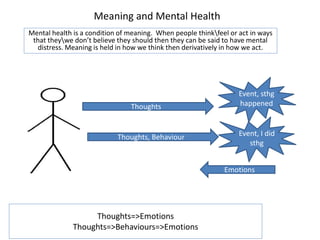
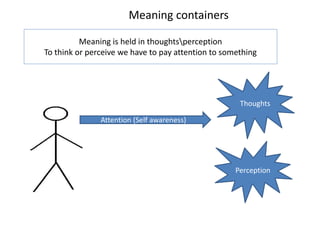
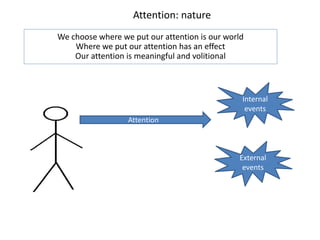
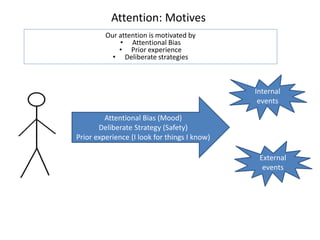
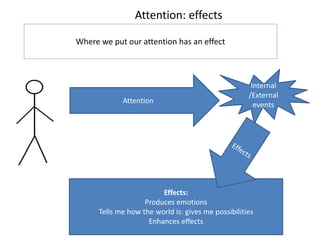
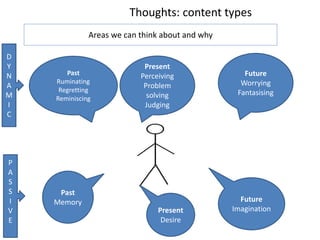
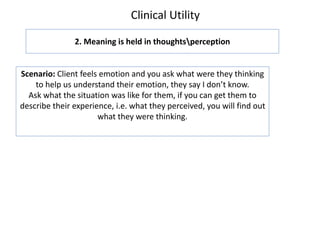
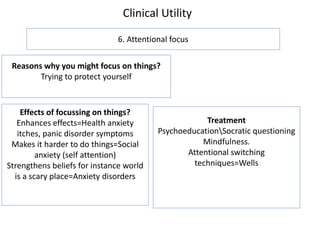
1. Meaning is core to mental health and is held in our thoughts and perceptions of events.
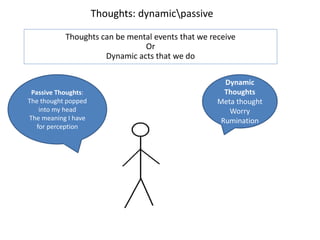
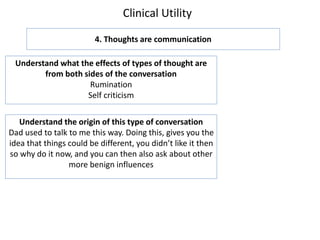
2. Thoughts can be either dynamic, such as worrying or rumination, or passive thoughts that pop into our heads.
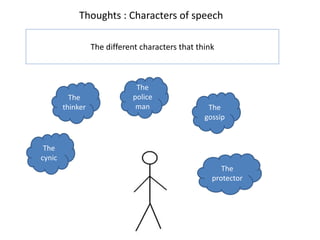
3. Our thoughts can take the form of internal dialogues or different "characters" that influence our perspectives and behaviors.