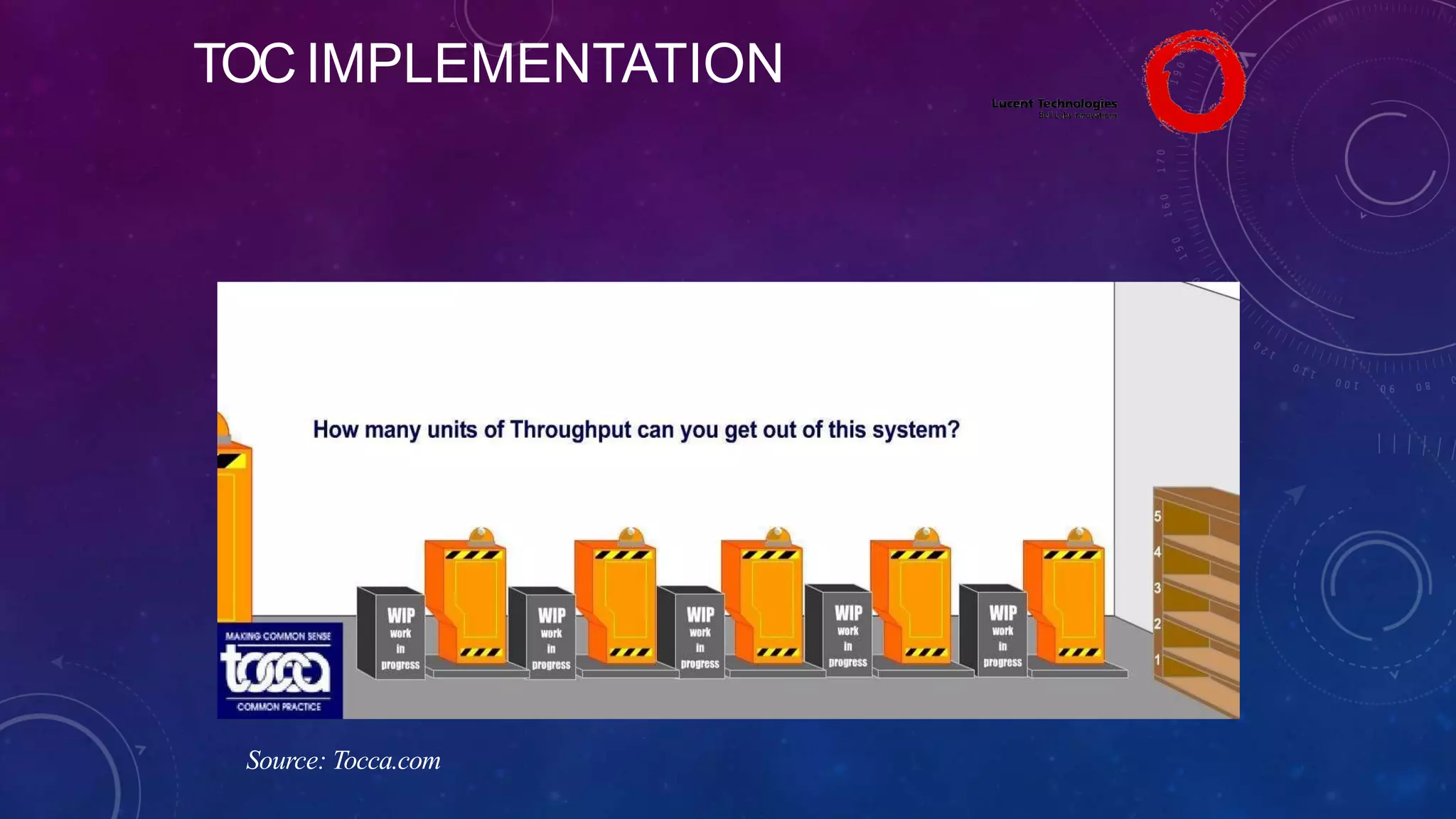
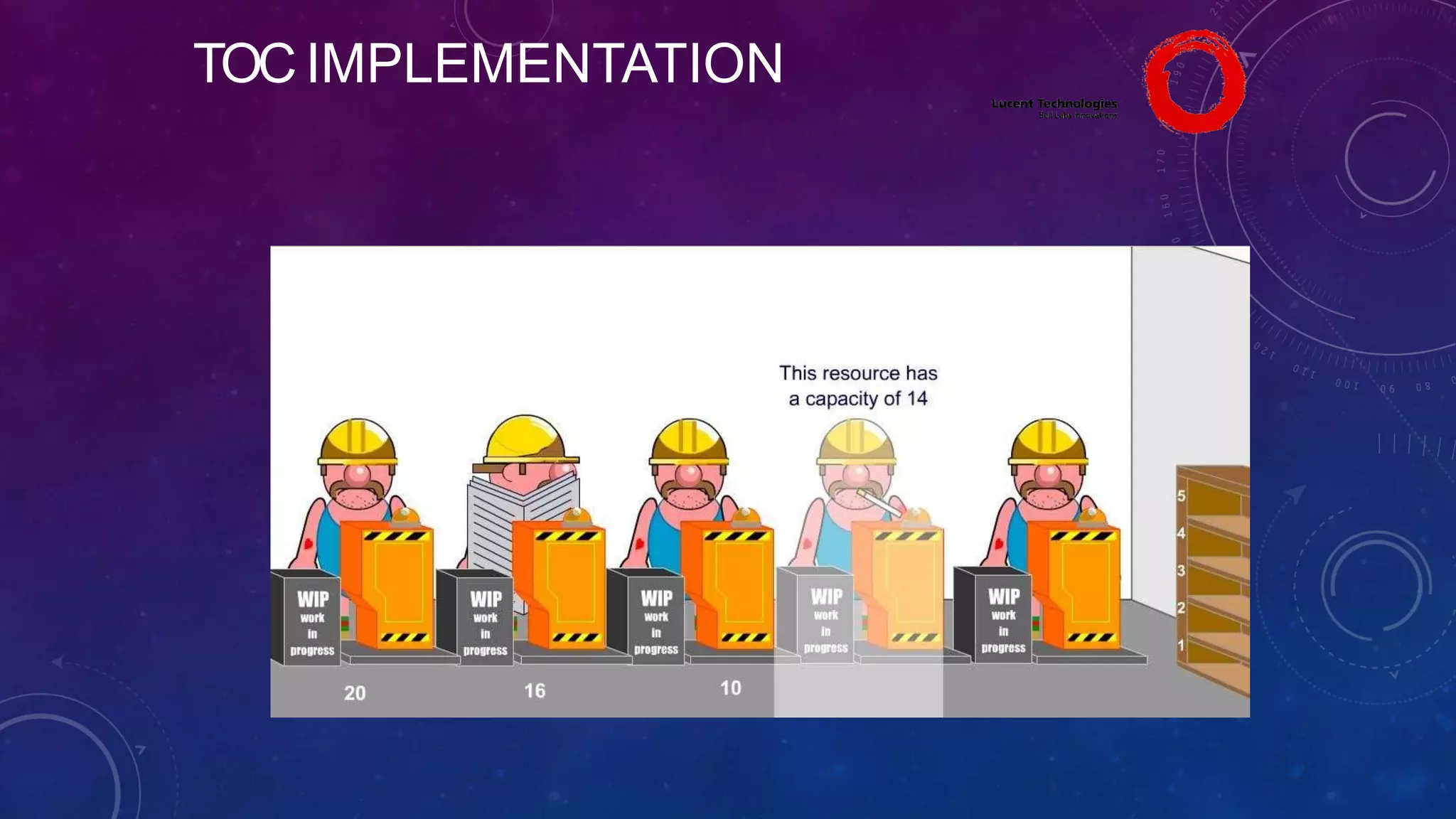
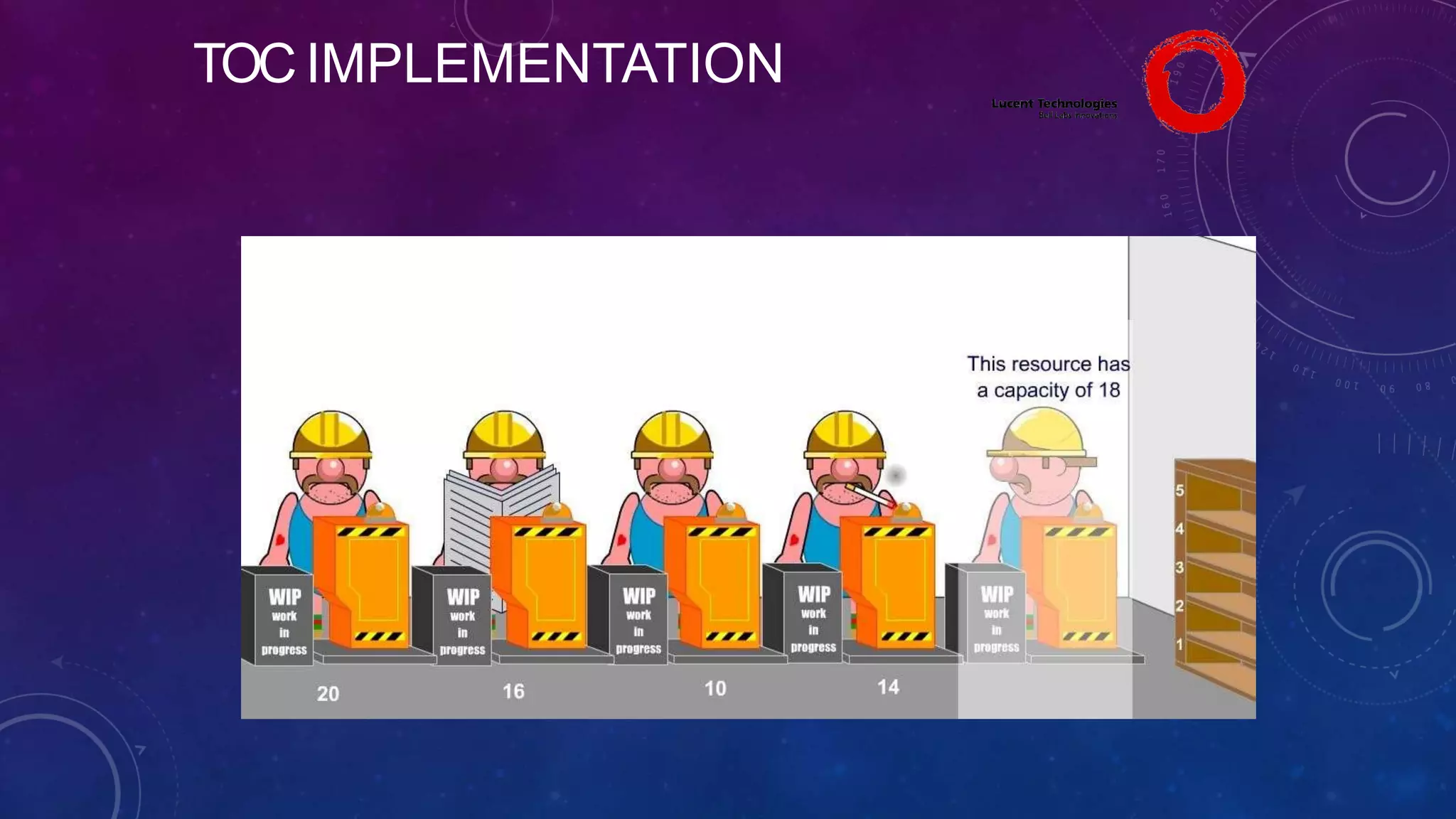
