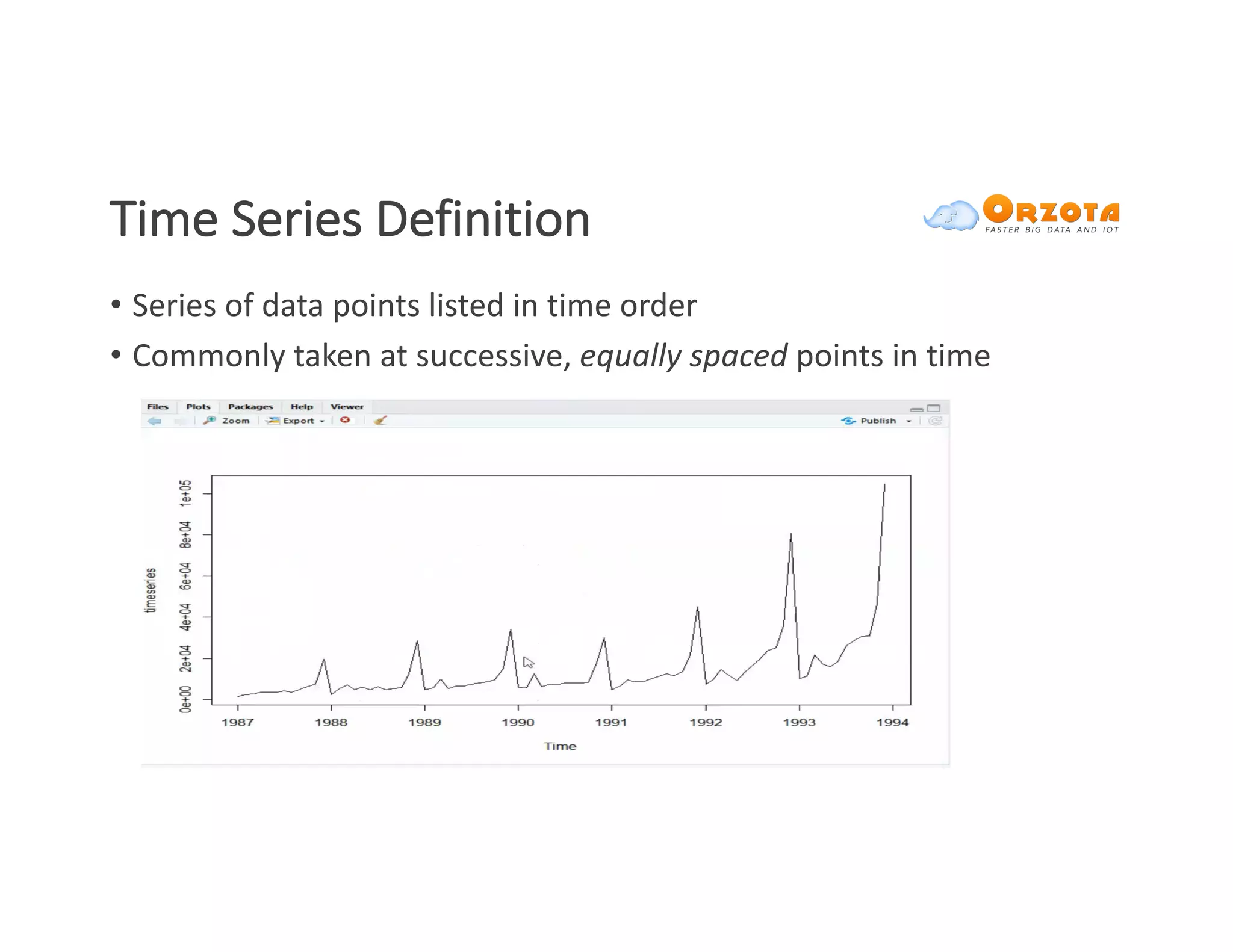
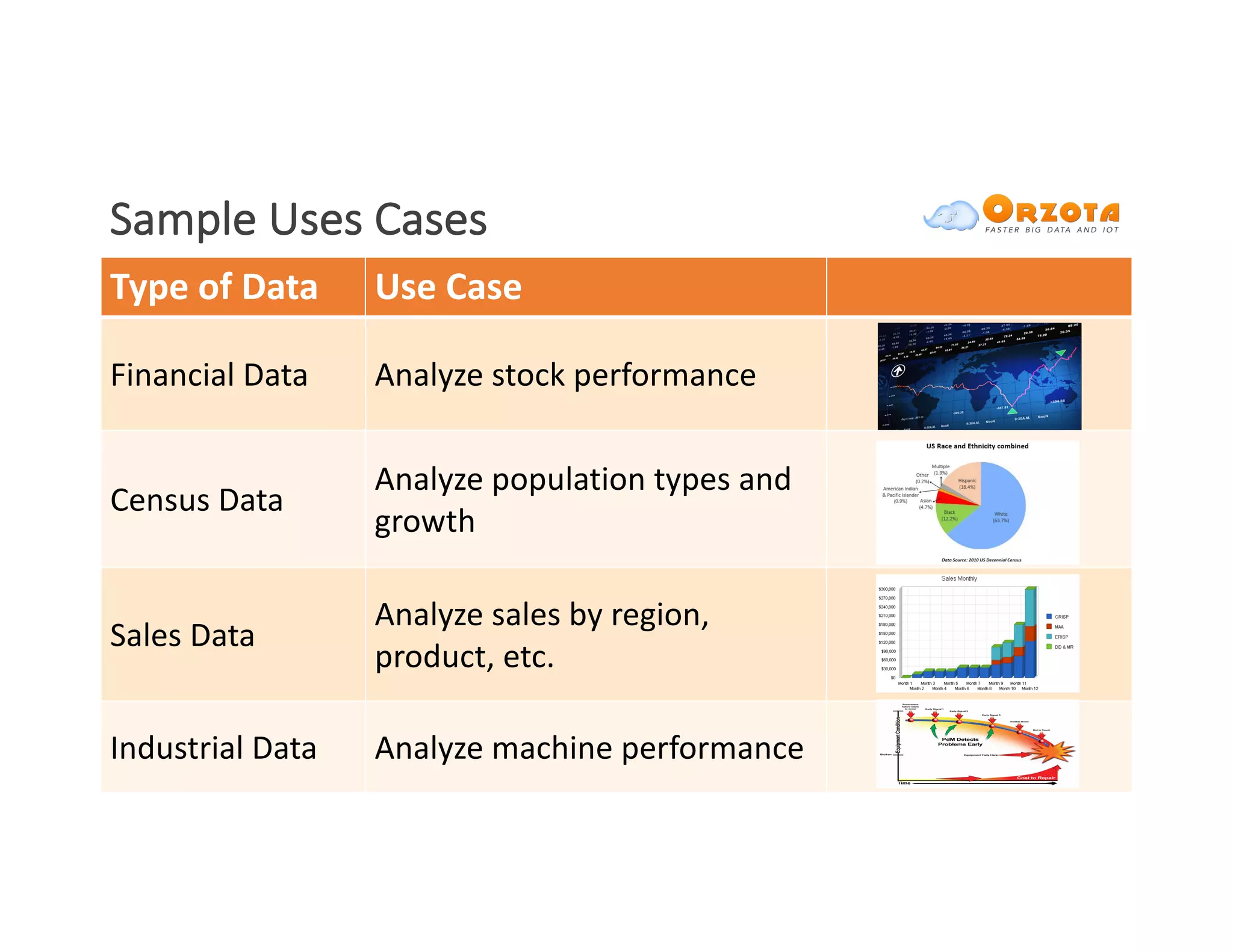
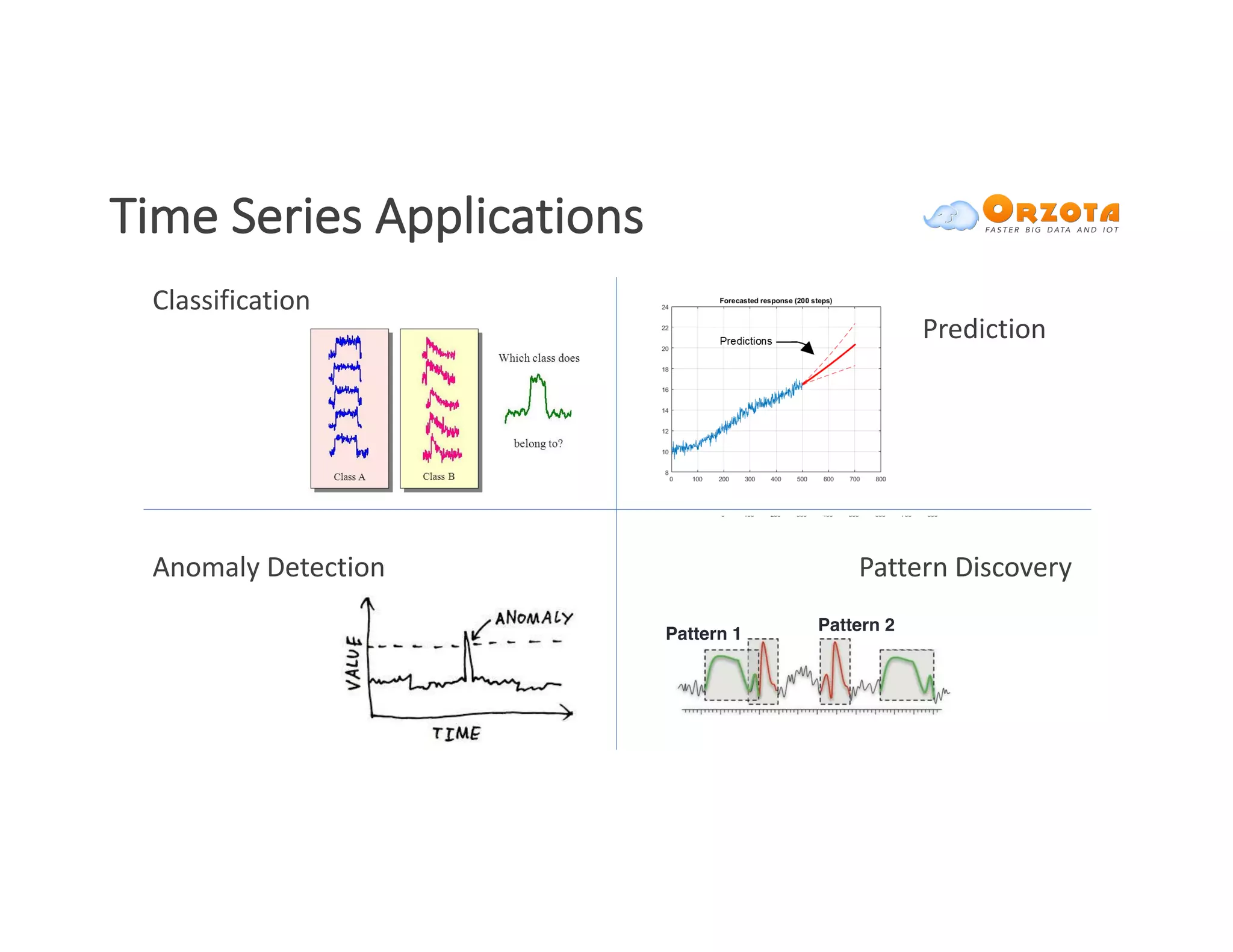
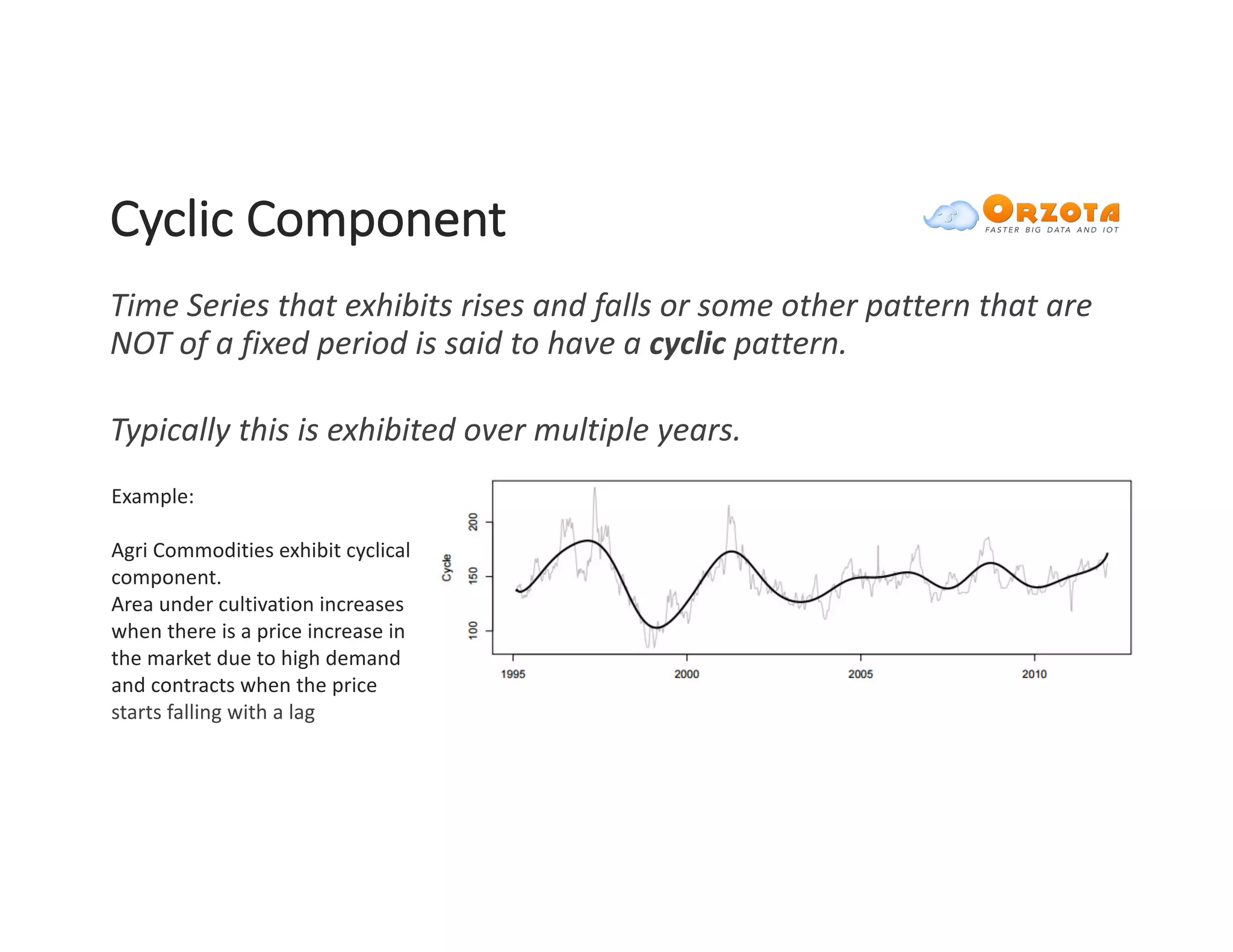
