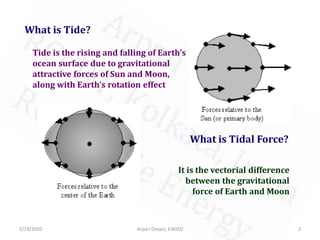
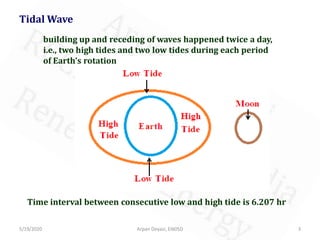
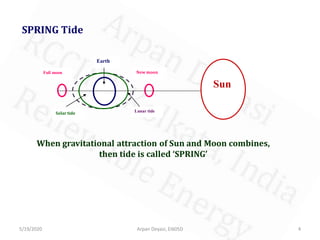
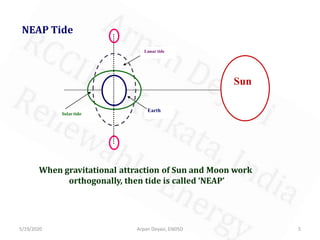
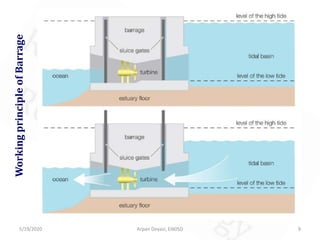
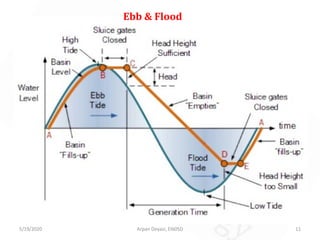
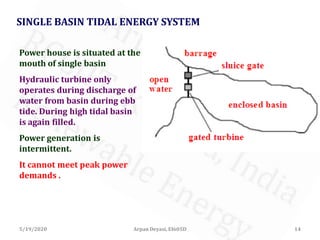
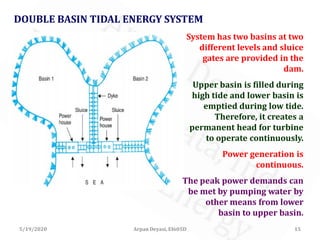
The document discusses tidal energy and its generation. It describes how tides are caused by gravitational forces from the sun and moon. Tidal energy can be harnessed using in-stream devices, barrages, or lagoons. Barrages use the potential energy difference between high and low tides to power turbines. Lagoons have self-contained structures to harness tidal energy at a lower cost than barrages. Tidal energy is a renewable source with predictable tides, but construction can be costly and disrupt aquatic ecosystems.