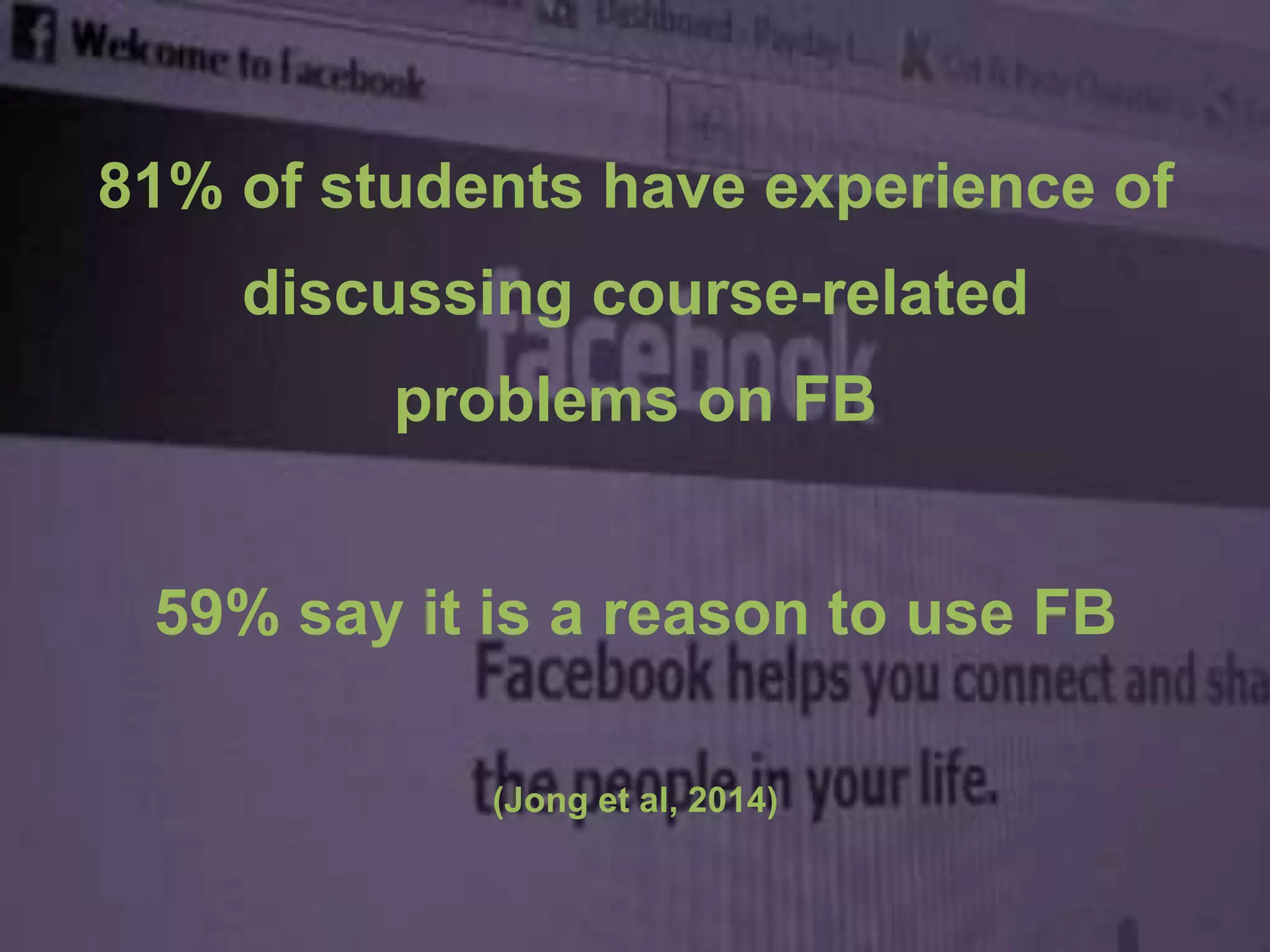
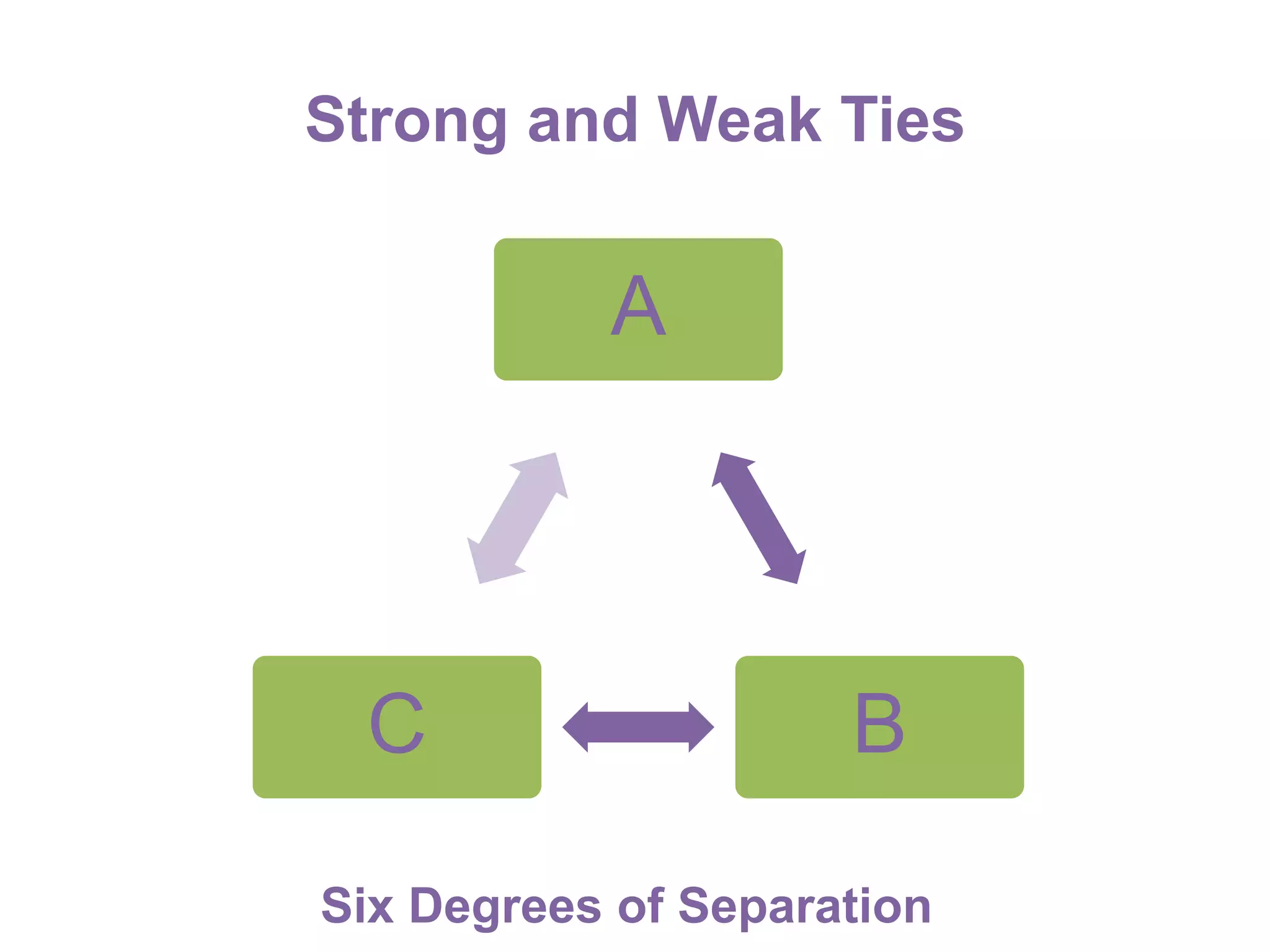
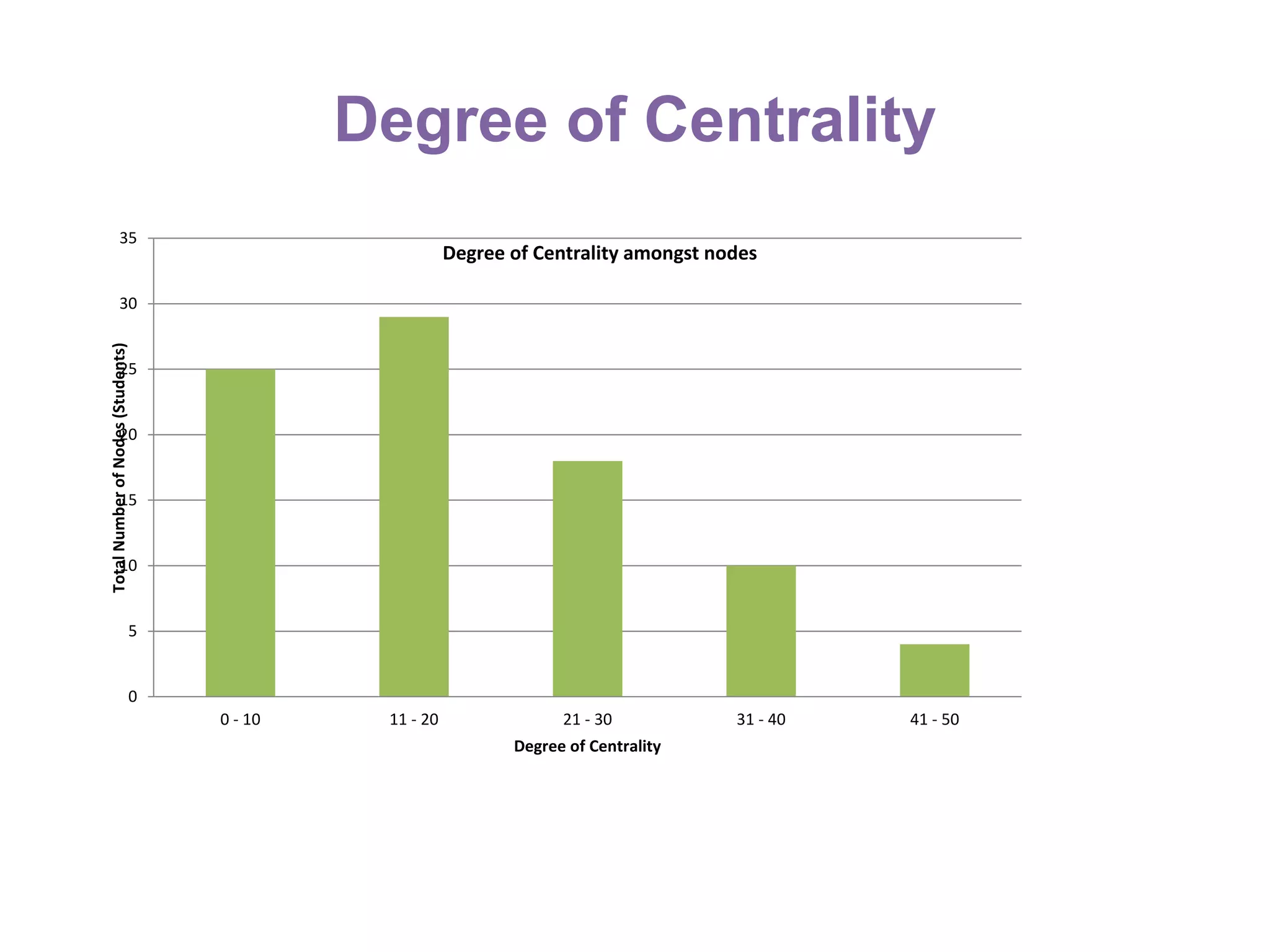
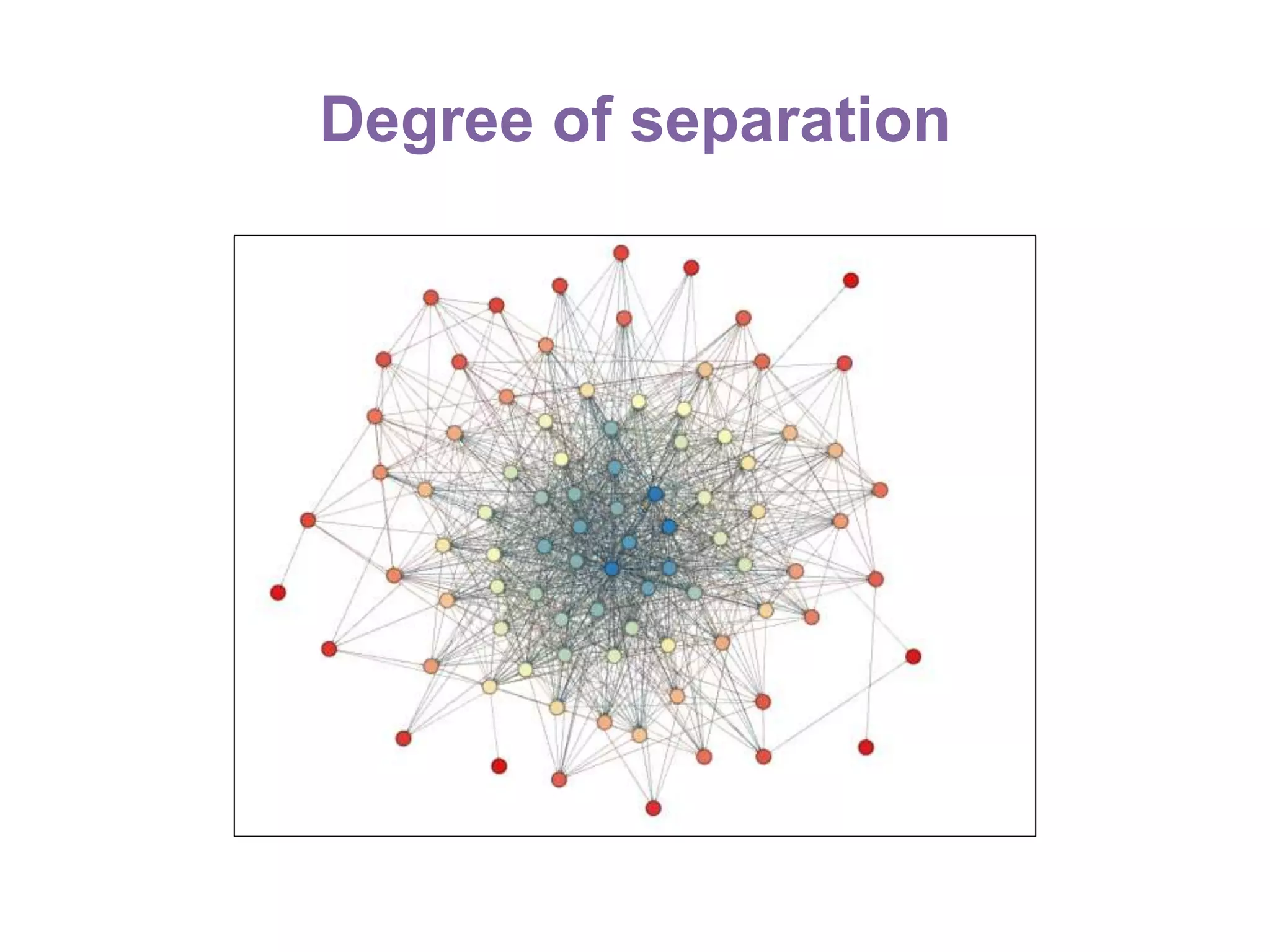