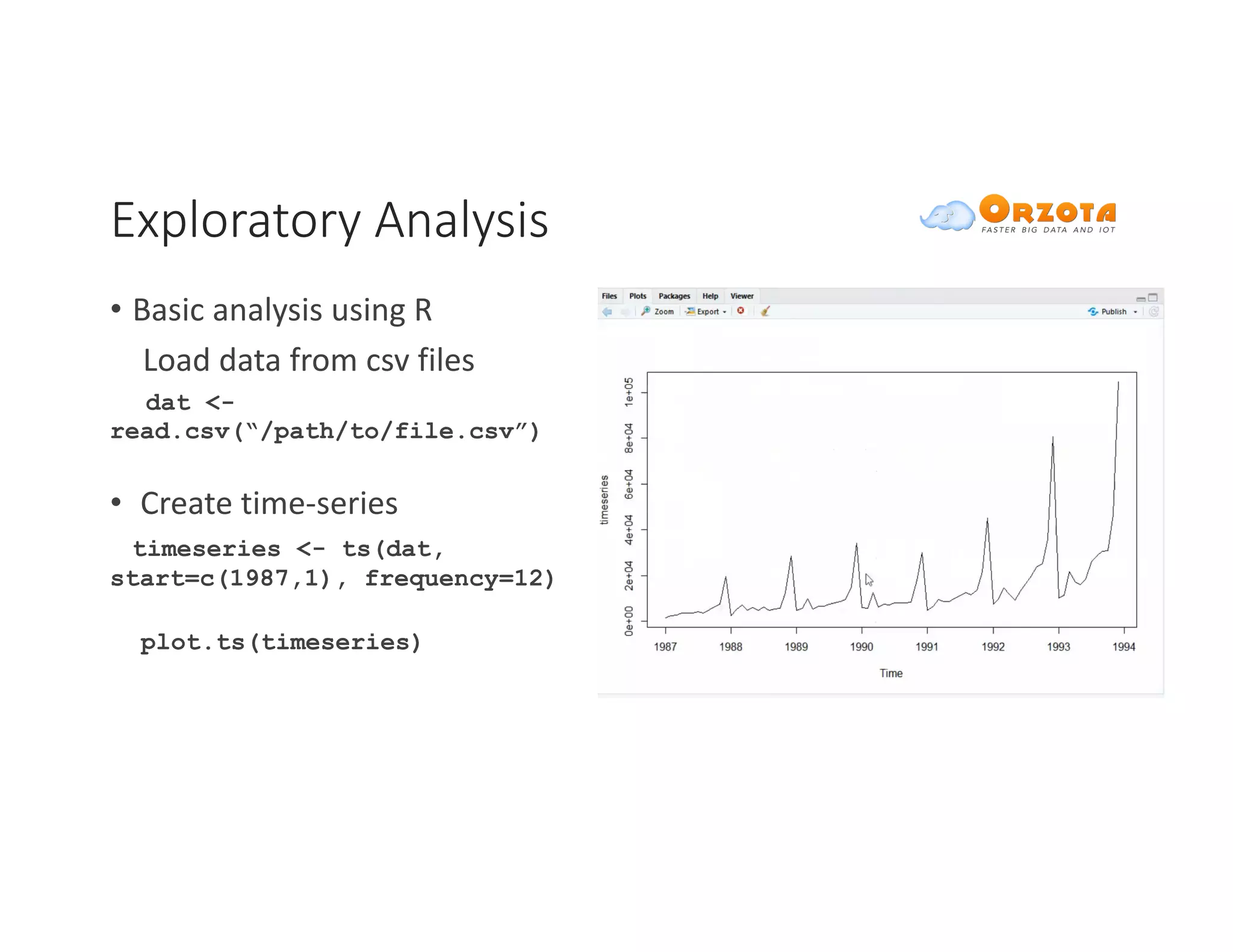
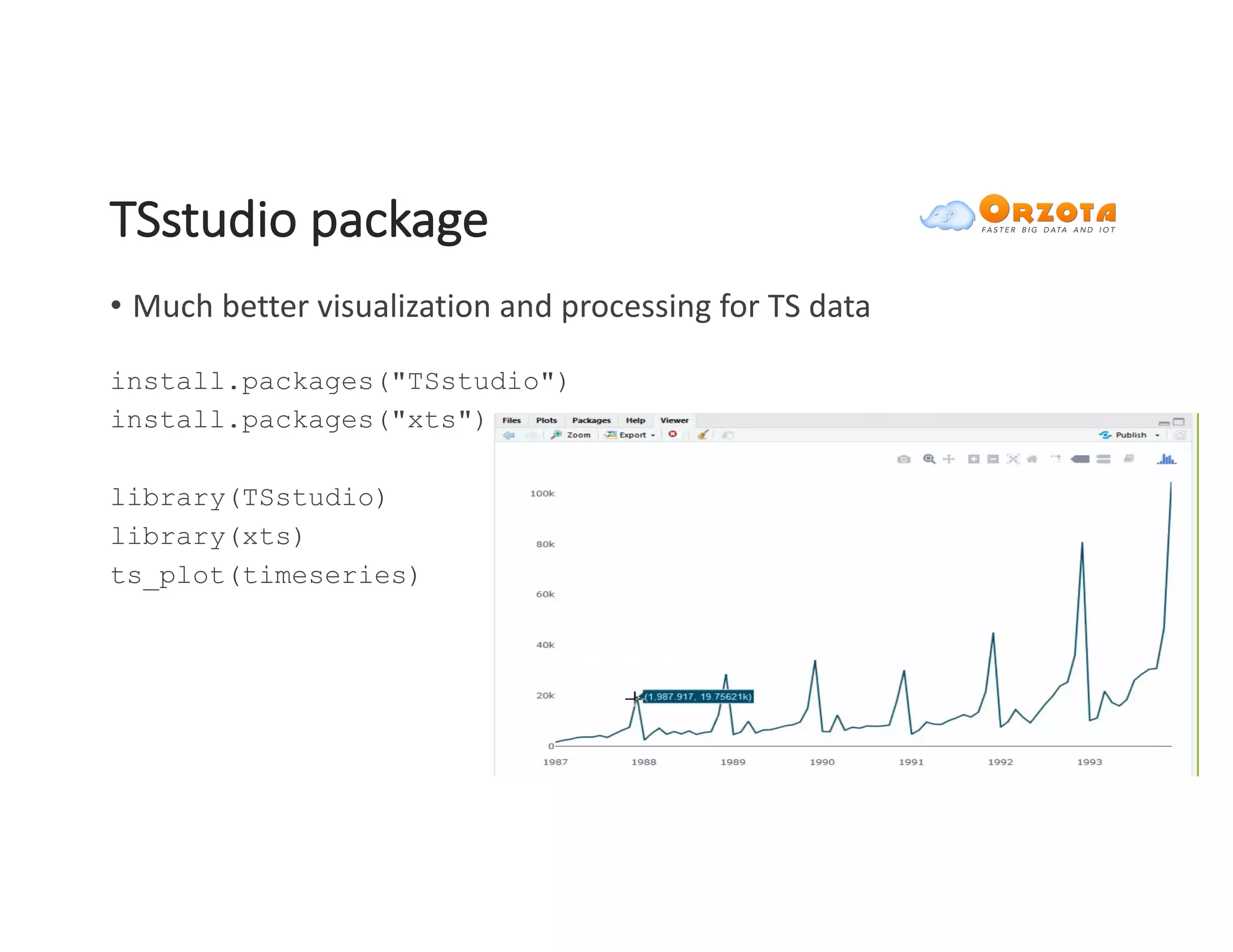
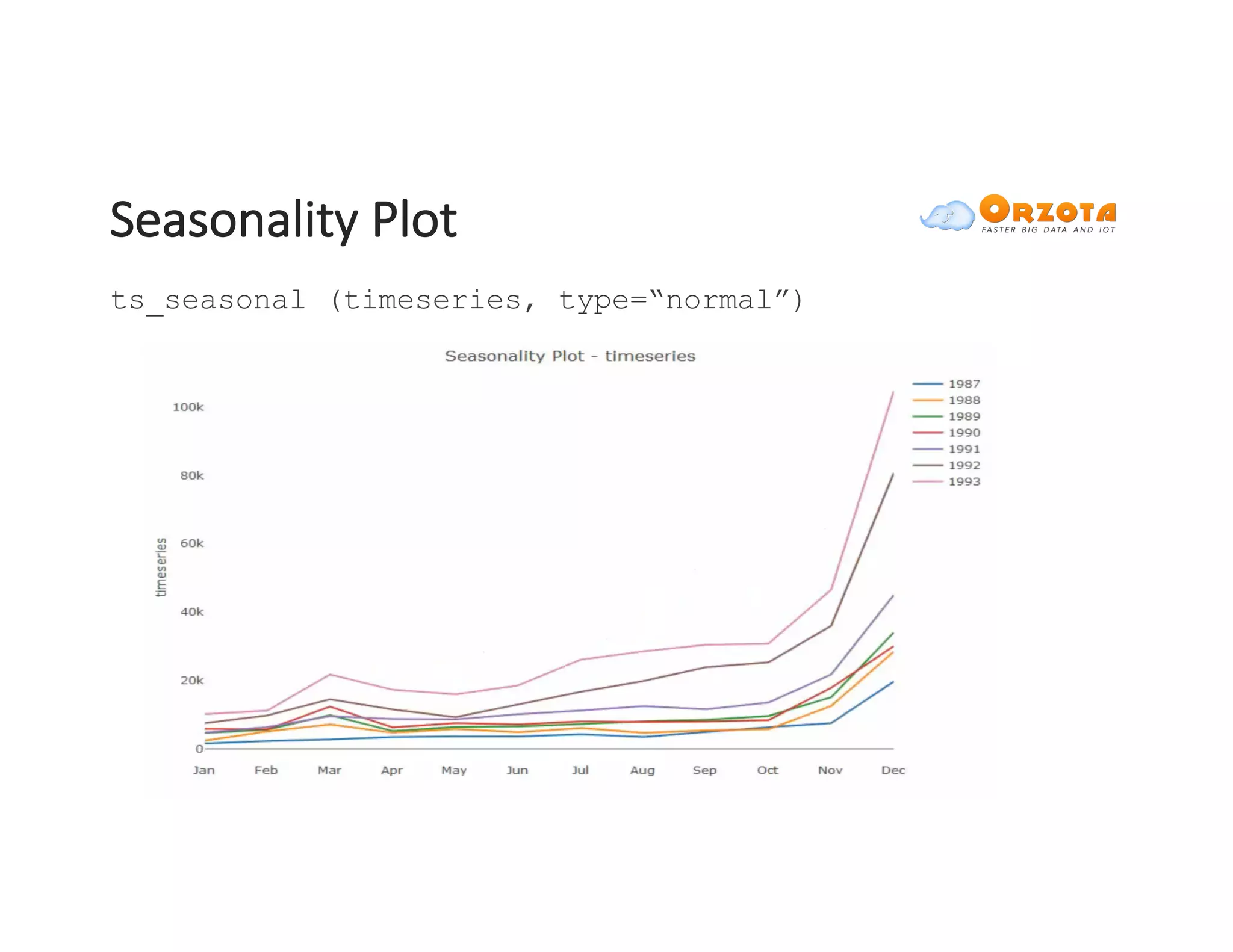
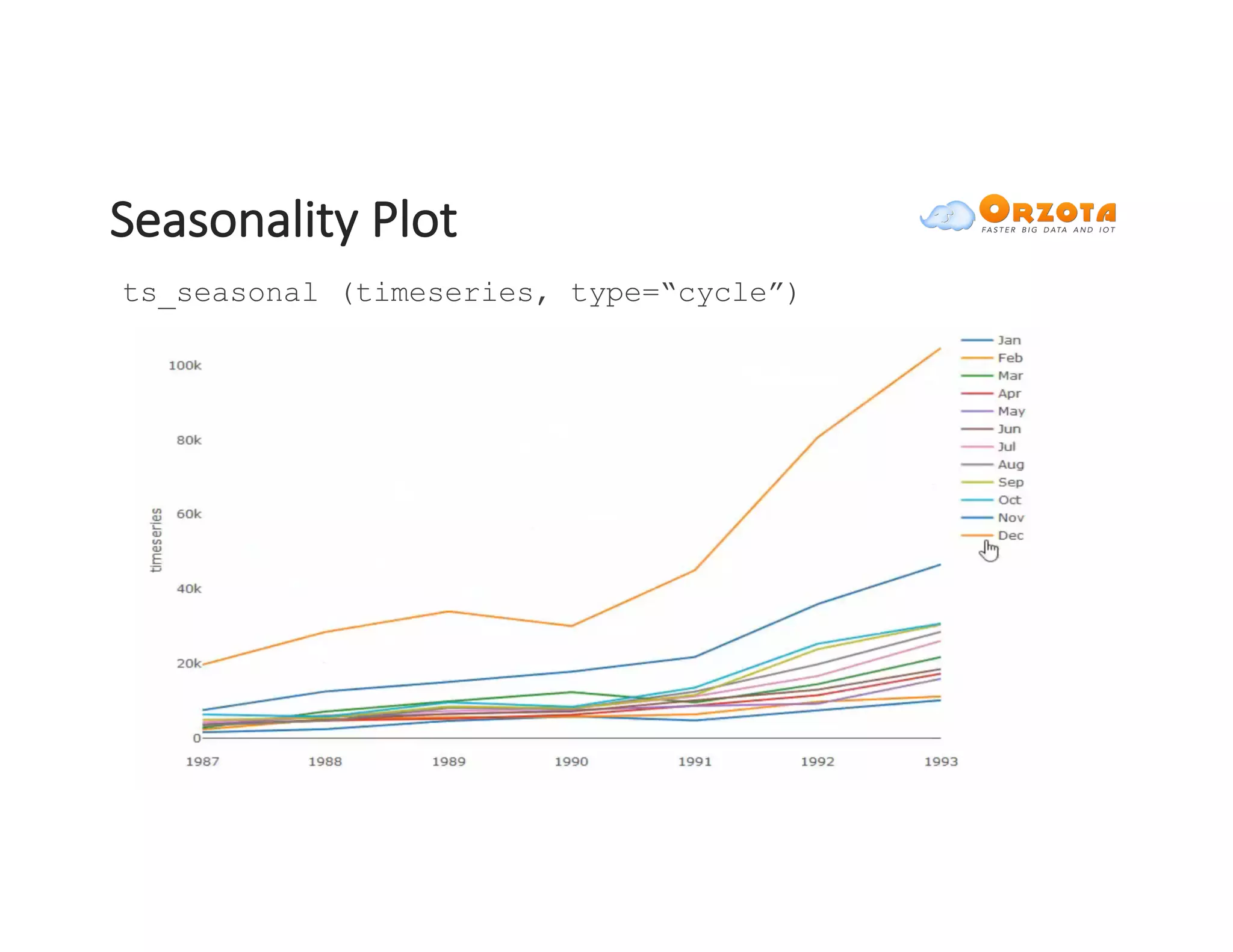
