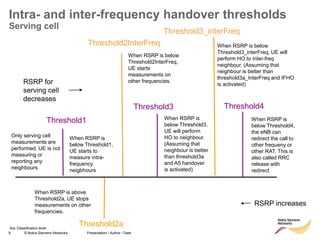
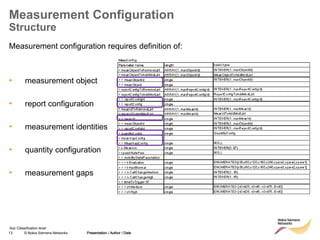
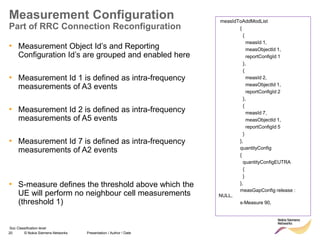
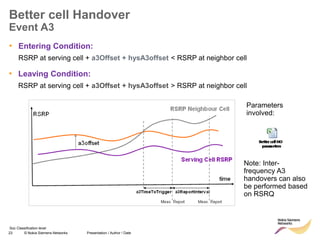
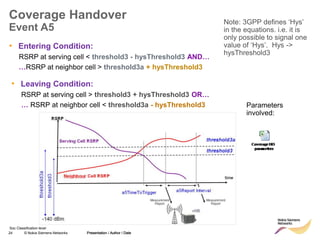
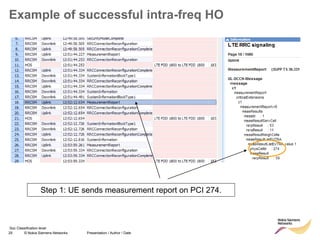
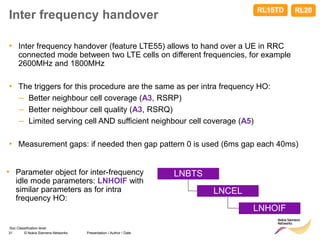
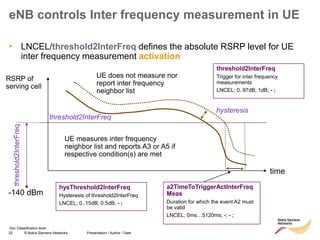
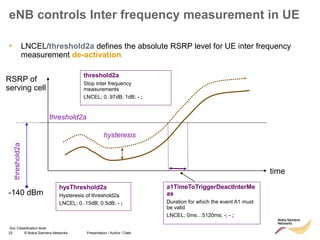
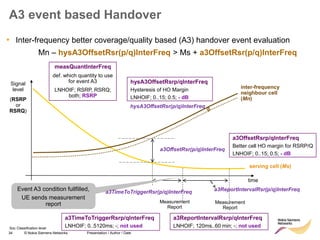
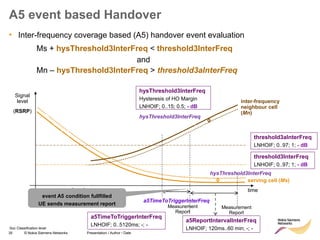
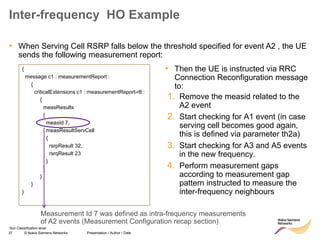
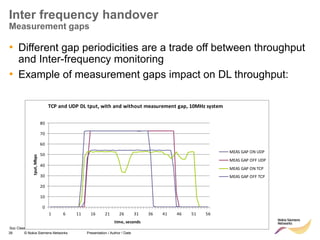
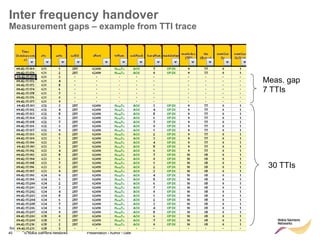
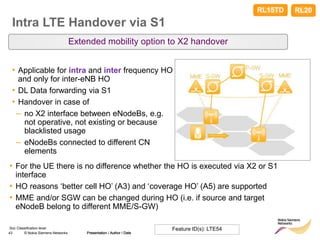
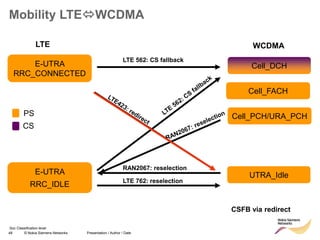
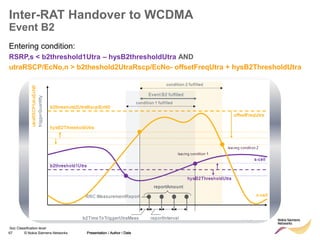
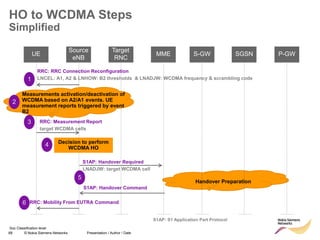
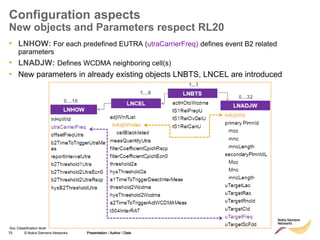
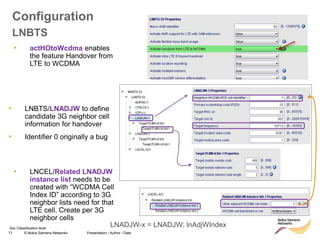
The document discusses mobility management in LTE networks. It covers connected mode mobility including an overview of mobility triggers and handover thresholds, measurement configuration, intra-frequency handovers, inter-frequency handovers, and inter-RAT handovers. It also discusses idle mode mobility including system information blocks and cell selection procedures for intra-frequency, inter-frequency, and inter-RAT mobility. The presentation provides details on the different mobility management procedures and configuration parameters in LTE networks.