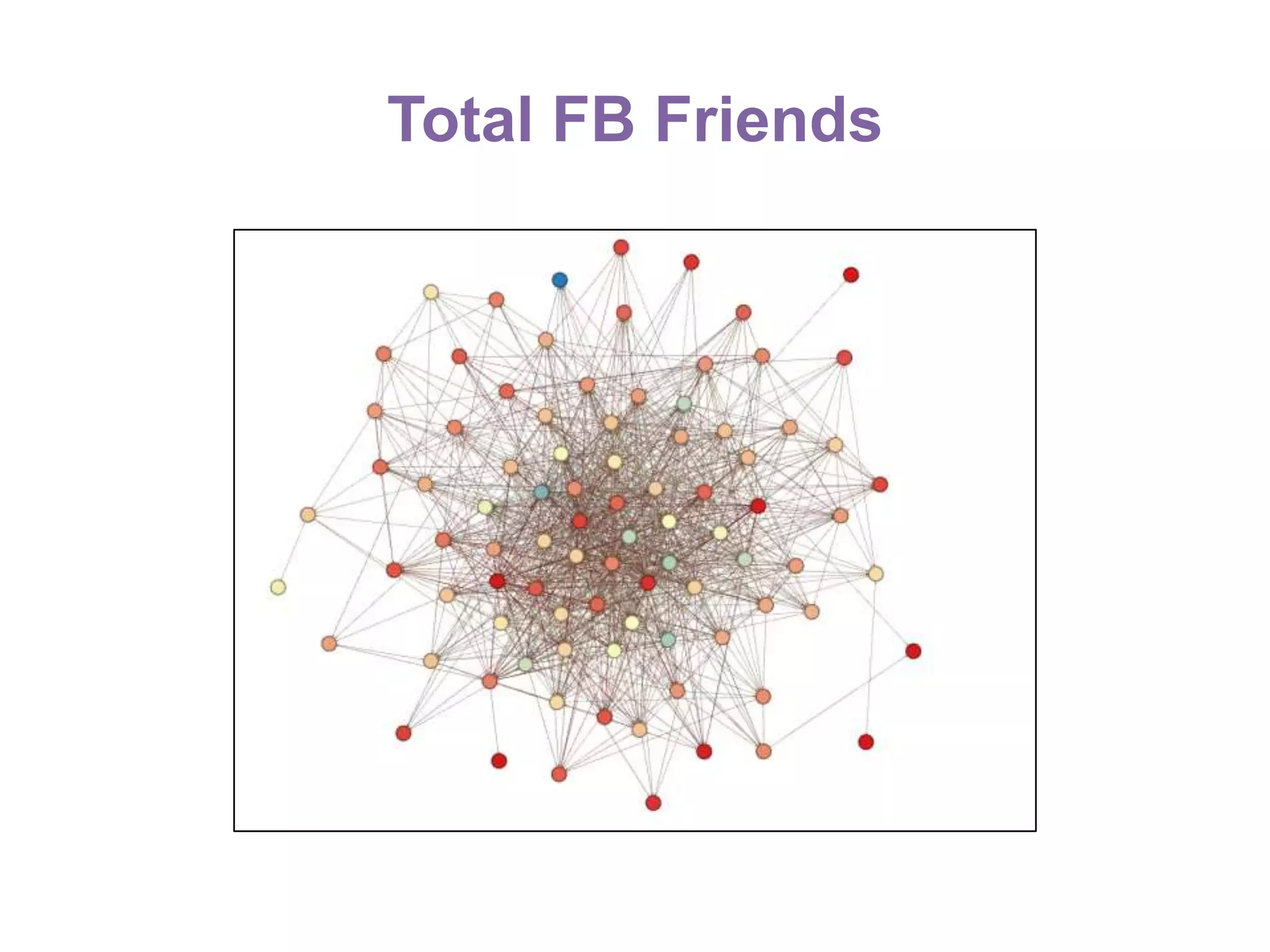
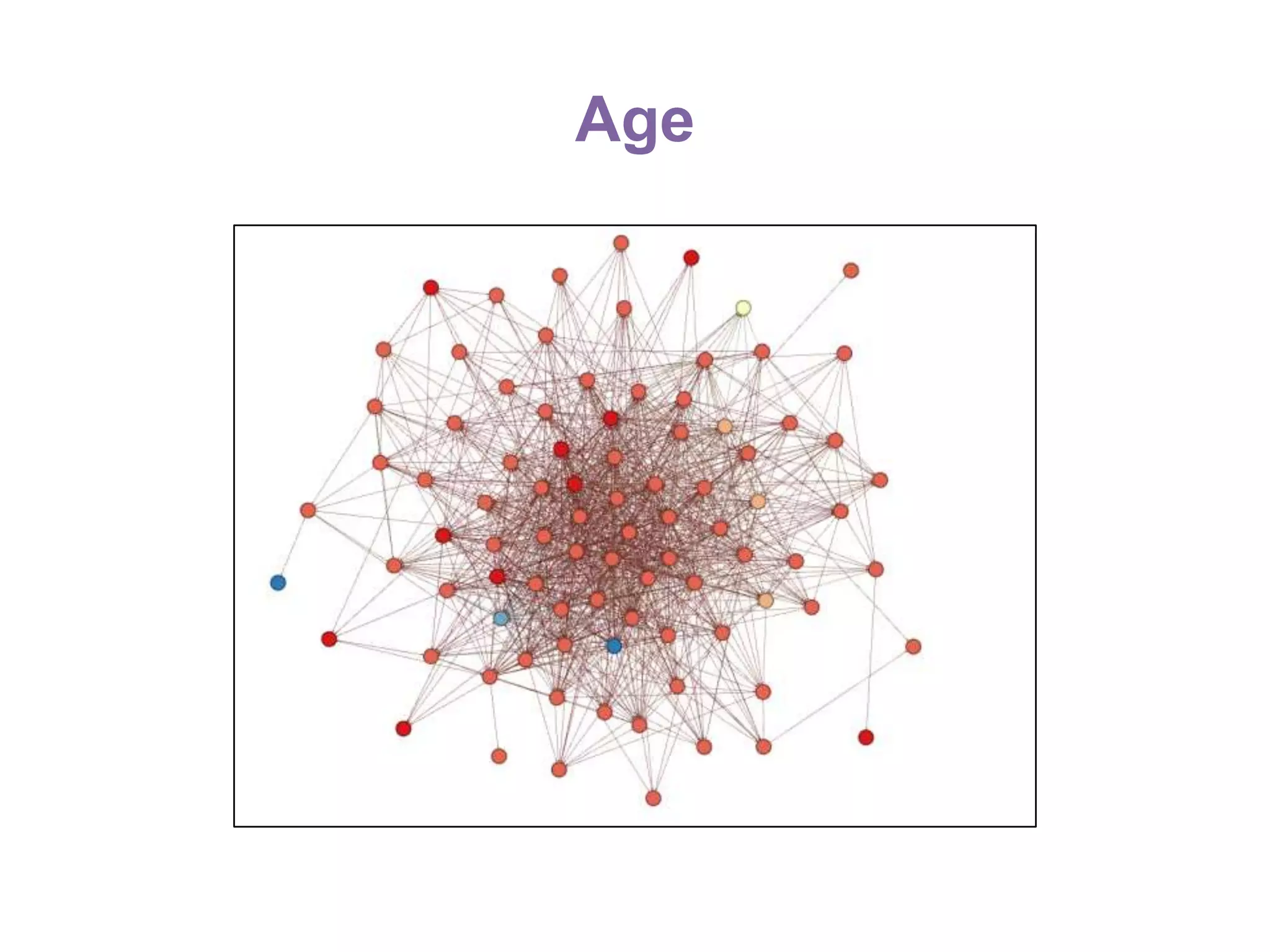
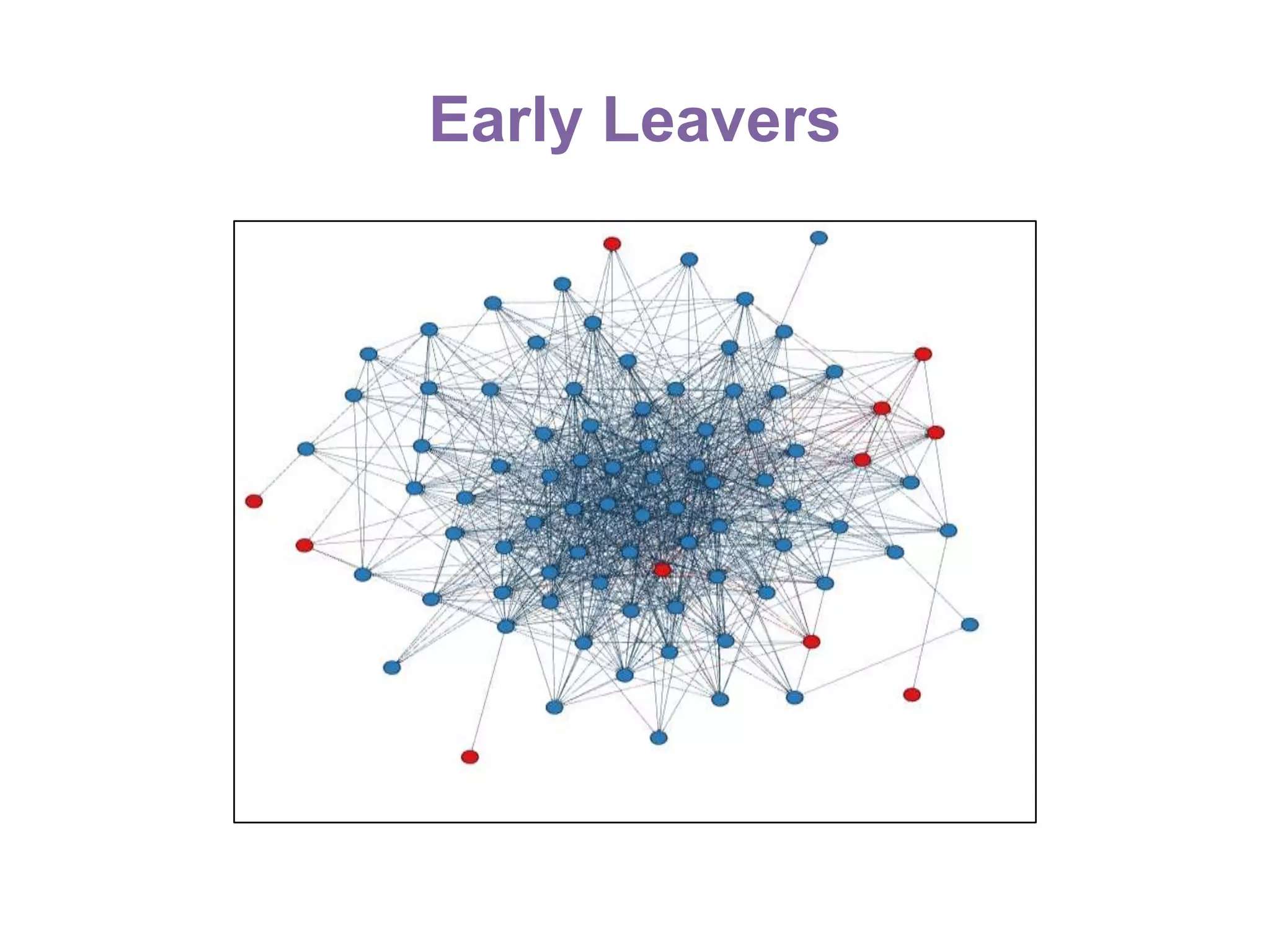