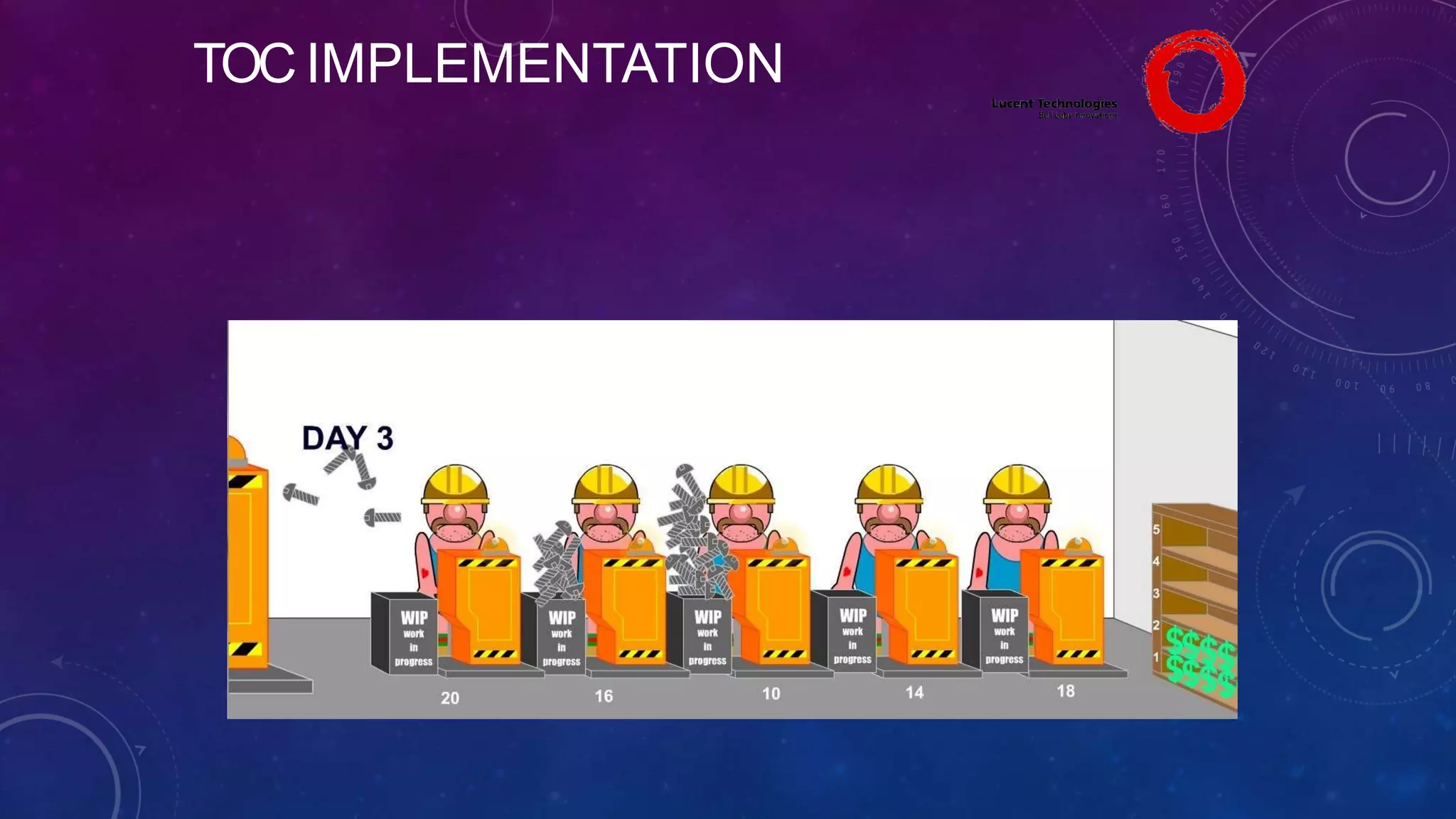
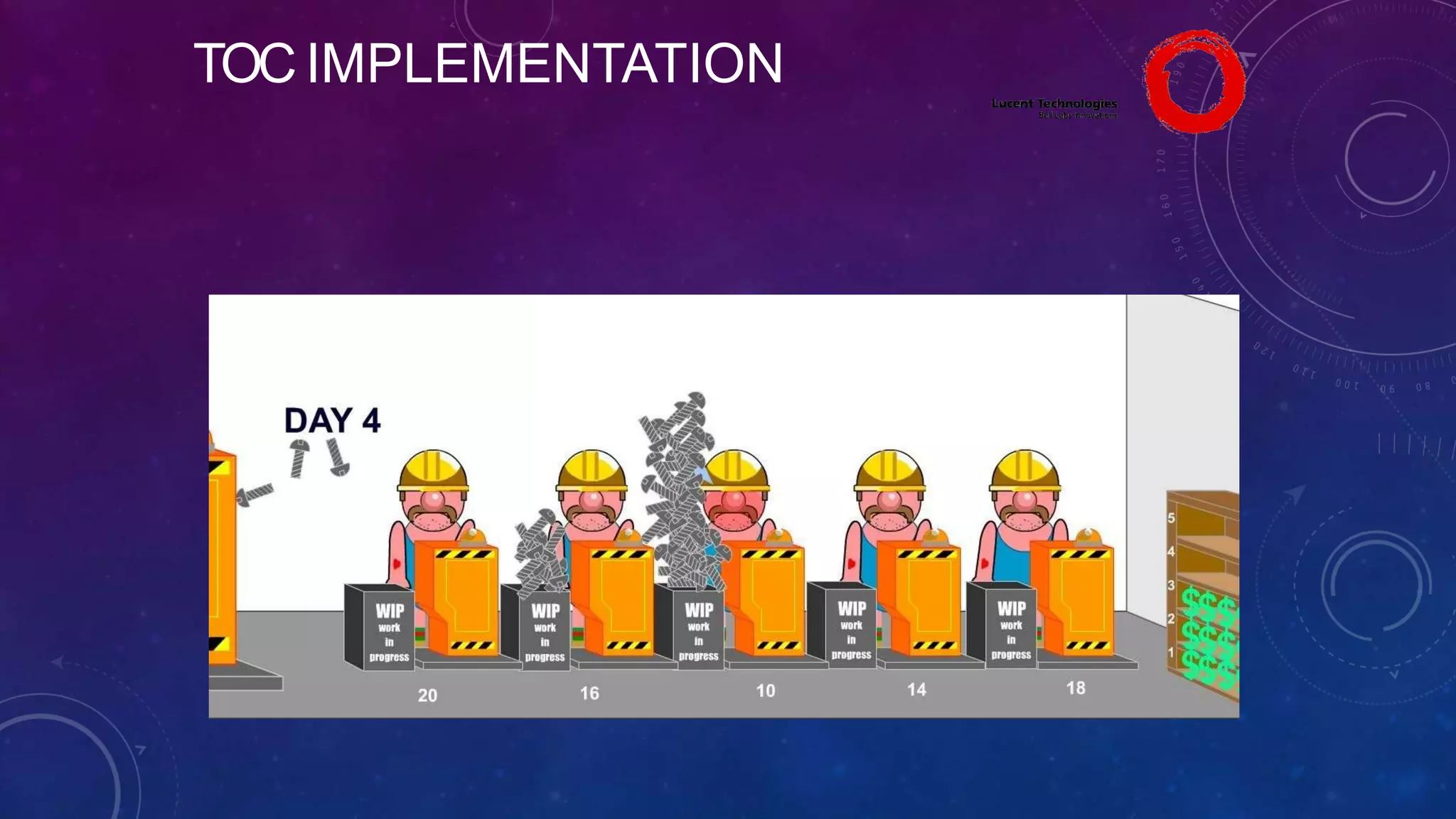
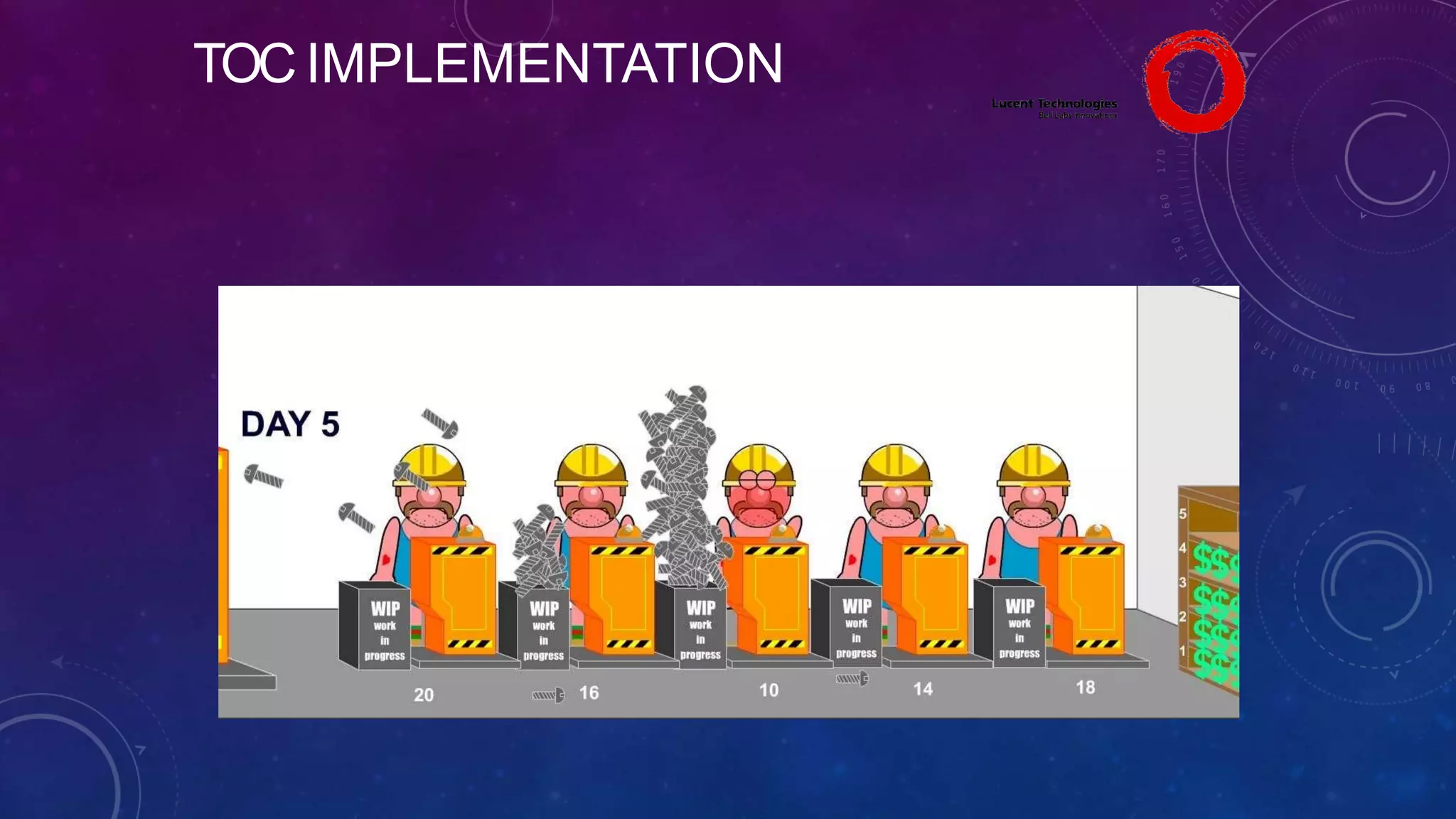
