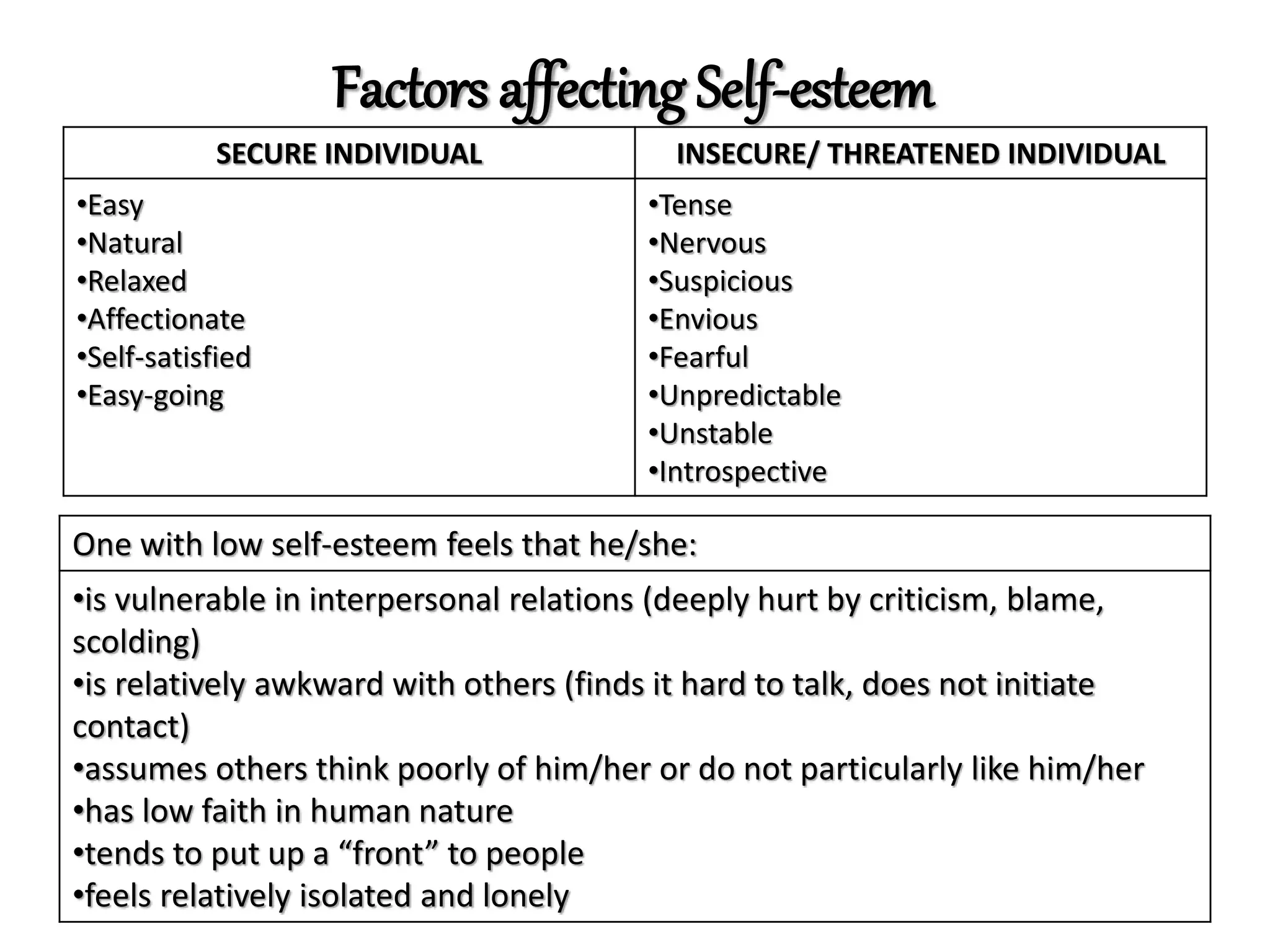
The document explores the concept of self, emphasizing the importance of understanding one's identity through the interplay of heredity, environment, and social interactions. It details the characteristics and development of the self, highlighting the transformative processes of self-concept, self-esteem, and authenticity. Additionally, it discusses various psychological mechanisms for self-adjustment and personal growth, reflecting on how these contribute to an individual's sense of meaning and value in life.