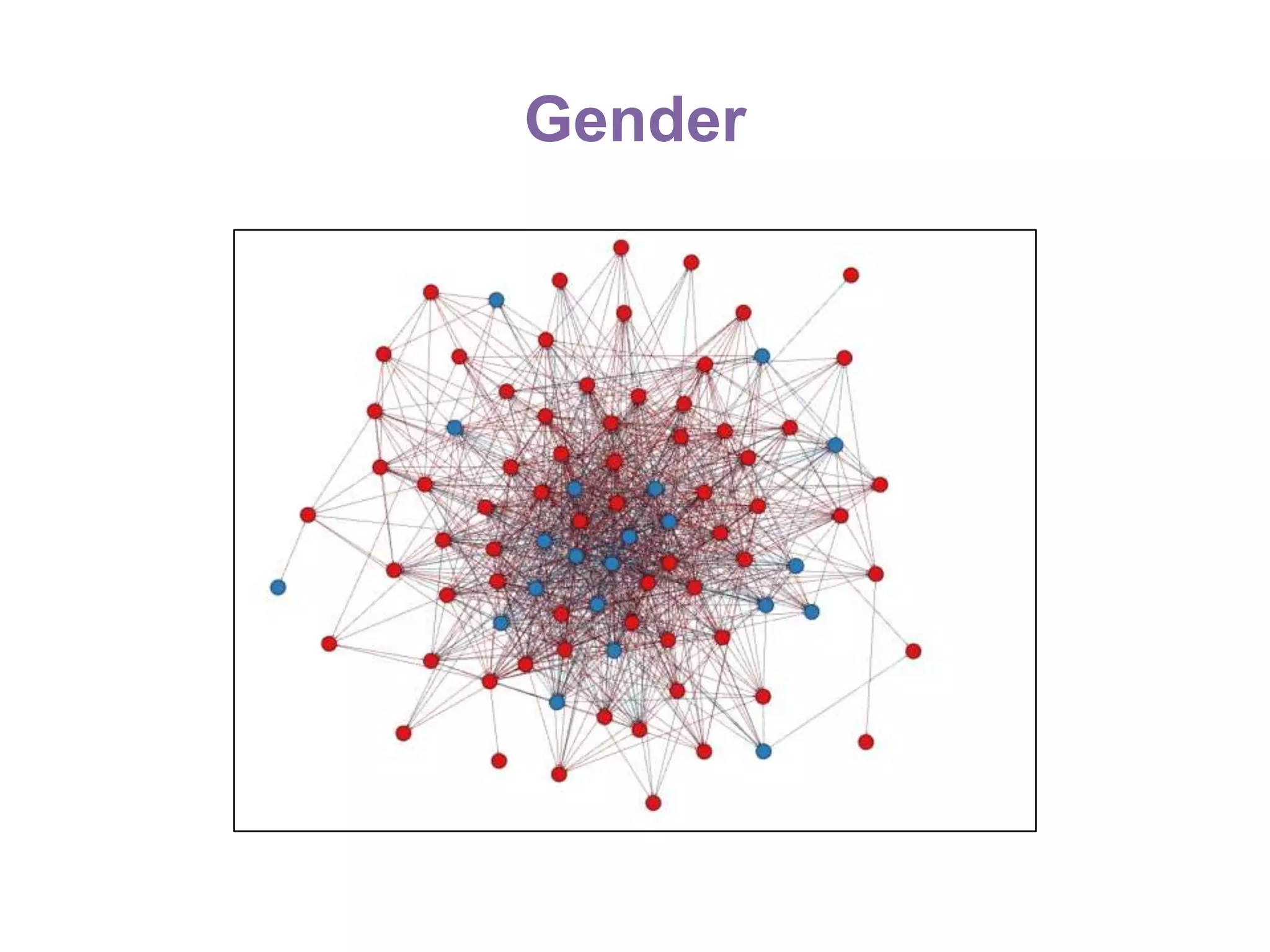
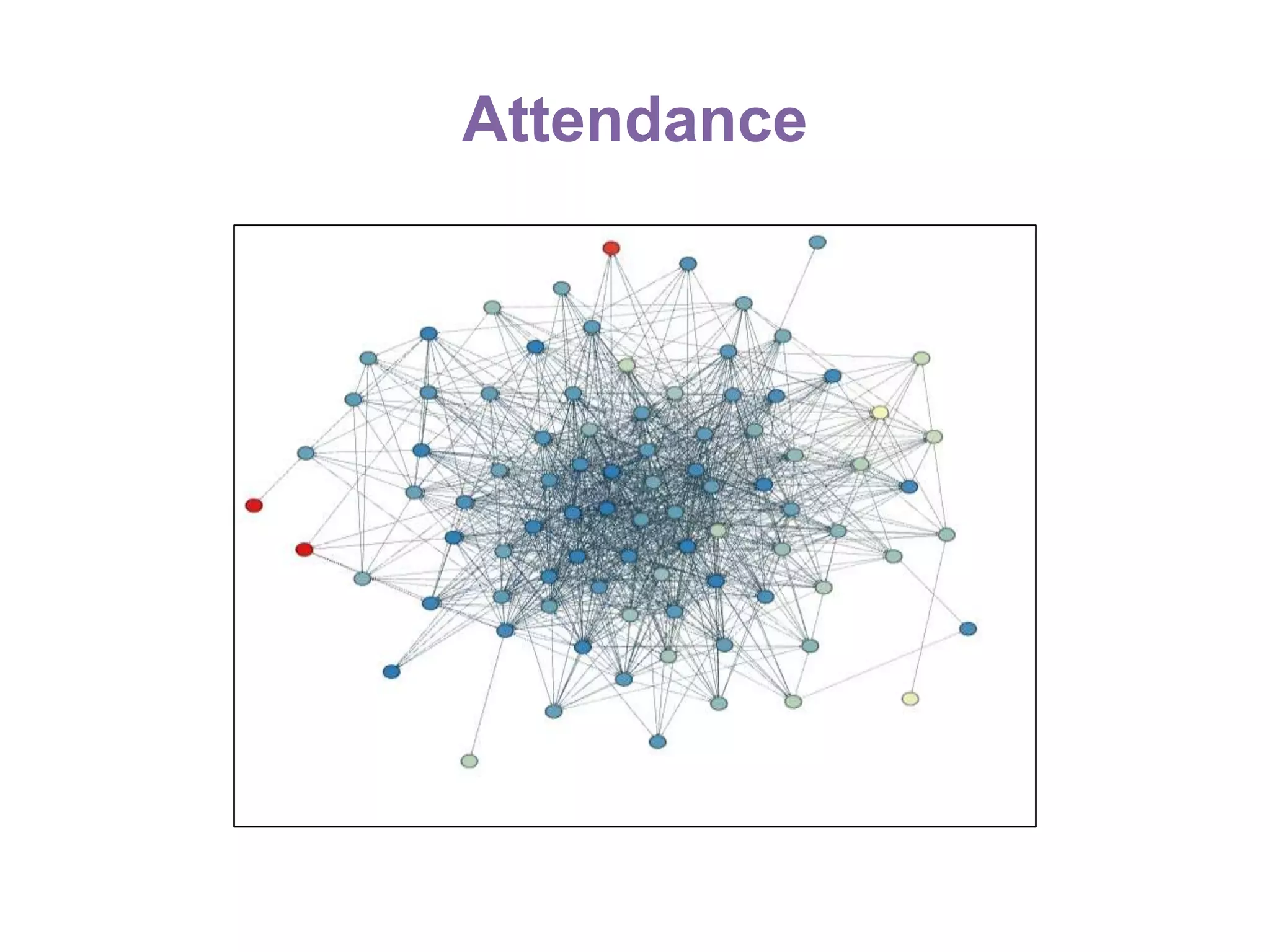
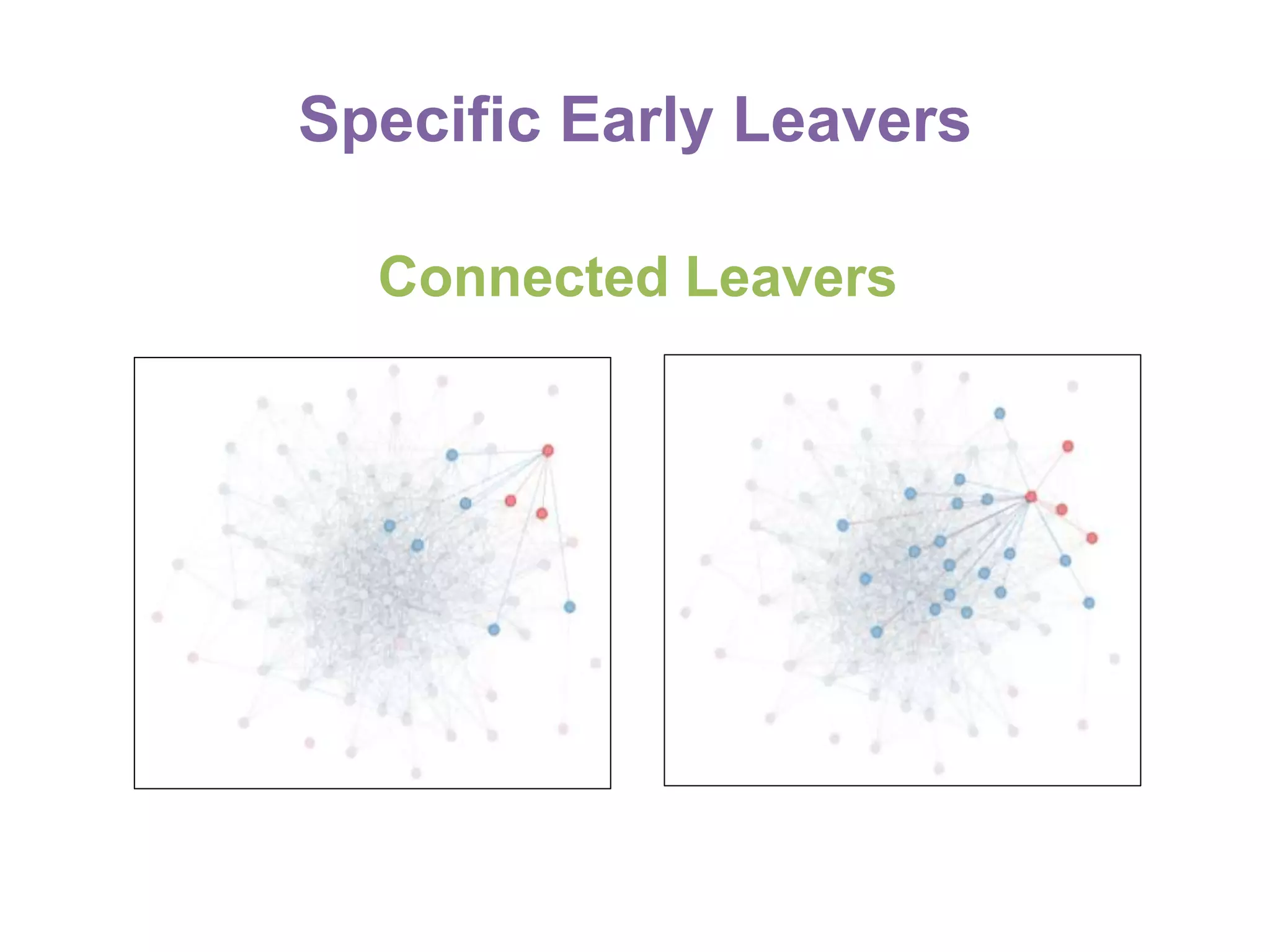
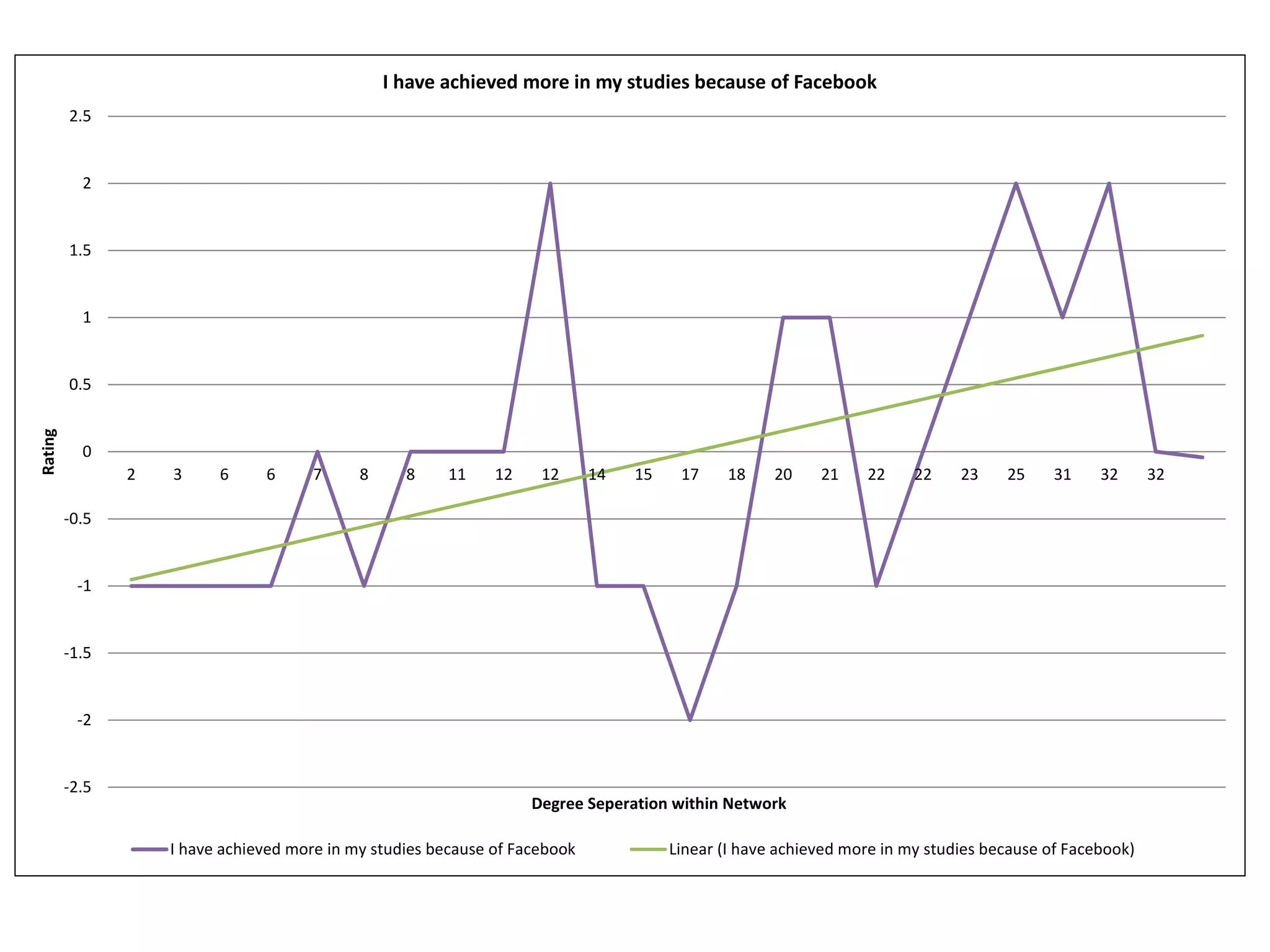