![14 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
Soc Classification level
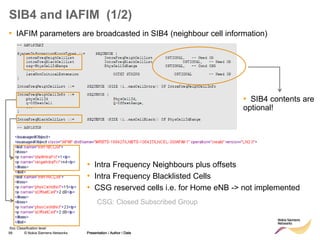
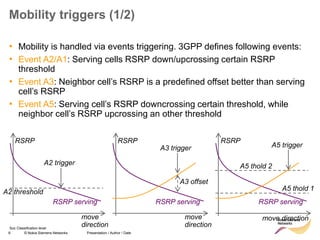
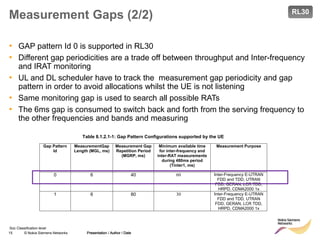
Measurement Gaps (1/2)
• Depending on UE capabilities measurement gaps may be required for several
types of handovers. E.g. inter-RAT-HO, inter-frequency-HO, network assisted cell
change
• During measurement Gaps the UE is measuring Inter-frequency/ I-RAT
candidates and does not transmit nor receive any data from the serving cell
MeasGapConfig
The IE MeasGapConfig specifies the measurement gap configuration and controls setup/ release of measurement gaps.
MeasGapConfig information element
-- ASN1START
MeasGapConfig ::= CHOICE {
release NULL,
setup SEQUENCE {
gapOffset CHOICE {
gp0 INTEGER (0..39),
gp1 INTEGER (0..79),
...
}
}
}
-- ASN1STOP
MeasGapConfig field descriptions
gapOffset
Value gapOffset of gp0 corresponds to gap offset of Gap Pattern Id “0” with TGRP = 40ms, gapOffset of gp1
corresponds to gap offset of Gap Pattern Id “1” with TGRP = 80ms. Also used to specify the measurement gap pattern
to be applied, as defined in TS 36.133 [16].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06altemobilitymanagementv10-220408214004/85/06a_LTE-mobility-management-v1_0-ppt-14-320.jpg)



