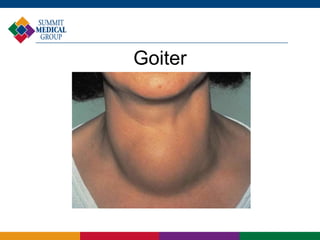
This document discusses thyroid health and various thyroid conditions. It begins by describing the anatomy and function of the thyroid gland. It then discusses hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), including causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment with levothyroxine replacement. Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) is also covered, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis using labs and imaging, and treatment options. Goiter and thyroid nodules are briefly described.