This document discusses requirements and technologies for autonomous vehicle systems. It outlines:
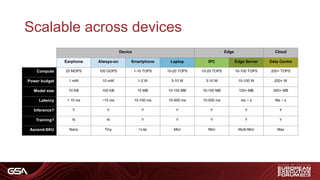
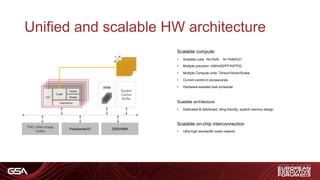
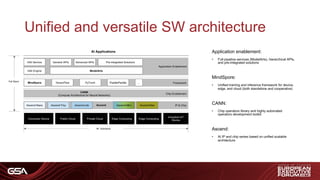
1) Requirements for automotive system-on-chips including high performance processors, CNN acceleration, memory, sensor interfaces, and safety/reliability standards.
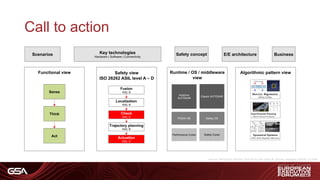
2) Levels of vehicle automation from driver assistance to full autonomy, describing example scenarios and hardware/software needs at each level.
3) An architecture for autonomous driving including sensor fusion, localization, safety checking, planning and actuation with varying Automotive Safety Integrity Level (ASIL) requirements.



![Strongest specialized cores, hundreds of cores, stacked memory with
highest bandwidth, strongest IO interface à 16 PCIe 3.0 lanes, special
interconnect for accelerator to accelerator communication,
acceleration for artificial intelligence à training and inference,
acceleration for linear algebra, strongest vector units, highest energy
consumption à 300W.
Stronger general cores, tens of cores à 12 – 24 cores, standard
memory interfaces with high memory bandwidth, strongest IO
interfaces à 48-128 PCIe 3.0 lanes, strong vector units, high energy
consumption à 120-170W.
Medium general cores à 8 – 16 cores, standard memory interface
with medium bandwidth, strong IO interface à 16 PCIe 3.0 lanes, low
energy consumption à10 – 30W.
Strong general cores, tens of cores à 48 - 64, standard memory
interfaces with high memory bandwidth, strongest IO interfaces à 48-
128 PCIe 3.0 lanes, strong vector units in high-end version, integrated
controllers à USB, SATA, cryptography, integrated network à
Standard Ethernet and RoCEE, medium energy consumption à 50-
60W.
Medium general cores à 12 – 24, specialized engines à [GPU,
image, vision, signal processing, artificial intelligence, security and
compression], integrated network à CAN/CAN-FD and Automotive
Ethernet, integrated camera interfaces à 8-12, integrated display
interface à 3 – 6, automotive functional safety à [dual execution
including lockstep operation, functional diversity, build-in self test] à
ASIL B – ASIL D, lower power mode à [adaptive voltage scaling,
dynamic voltage and frequency scaling, power and power gating],
high energy efficiency à 15W – 60W.
Weak to medium general cores à 8, very specialized engines à
[GPU, image, vision, signal processing and artificial intelligence], high
memory bandwidth, strongest IO interface à 16 PCIe 3.0 lanes,
integrated network à CAN/CAN-FD and Automotive Ethernet,
integrated camera interfaces à 12-18, automotive functional
safety à [dual execution including lockstep operation, functional
diversity, build-in self test] à ASIL B – ASIL D, highest energy
efficiency à 5W – 30W.
IT & Cloud Embedded & Edge Automotive
Accelerators
CPUs
Integrated
Systems
Smart
Devices
Cloud Embedded
Specialization in vertical industry HighLow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2019eefheikojoergschickv4-linkedin-200209150917/85/The-Smarter-Car-for-Autonomous-Driving-5-320.jpg)