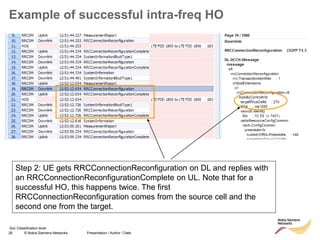

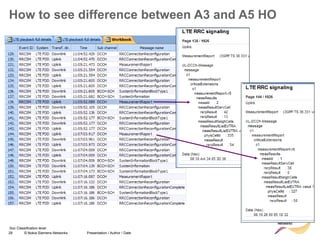








![49 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
Soc Classification level
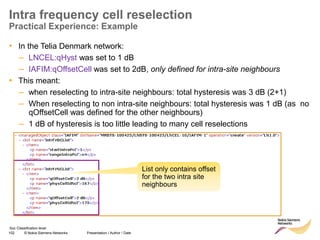
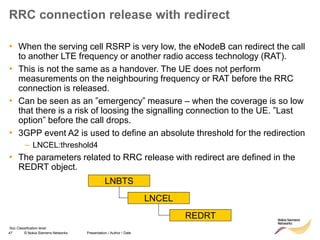
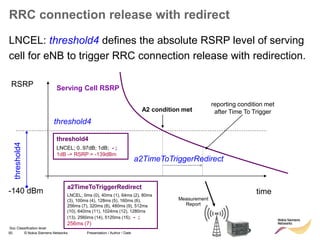
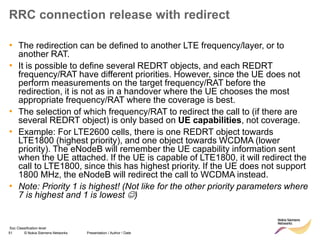
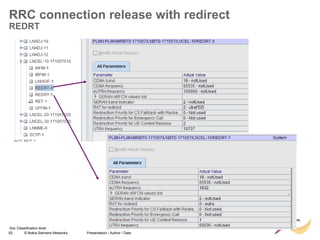
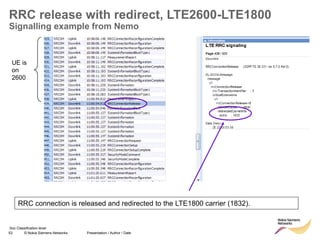
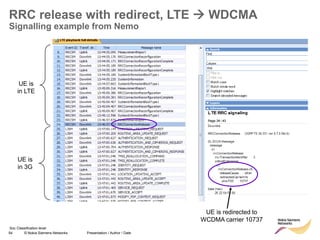
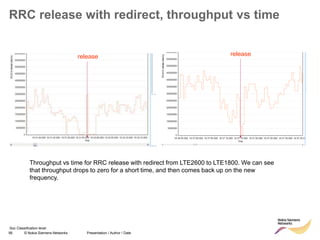
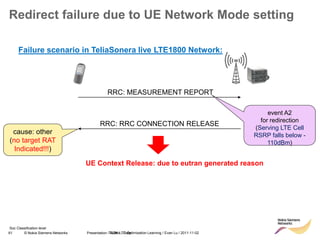
RRC connection release with redirect
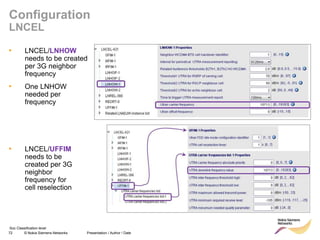
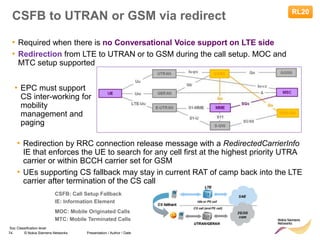
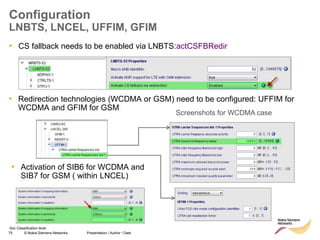
• Redirect feature can be enabled on LNBTS level:
[..] RRC: MEASUREMENT REPORT
RRC: RRC CONNECTION RELEASE
event A2
for redirection
target RAT
indicated
enableCovHo
LNBTS; 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled);
1 (enabled)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06altemobilitymanagementv10-220408214004/85/06a_LTE-mobility-management-v1_0-ppt-49-320.jpg)

