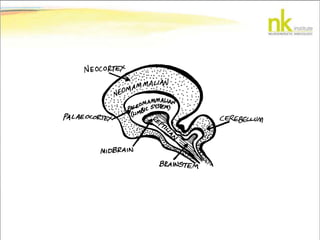
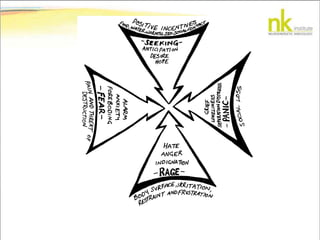
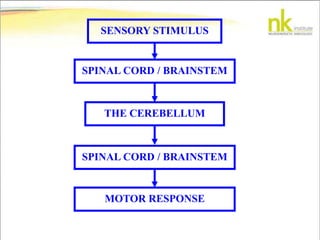
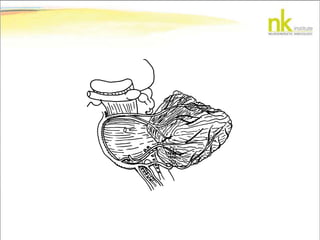
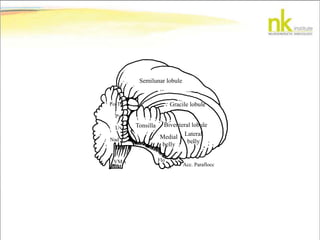
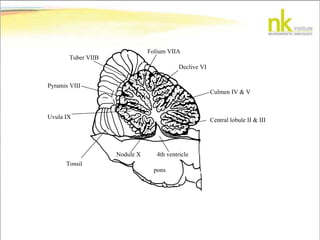
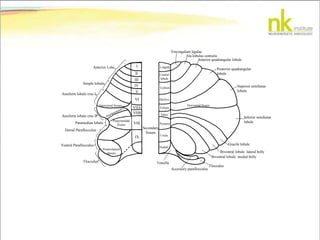
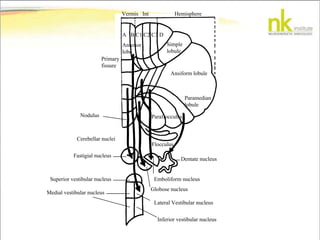
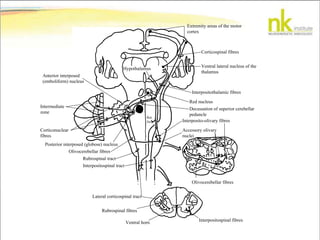
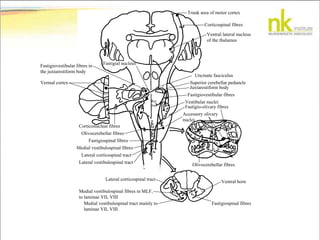
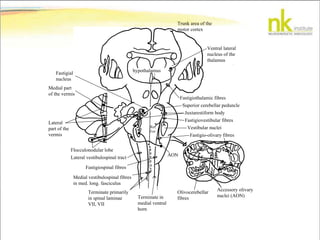
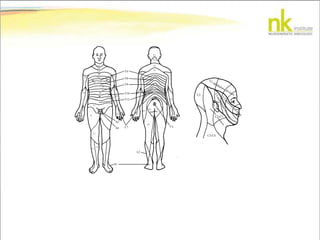
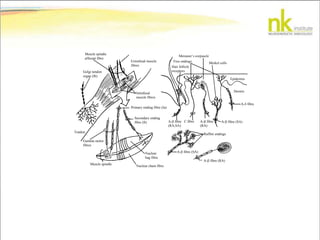
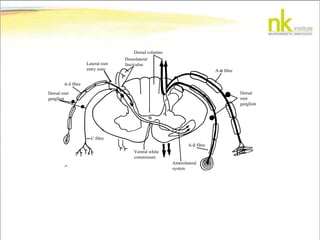
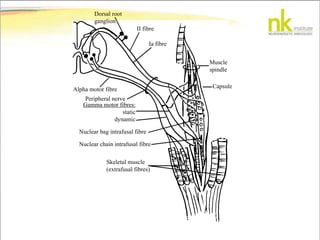
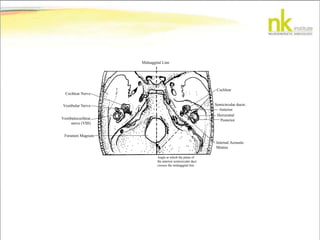
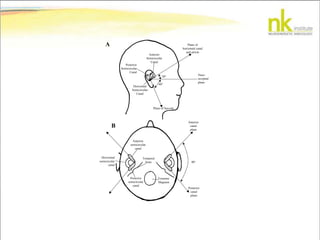
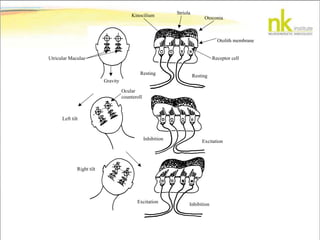
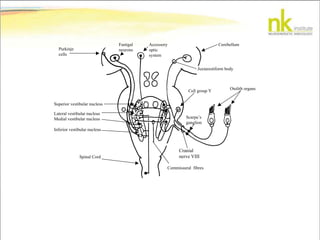
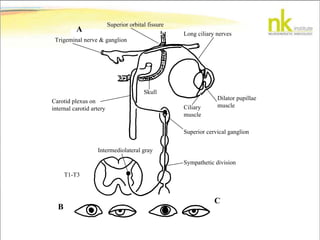
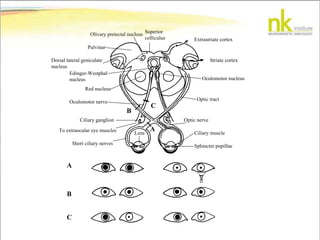
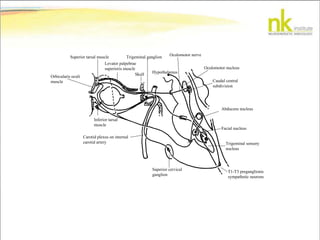
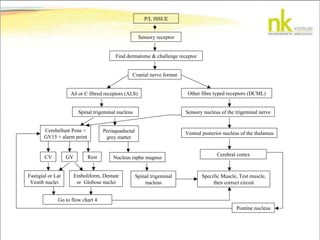
The document discusses Jaak Panksepp's model of the brain's emotional systems, known as the "triune brain". It describes seven core emotional systems - SEEKING, RAGE, FEAR, PANIC/DISTRESS, CARE/NURTURE, PLAY, and LUST - each of which is associated with different affective feelings and motivations. It also outlines Panksepp's three-level model of motor control in the brain - the neomammalian cortex, limbic system, and reptilian reflex system. Finally, it provides diagrams of the neurological pathways and structures involved in sensory processing and motor control.