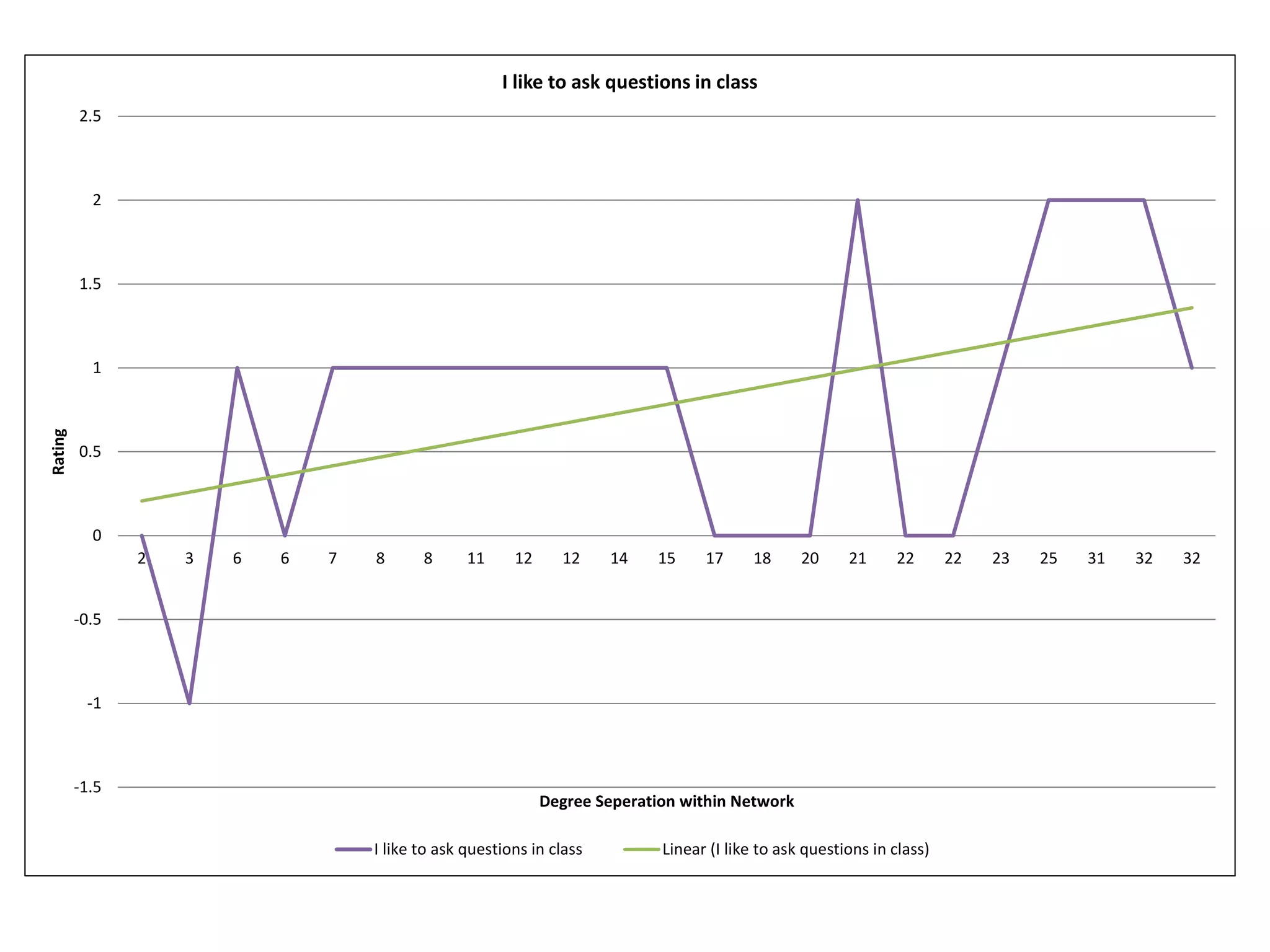
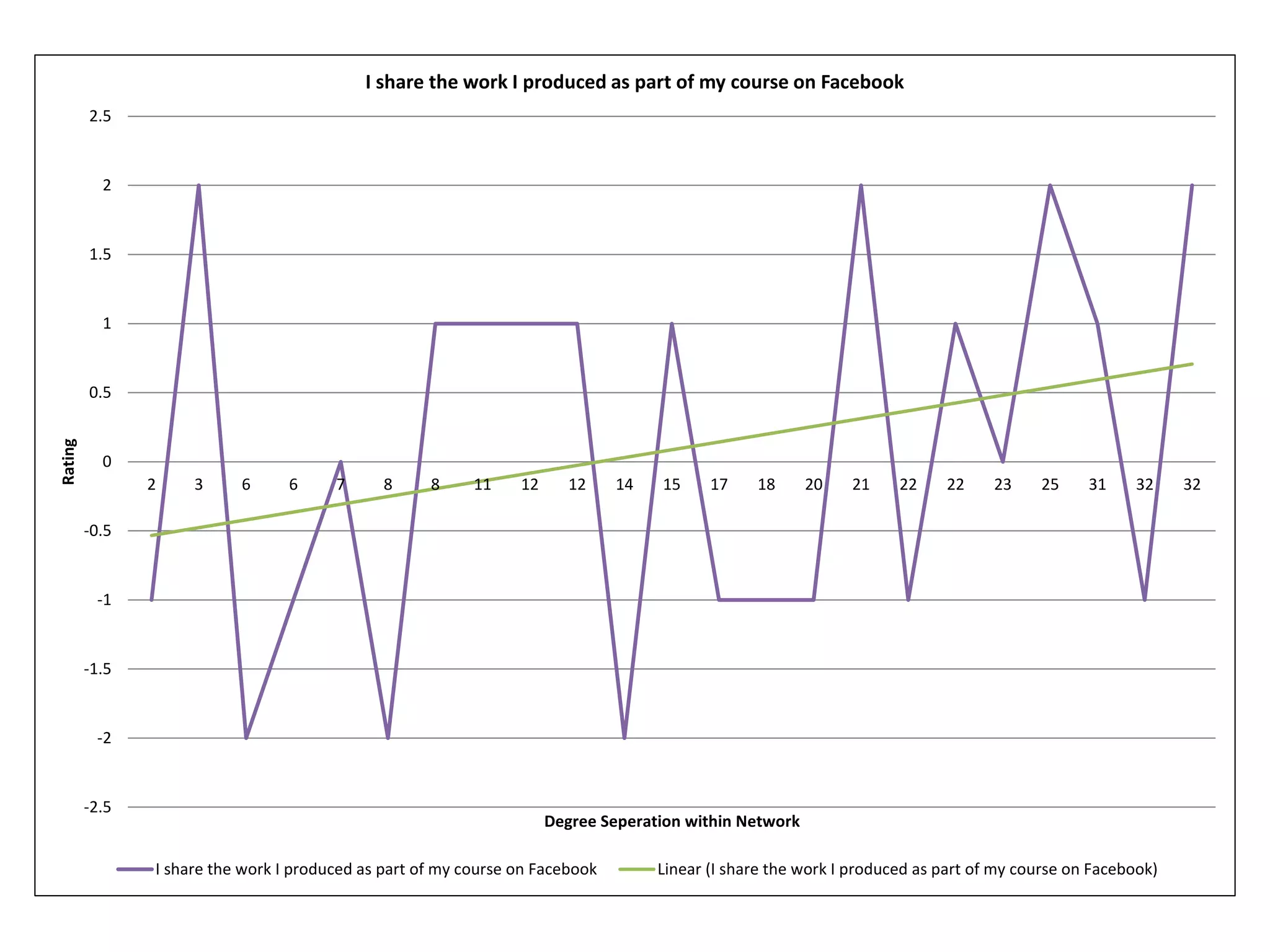
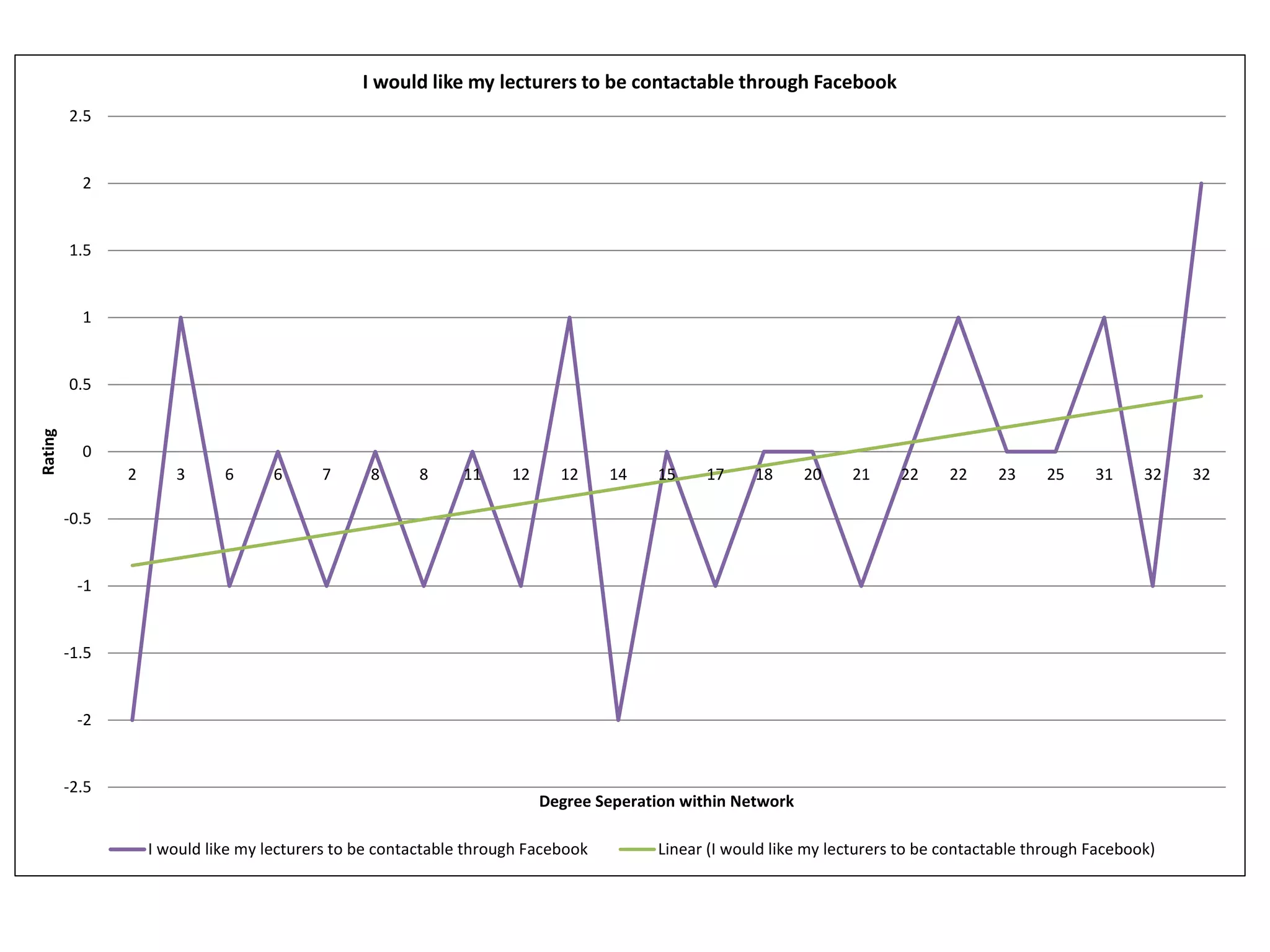