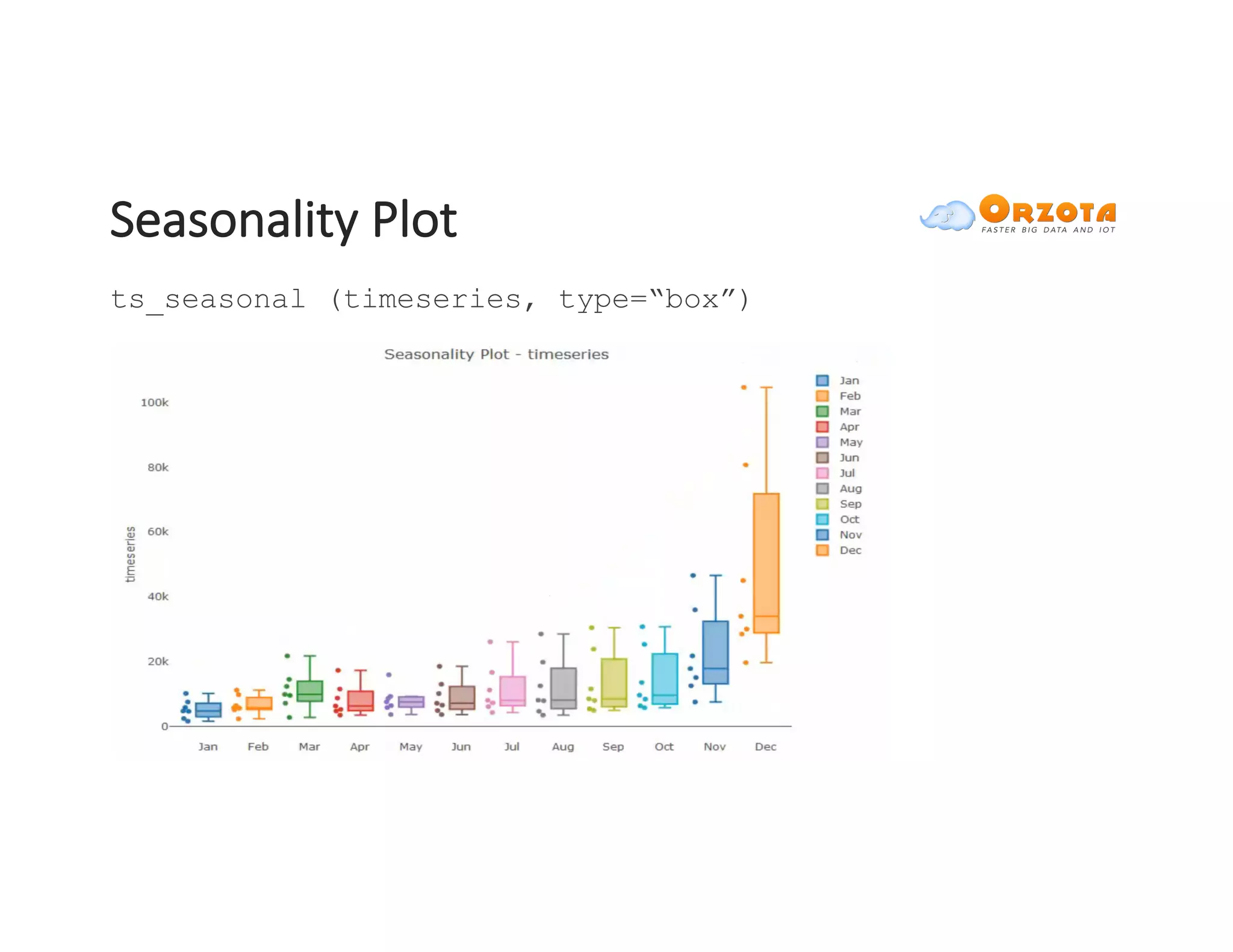
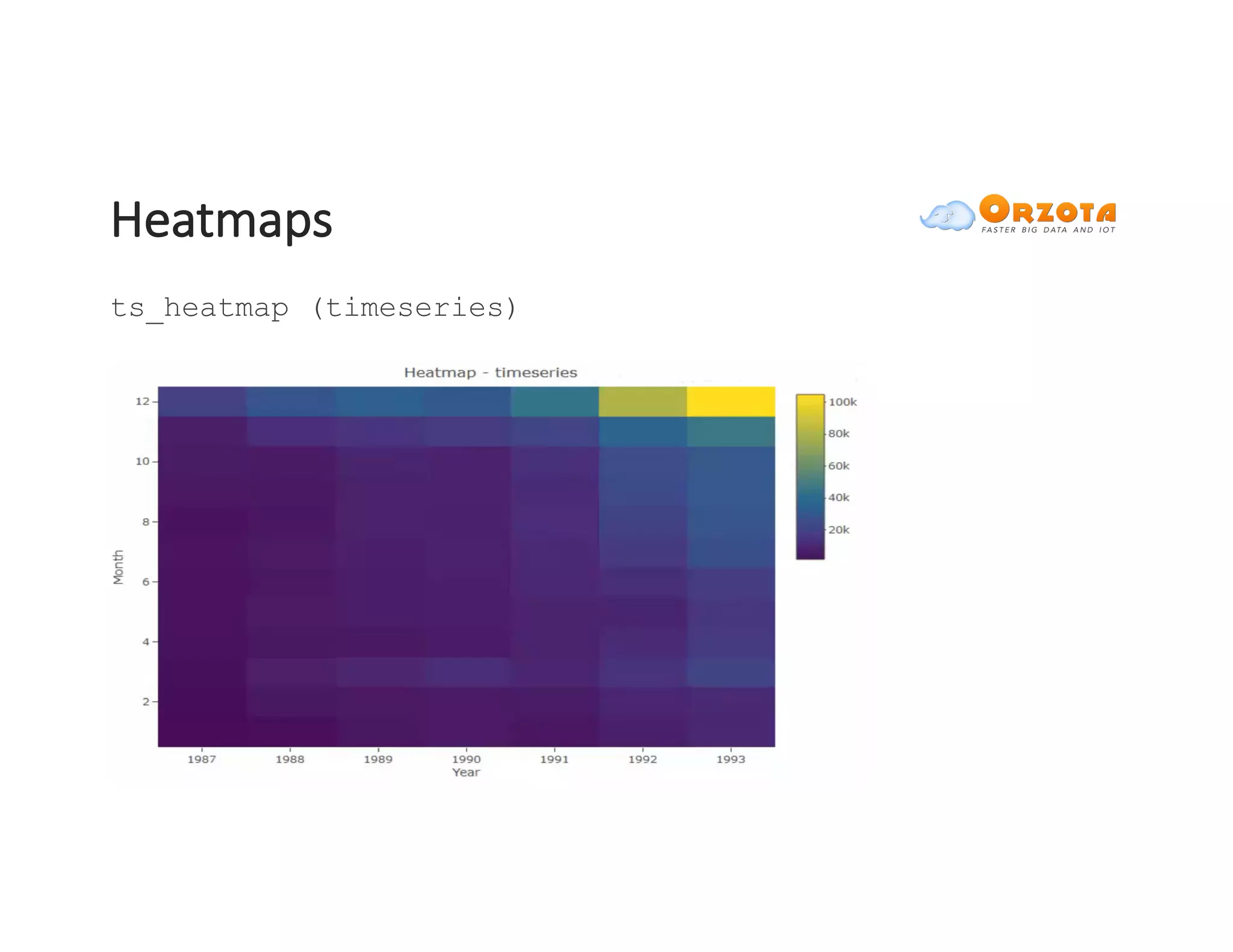
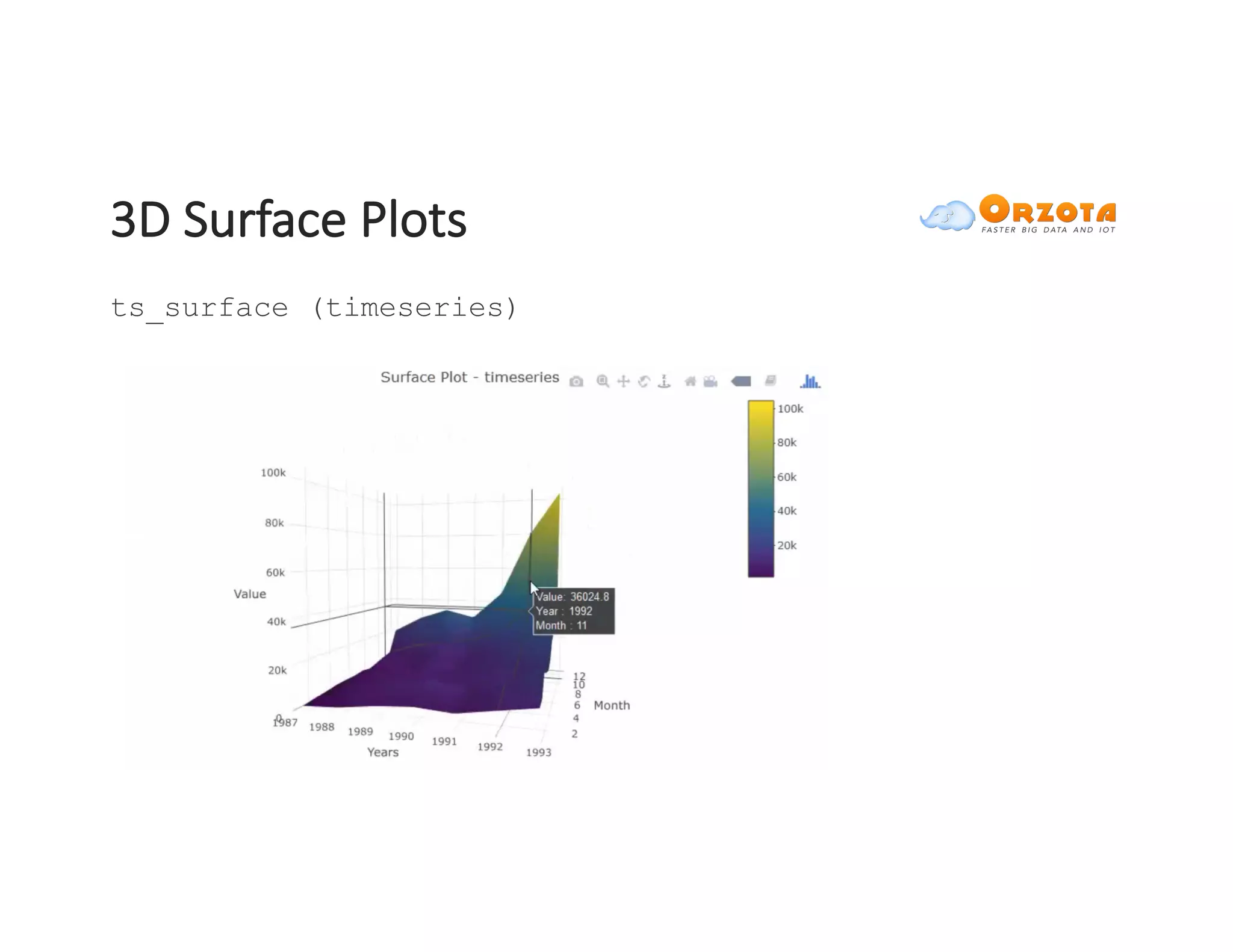
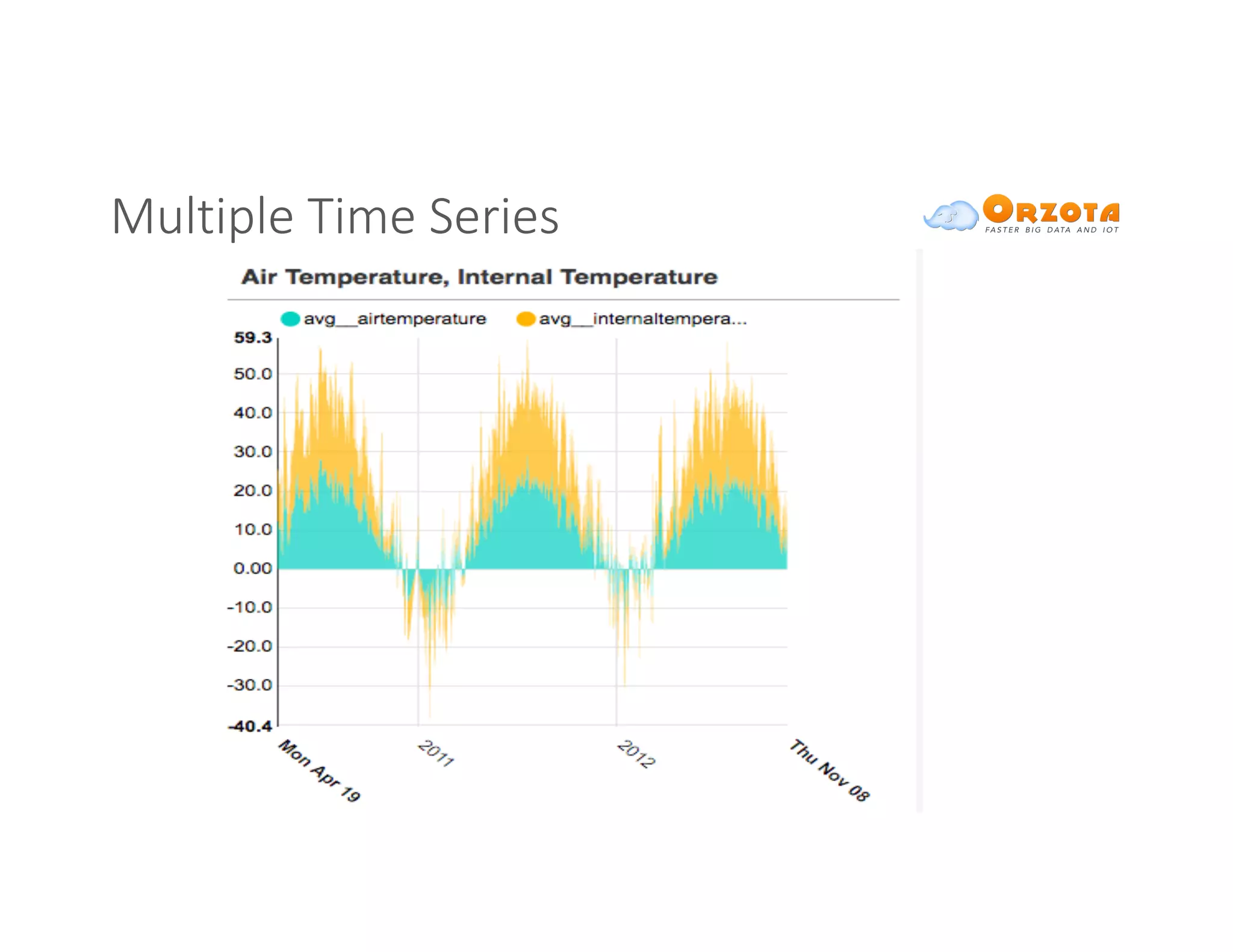
