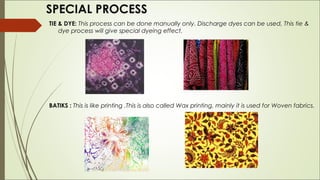
Value addition involves processes that increase the aesthetic appeal and price of garments without affecting quality. This includes finishing techniques, printing designs, and adding embellishments like embroidery. Finishing prepares fabrics for specific uses and makes them more attractive. Printing involves applying dye designs through various methods. Embellishments such as buttons, zippers, and embroidery are also forms of value addition. Special processes like tie-dye, batik, and quilting can further enhance garments. Overall, value addition improves garments both visually and economically.