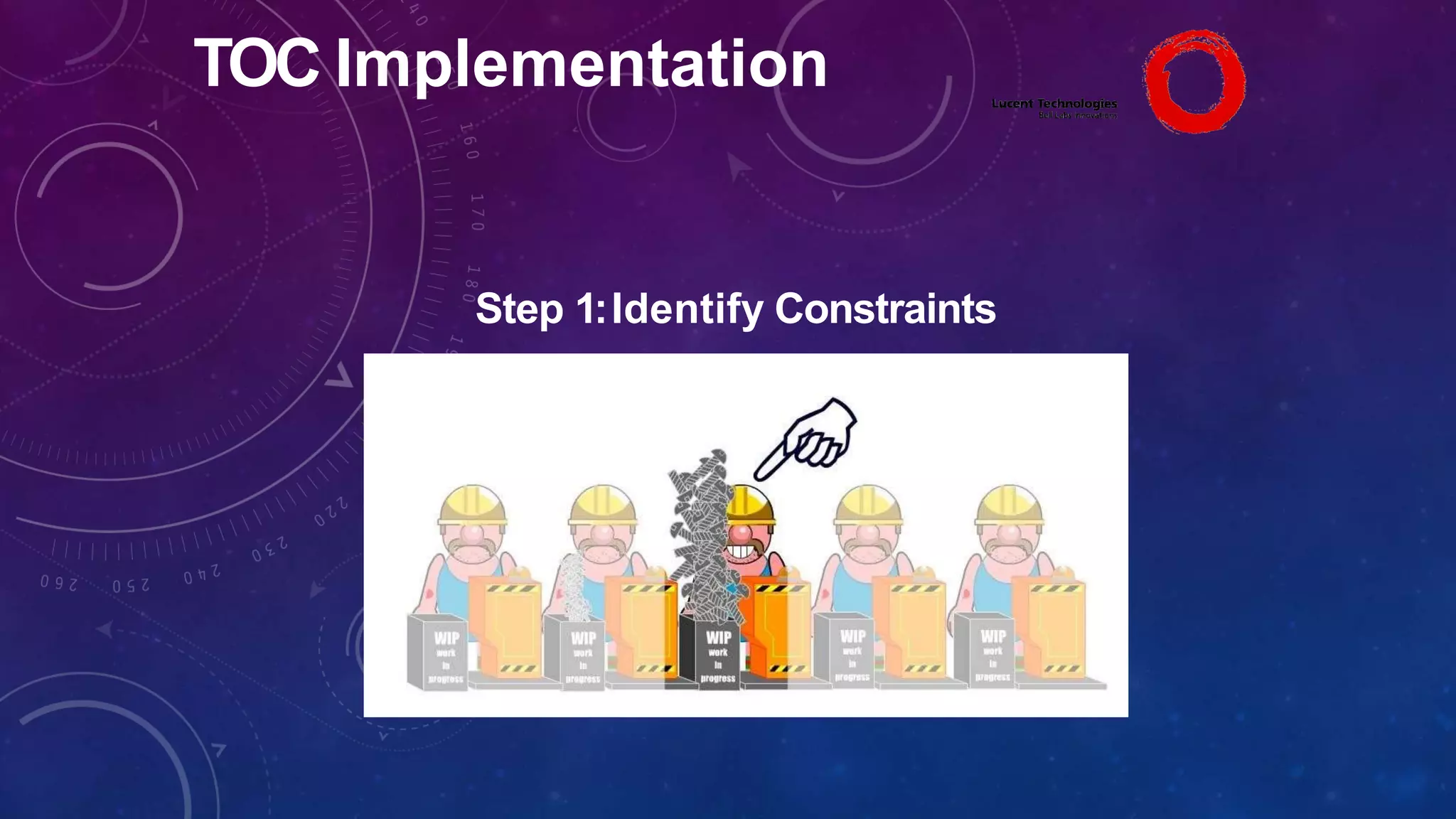
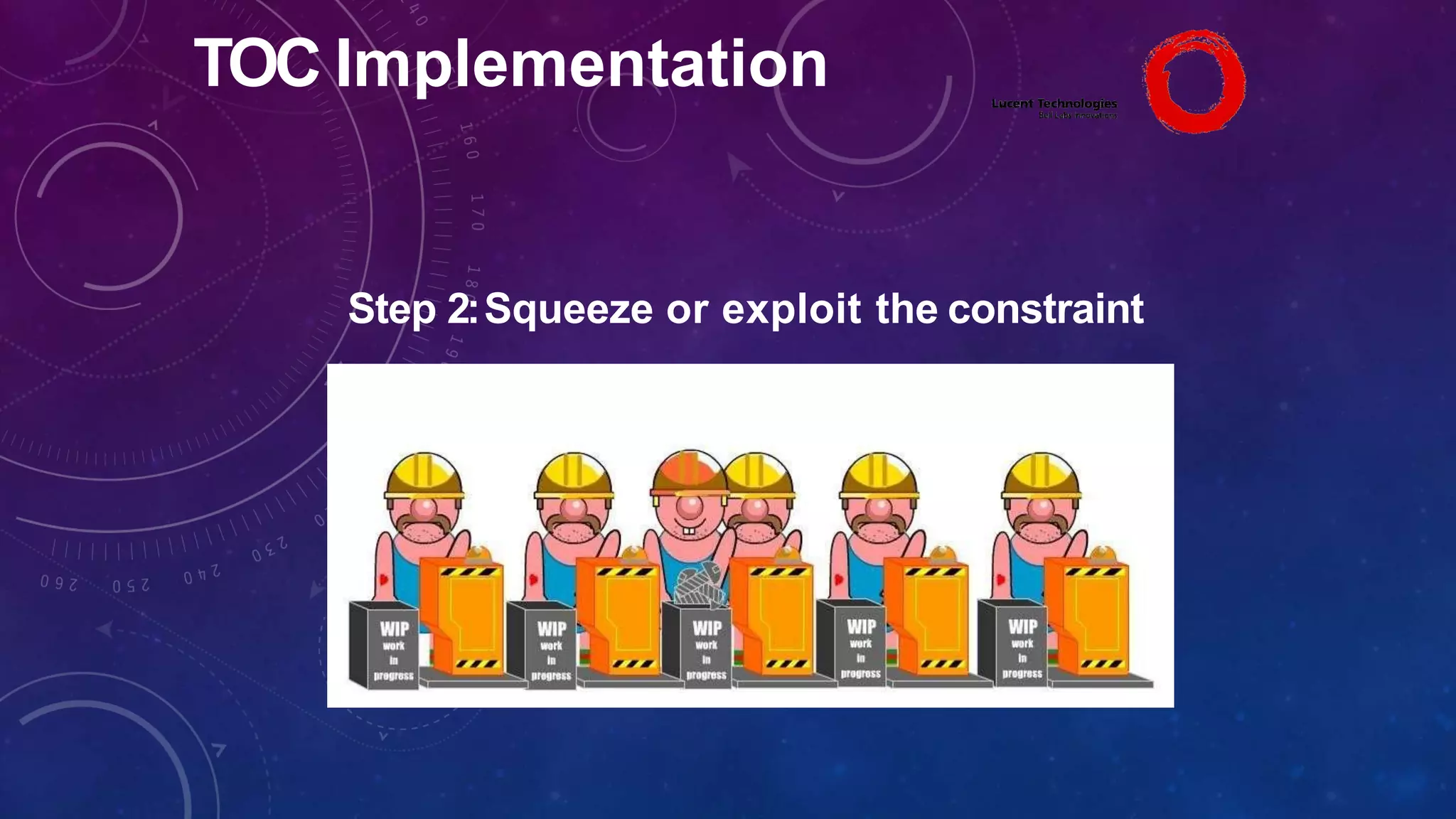
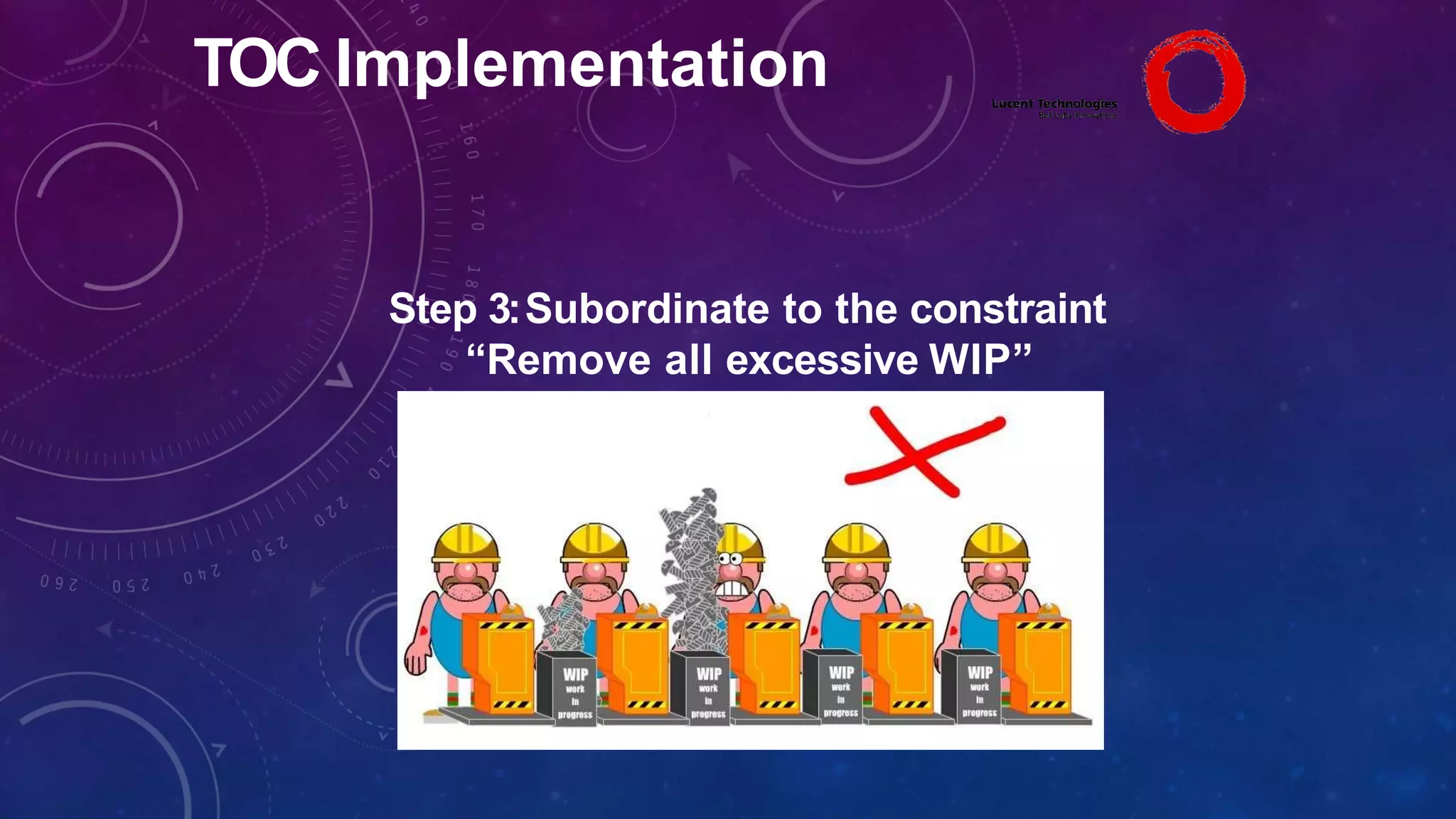
