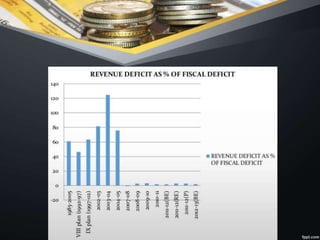
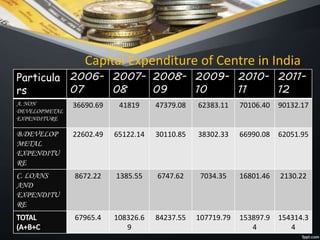
The document discusses fiscal imbalances and deficit financing, outlining key concepts such as budget balance, fiscal deficit, and revenue spending in government budgets. It highlights causes of fiscal deficits, including poor public sector performance and excessive borrowing, and the consequences like inflation and investment issues. The document also covers the objectives and limitations of deficit financing, particularly in the context of economic development in underdeveloped countries like India.