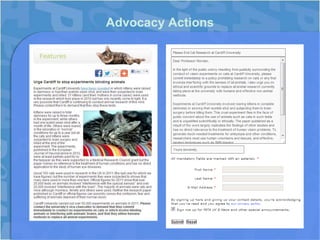
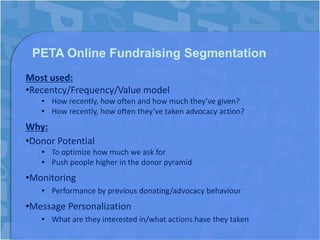
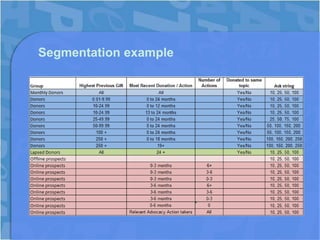
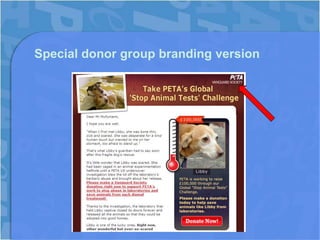
This document discusses segmentation in charity communications. [1] It provides examples of how PETA segments its online supporters based on data from petitions, pledges, donations and advocacy actions. [2] PETA tracks supporter interests in different animal issues and behaviors like location, frequency of support and recency of donations to personalize fundraising emails. [3] This results in higher donations, engagement and retention of supporters.