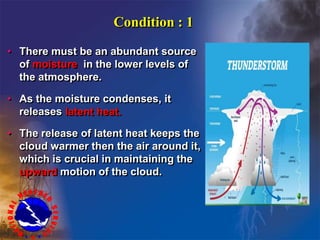
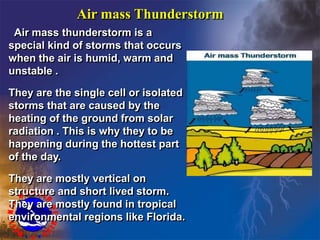
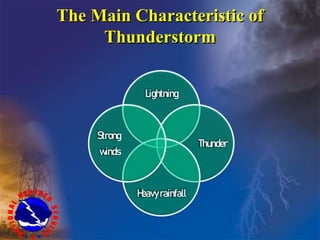
Group 7's presentation was about thunderstorms. It defined thunderstorms, explained how they form through 3 stages (cumulus, mature, dissipating), and described the main types (orographic, air mass, frontal). It covered key characteristics like lightning, thunder, heavy rainfall, strong winds. Both positive impacts like natural rainfall and nitrogen fixation, and negative ones like lightning hazards, hail damage, tornadoes, and rainfall floods were discussed. The presentation ended with thunderstorm safety tips.