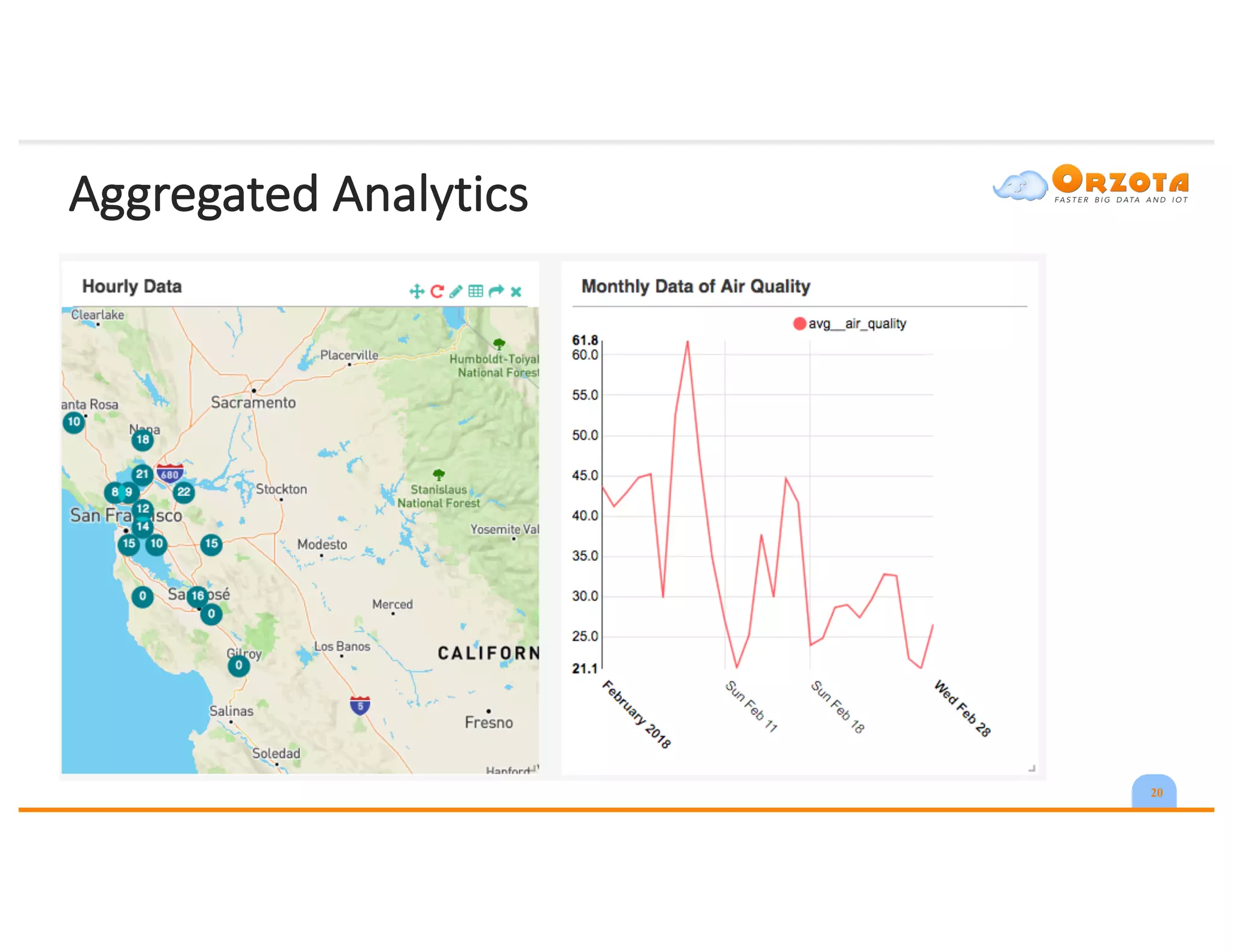
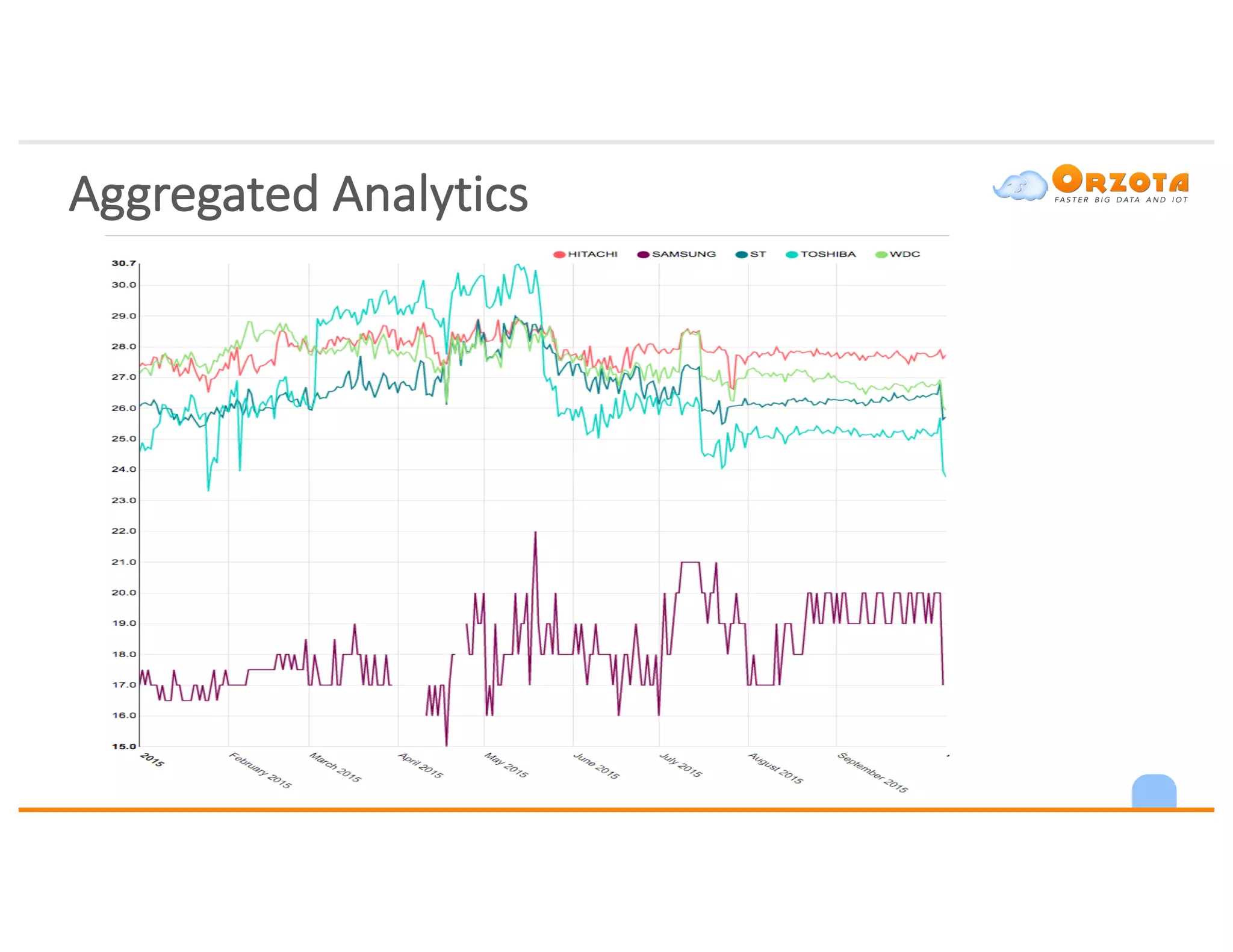
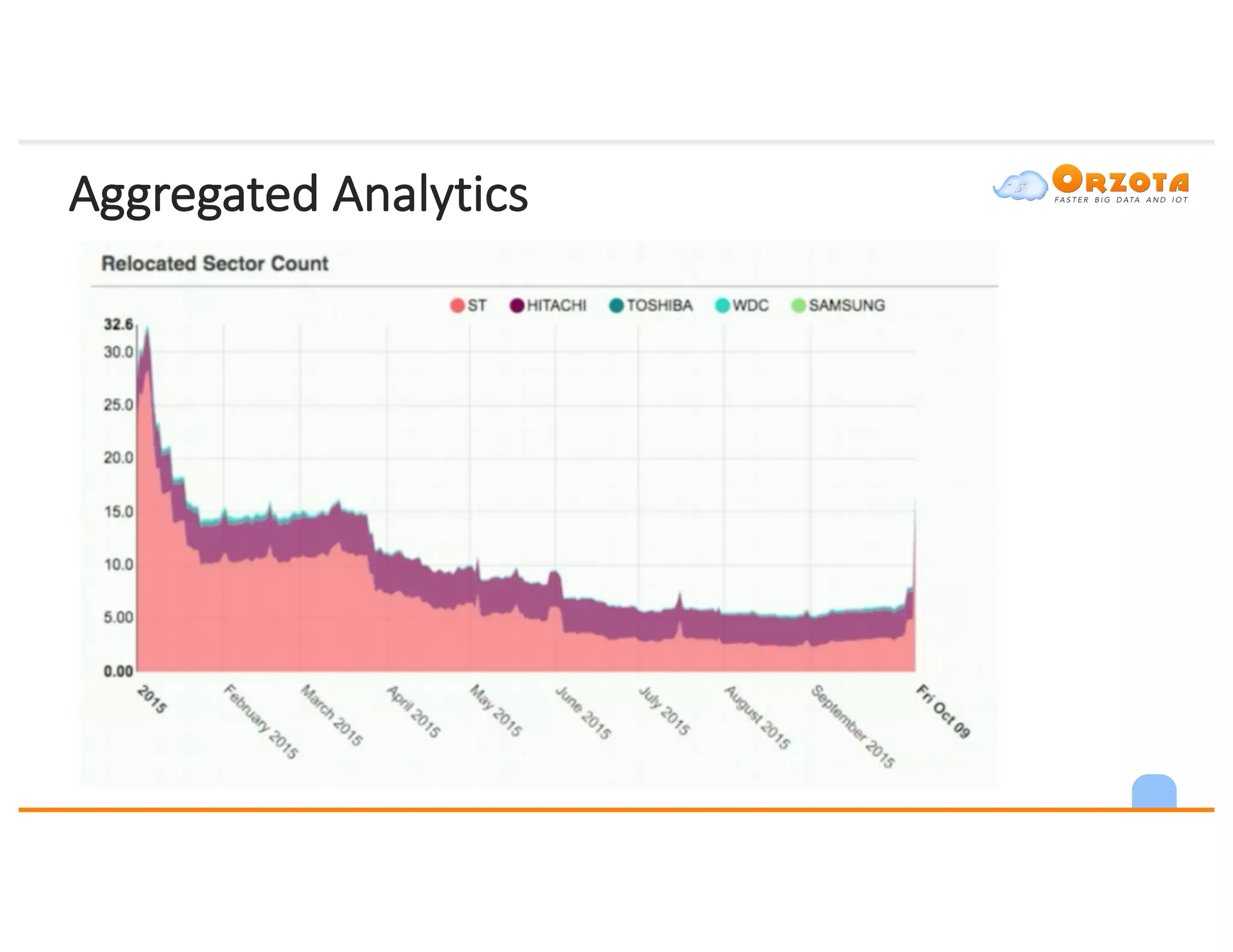
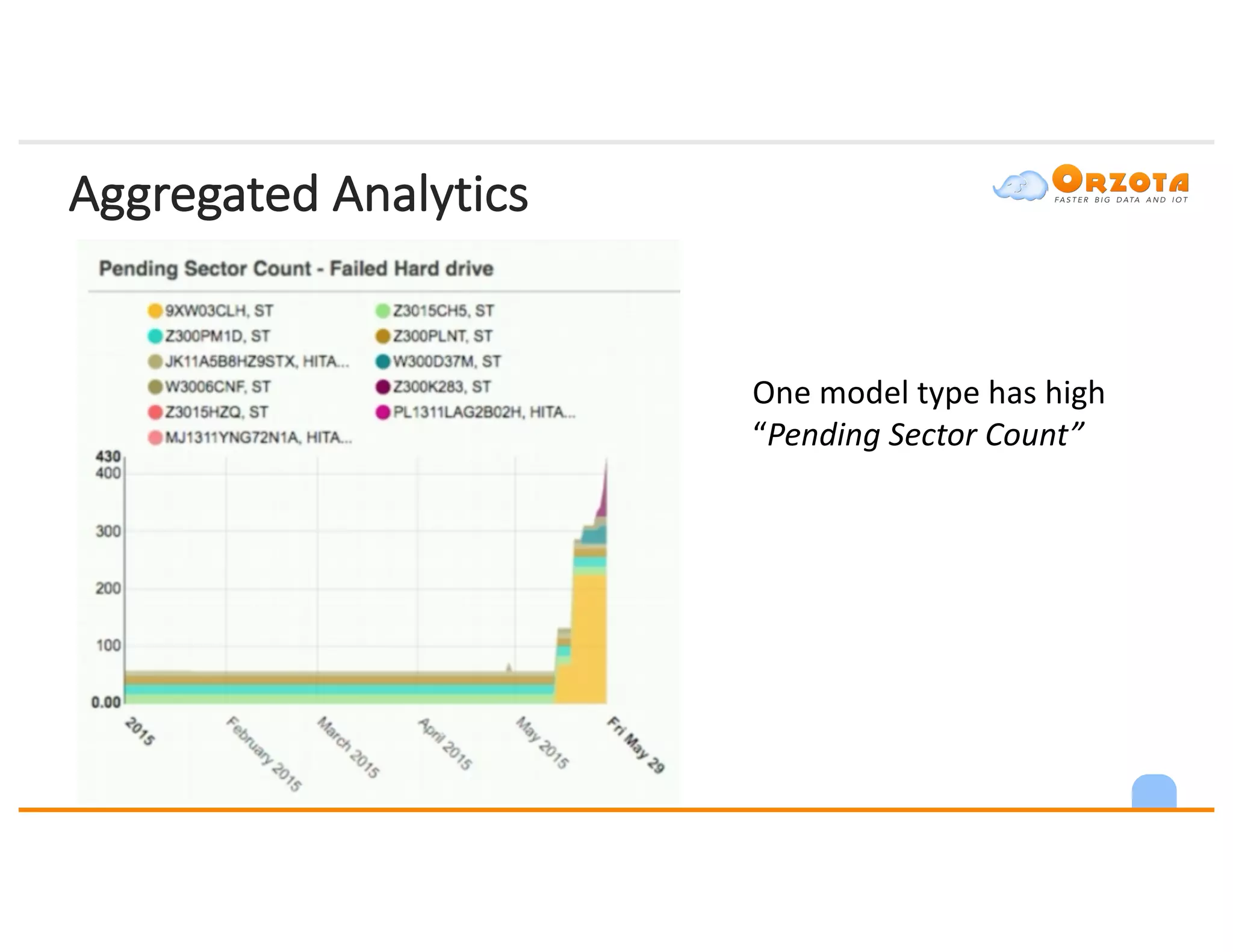