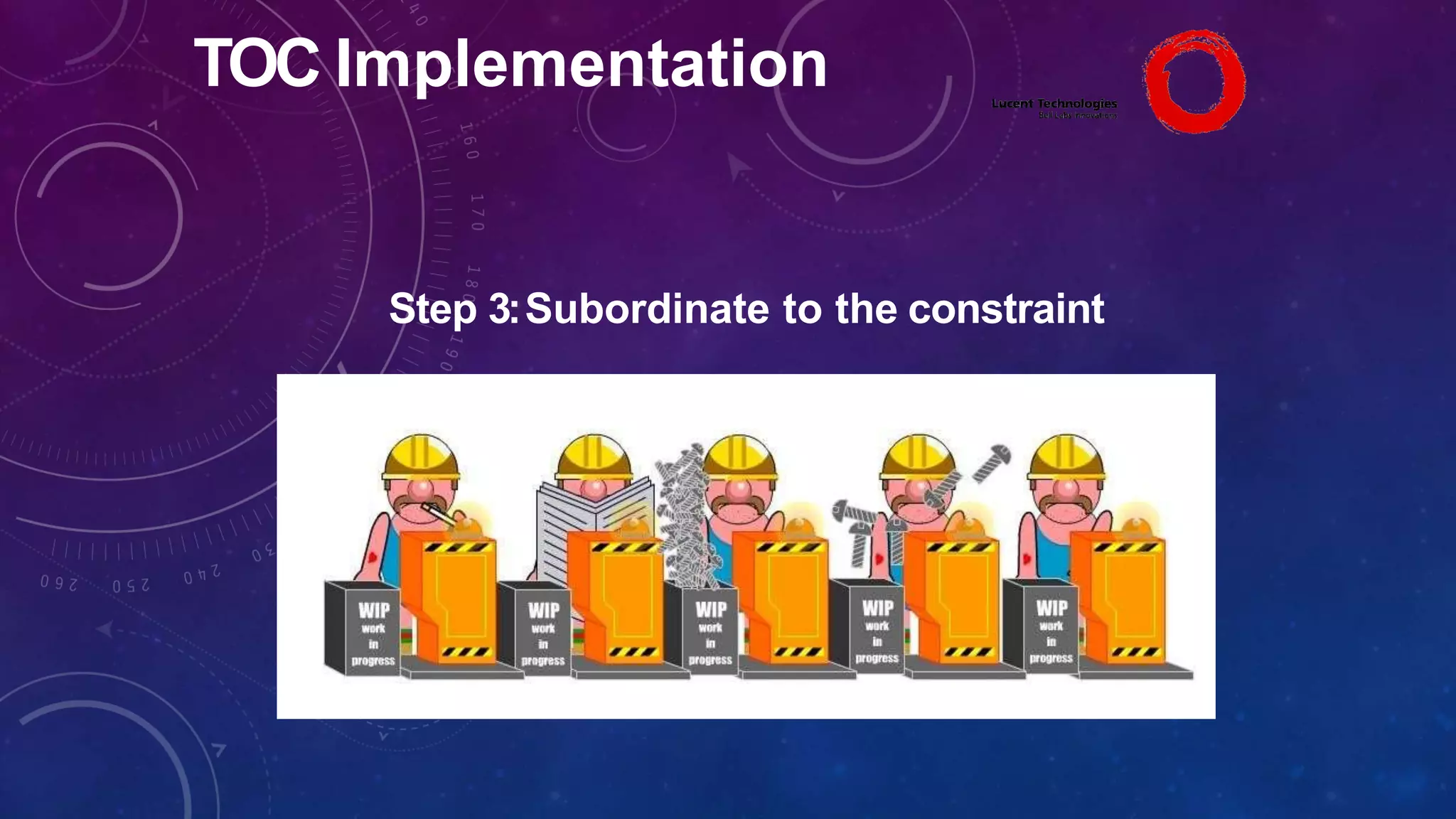
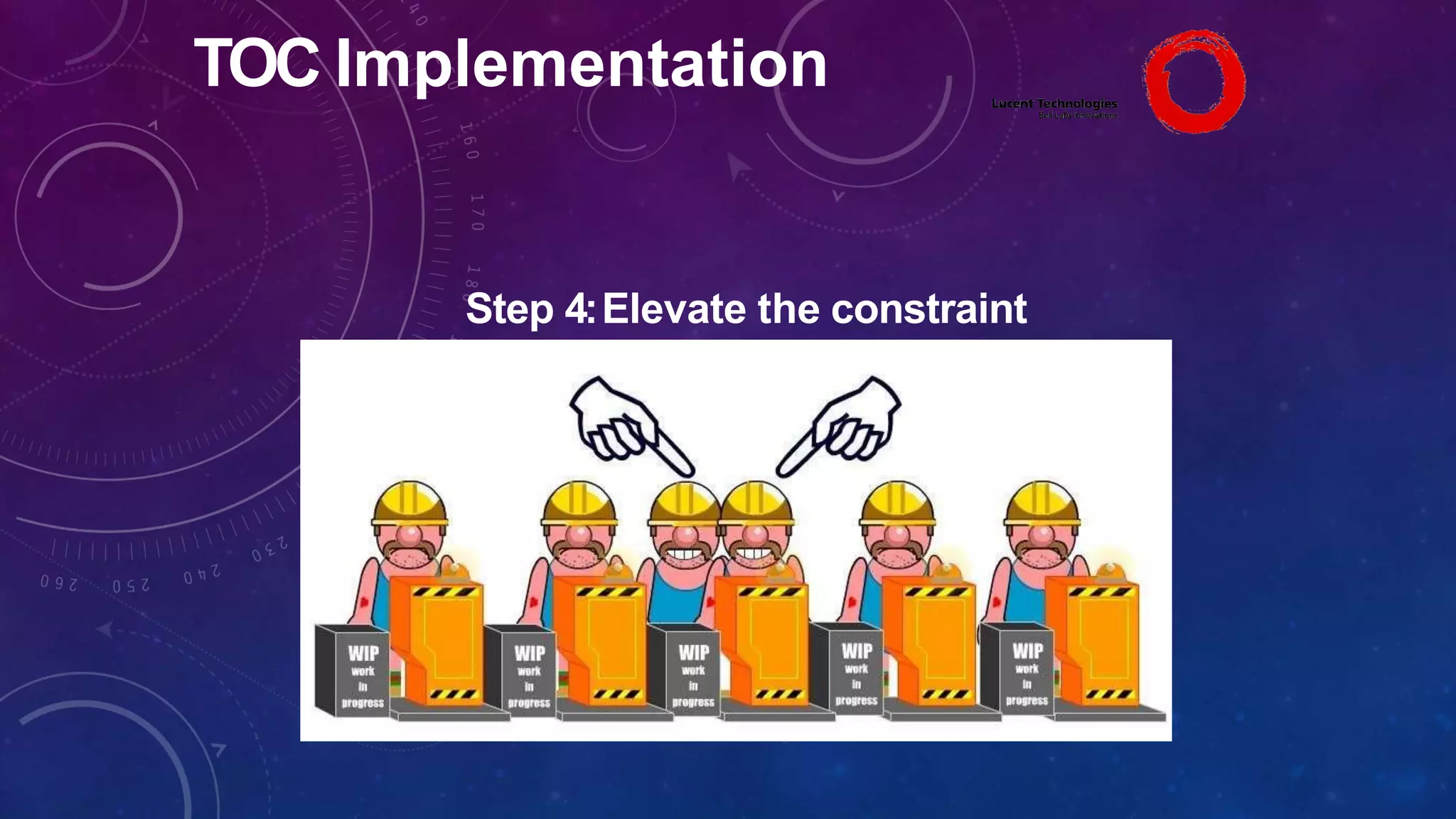
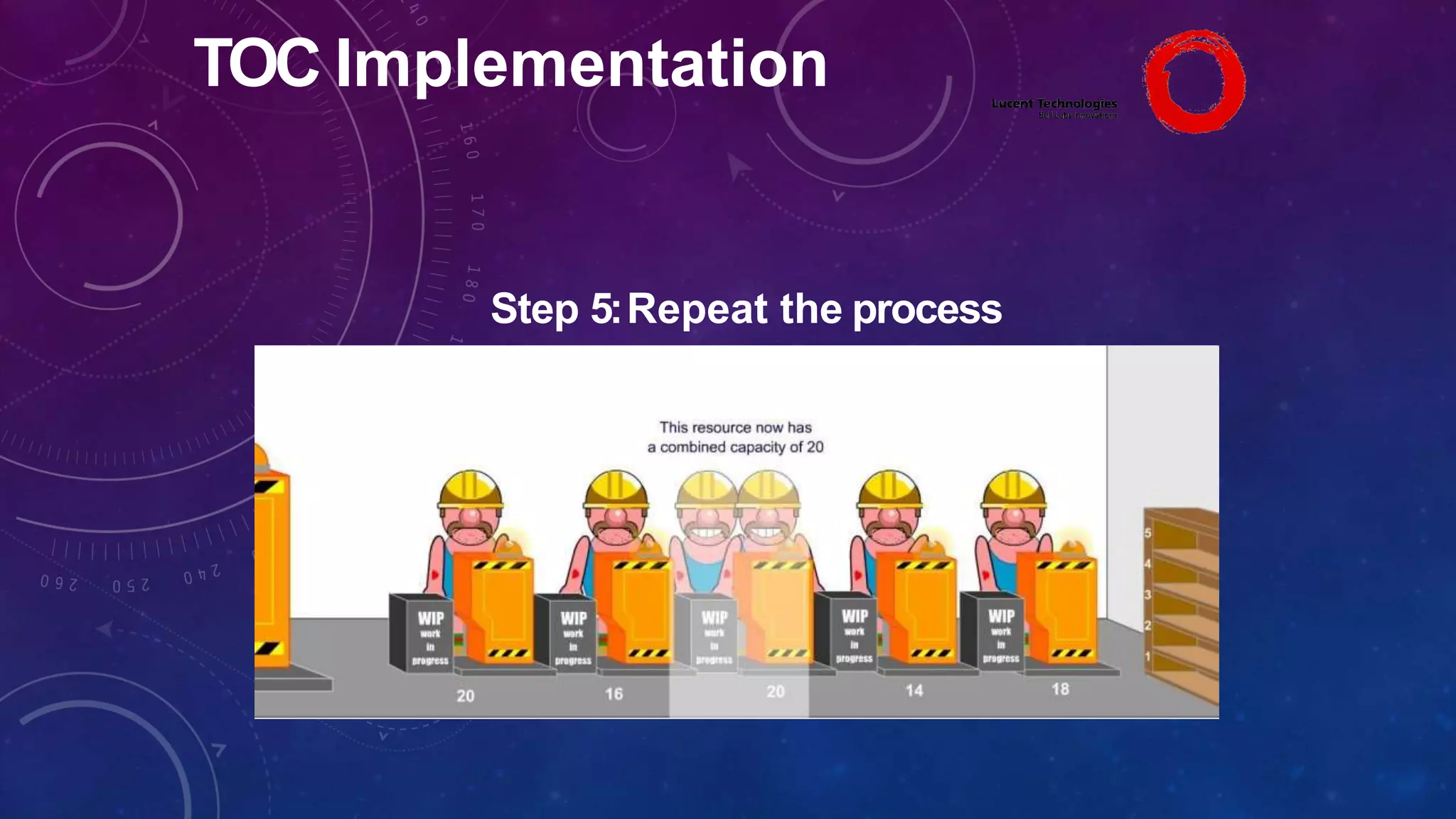
The Theory of Constraints (TOC), developed by Eliyahu Goldratt, is a method for organizational change focused on profit improvement by identifying and managing constraints. The process includes five steps: identifying constraints, exploiting them, subordinating other processes, elevating the constraints if necessary, and repeating the process. A case study on Lucent demonstrated the successful implementation of TOC, leading to increased throughput, faster product development, timely project completion, and higher profits.