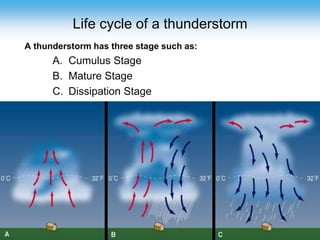
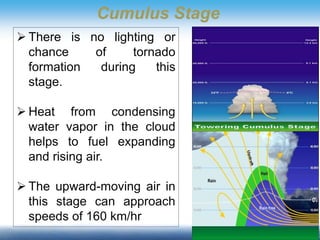
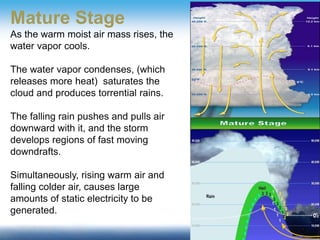
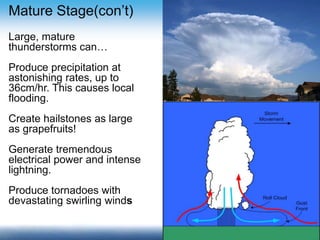
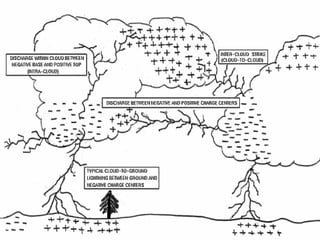
Thunderstorms require moisture, an air lifting mechanism, and instability to form. They have three stages: cumulus, mature, and dissipating. During the mature stage, rising warm air and falling cold air cause static electricity to build up, resulting in lightning. Lightning is a high-voltage electrical discharge between clouds, air, or clouds and the ground. It can heat the nearby air to 50,000 degrees Celsius and travel at 300,000 m/s. Indoors, one should avoid contact with electrical equipment or plumbing, while outdoors the safest shelters are enclosed buildings or hard-top vehicles.