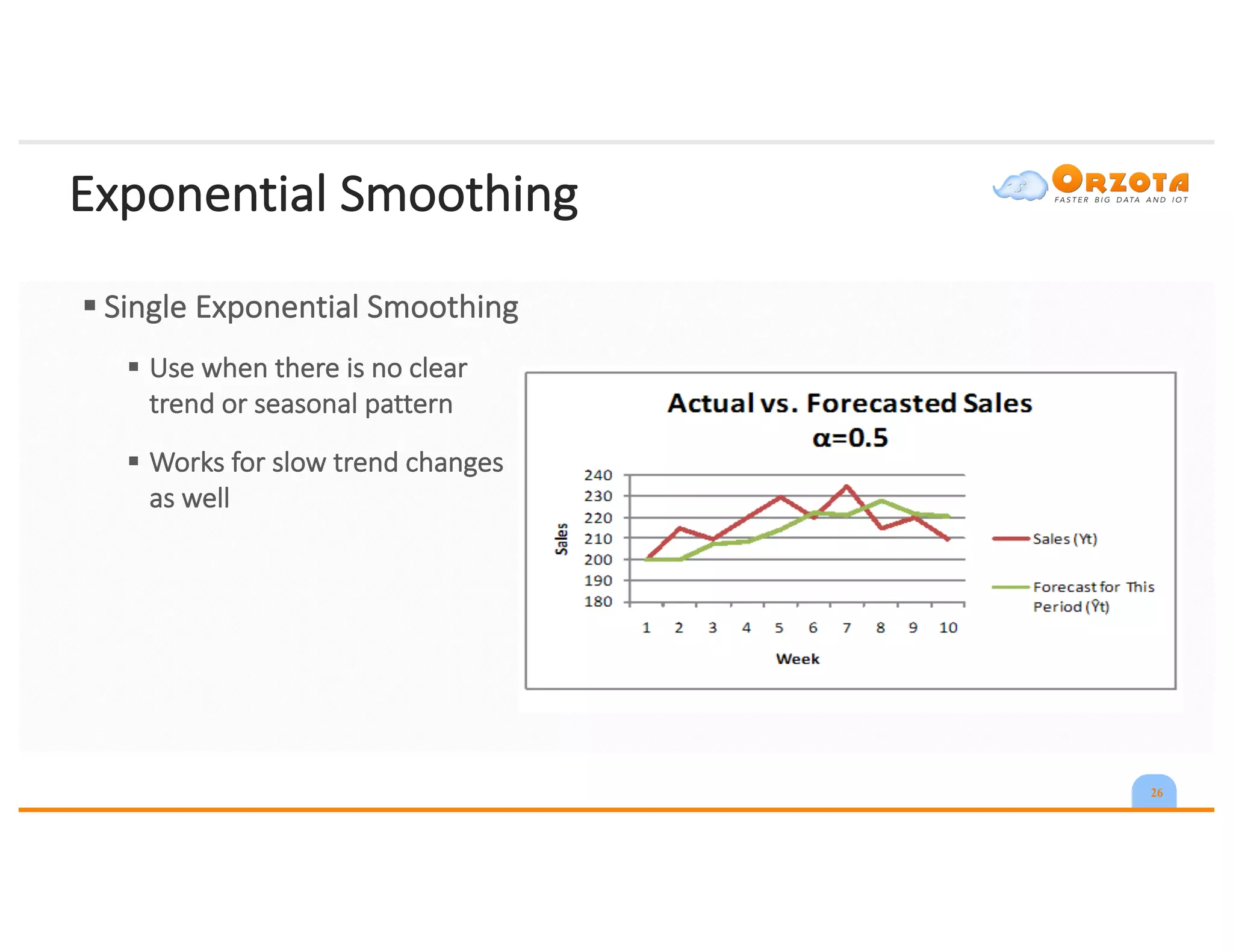
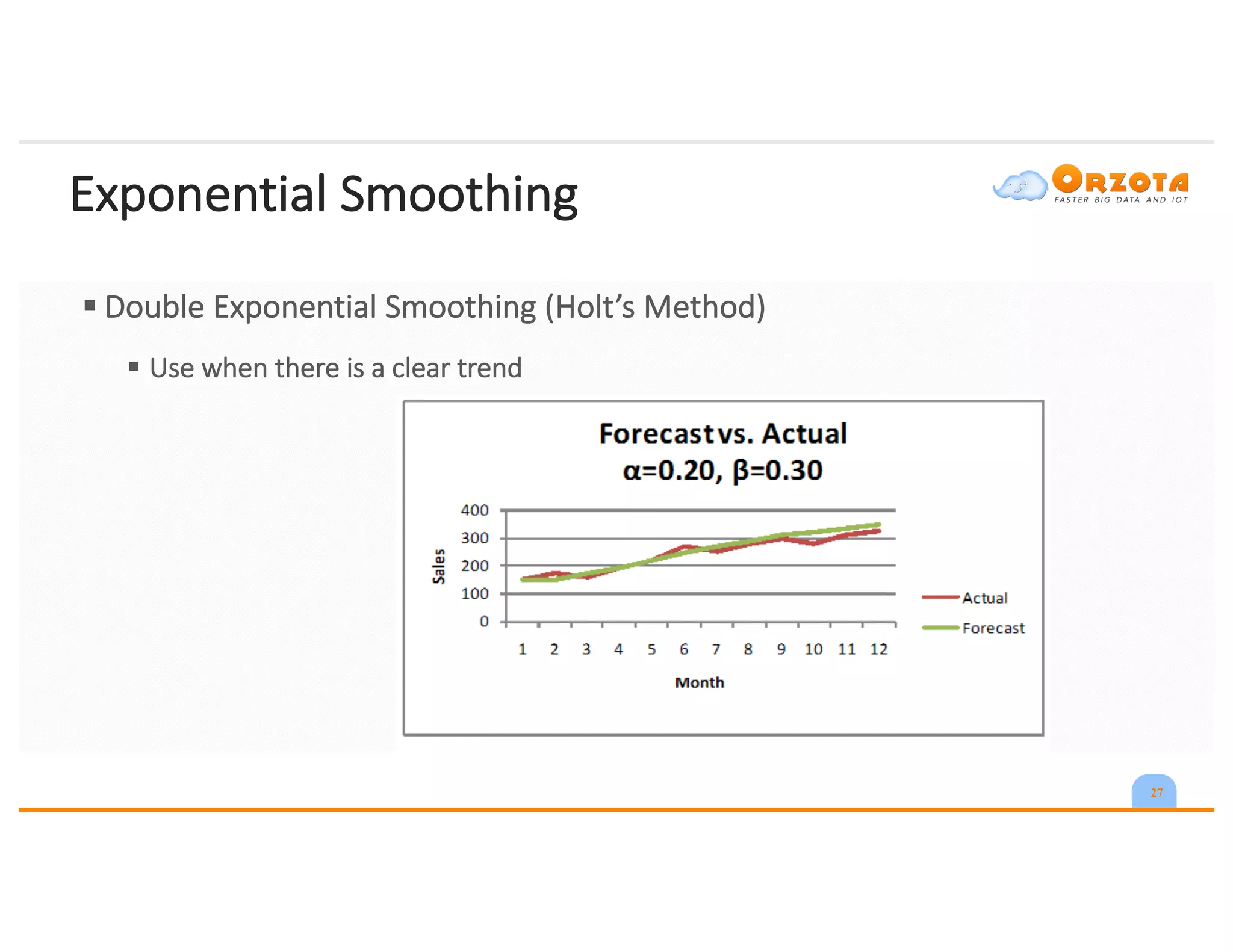
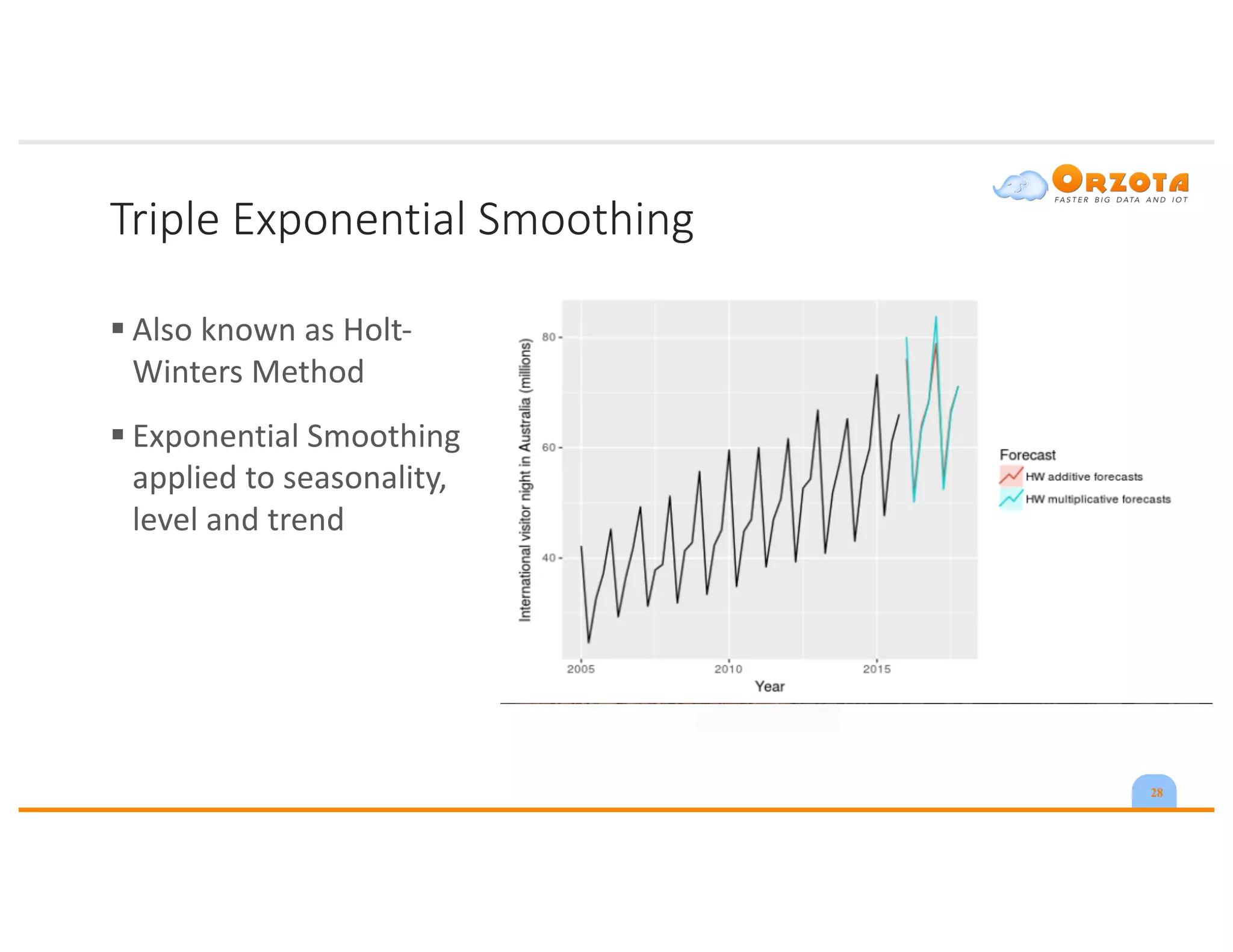
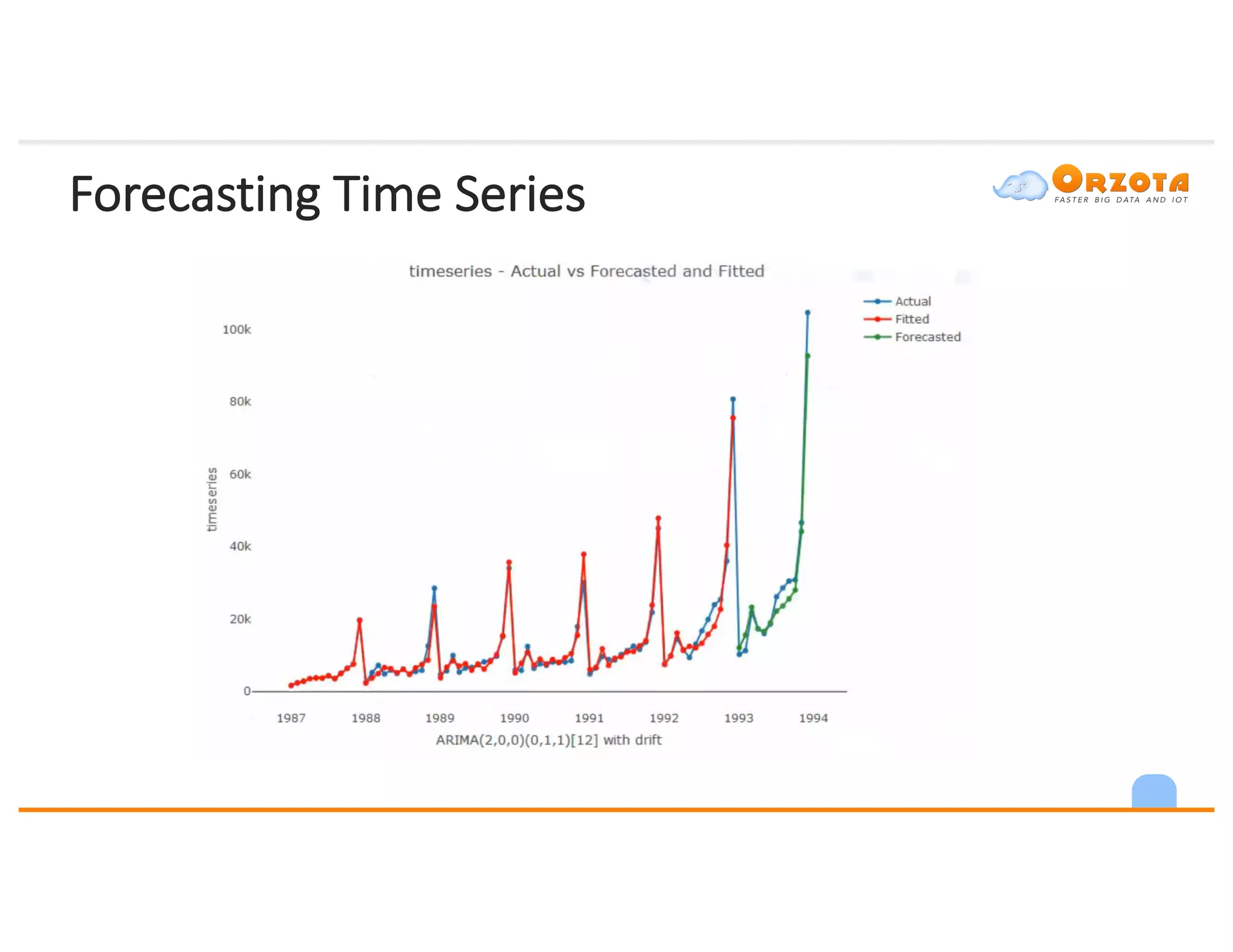
The document discusses time-series analysis, outlining its definition, components, and various applications, including classification, prediction, and anomaly detection. It covers exploratory analytics using R for visualization and data management tools suited for large datasets. Additionally, it presents predictive analytics techniques such as exponential smoothing and ARIMA models, along with the use of neural networks for improved forecasting and anomaly detection.