The document discusses several theories of language acquisition, including:
- Behaviorist theory, which assumes that language is learned through imitation and conditioning. Children imitate sounds and are reinforced through rewards like attention.
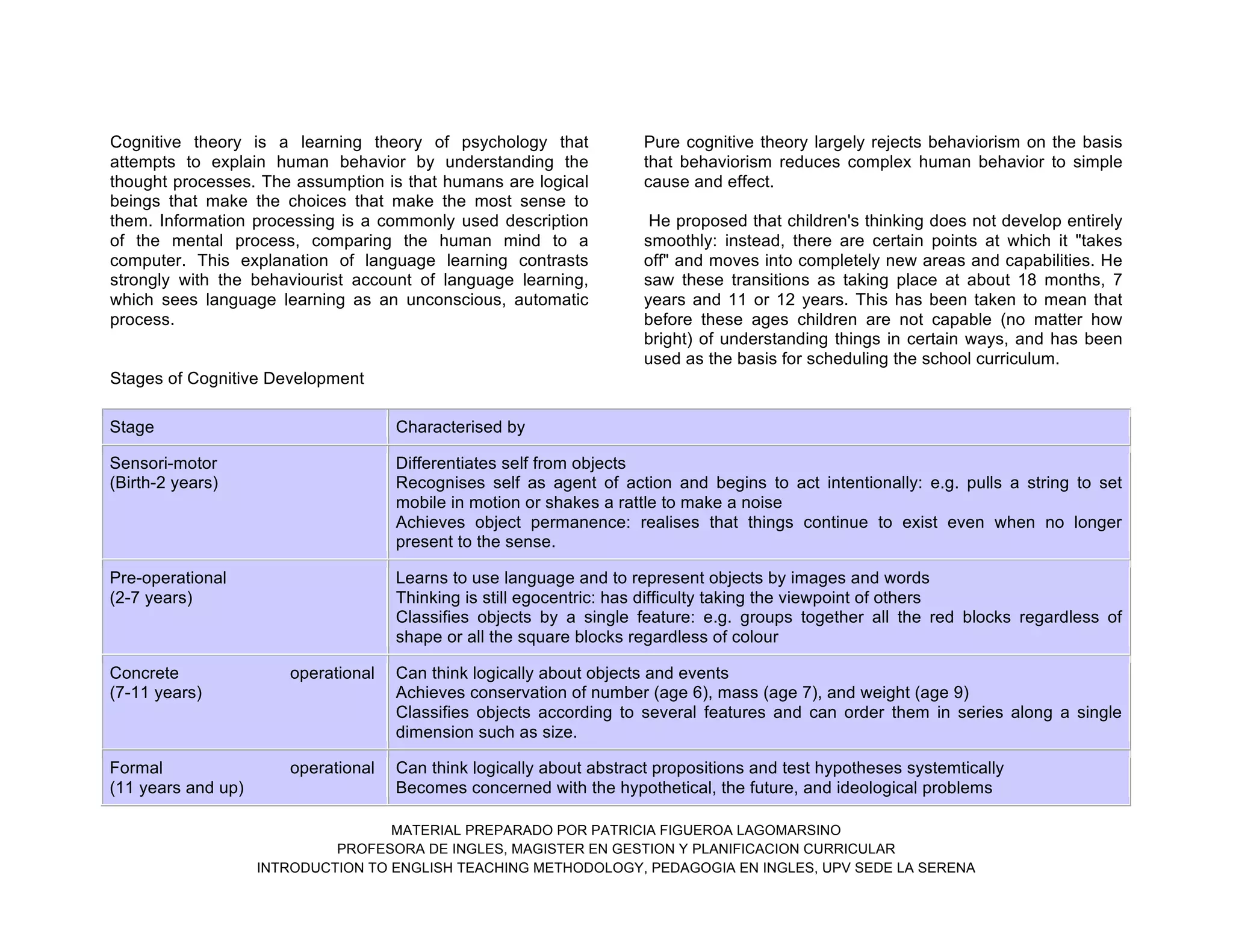
- Cognitive theory, influenced by Piaget, which sees language acquisition as dependent on children's developing thought processes and abilities at different stages.
- Nativist theory, proposed by Chomsky, which argues that humans are born with an innate, biologically-determined language acquisition device that allows them to unconsciously learn the rules of their native language quickly based on limited exposure.