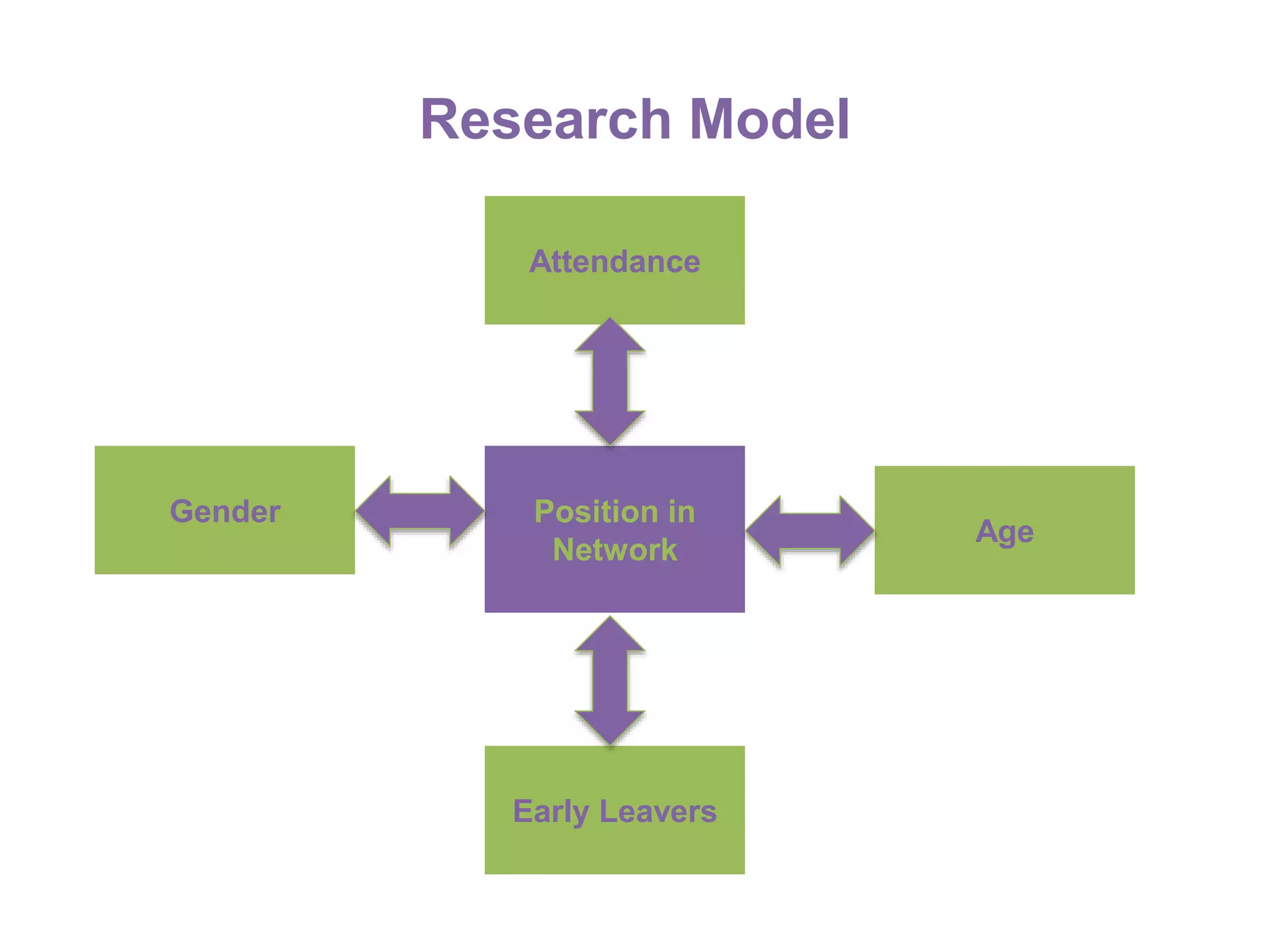
The document summarizes research on using Facebook and social network analysis to predict which students may be at risk of not completing a further education course. A study was conducted analyzing the Facebook networks and survey responses of 90 students. Key findings included identifying "hub" students with many connections, and correlations between centrality in the network and factors like gender, age, attendance, and early departure. The conclusion recommends continued testing of this model to help identify at-risk students earlier and maximize weak social ties.