The document discusses thyroid dysfunction in pregnancy, including physiological changes in the thyroid gland during pregnancy, screening and management of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, and the effects of thyroid disorders and iodine deficiency on maternal and fetal health. Key points covered include the increased demand for thyroid hormones during pregnancy, screening guidelines for thyroid disorders, and treatment approaches for hypothyroidism including levothyroxine dosage optimization.






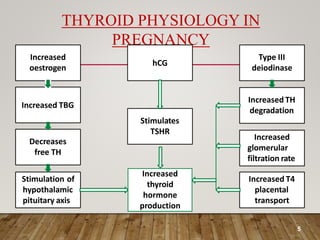
![PHYSIOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THYROID
GLAND IN PREGNANCY
• Throughout pregnancy there is increased demand of
thyroid hormone because pregnancy is the state of
increased BMR[20-25%] , increased oxygen
consumption by mother and baby.
• Size of the gland increases but any visible increase in
size must be considered pathological.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thyroiddisorderinpregnancy-kamal-230426163524-74791abe/85/THYROID-DISORDER-IN-PREGNANCY-Kamal-pptx-7-320.jpg)