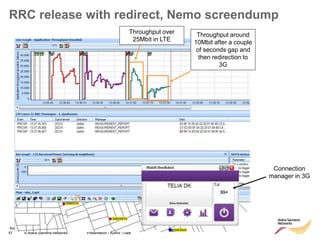
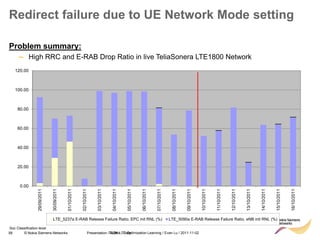
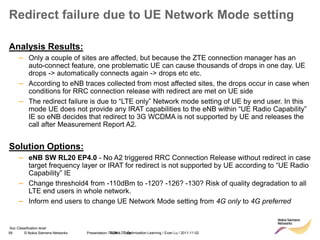
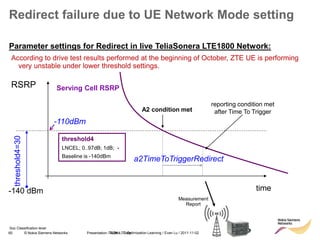








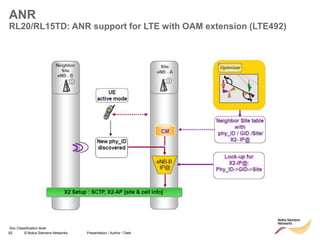

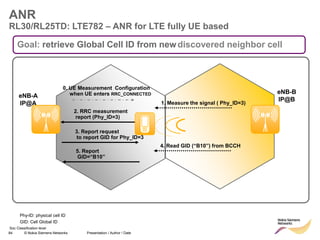
![85 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
Soc Classification level
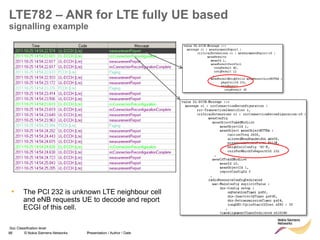
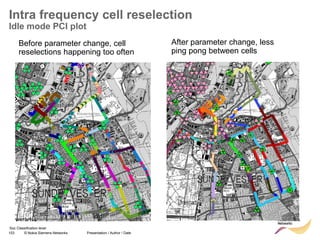
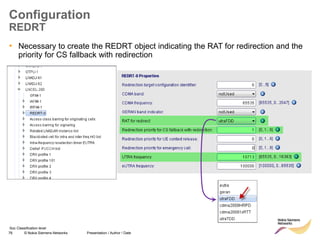
MME
ANR
RL30/RL25TD: LTE782 – ANR for LTE fully UE based
Site
eNB - A
Neighbor
Site
eNB - B
New cell
discovered
New cell
identified
by GID
CM
X2 Setup : IPsec, SCTP, X2-AP [site & cell info]
UE
connected
S1 : Request X2 Transport Configuration (GID)
S1: Request X2 Transport Configuration
relays
request
S1: Respond X2 Transport Configuration (IP@)
S1 : Respond X2 Transport Configuration (IP@)
CM
relays
response
Add Site & Cell
parameter of
eNB-A
CM CM
Add Site & Cell
Parameter of
eNB-B
Neighbor Cell Tables in both eNB updated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06altemobilitymanagementv10-220408214004/85/06a_LTE-mobility-management-v1_0-ppt-84-320.jpg)