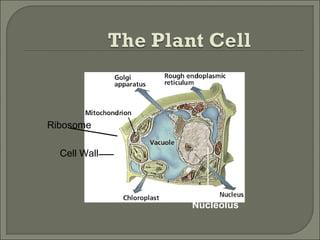
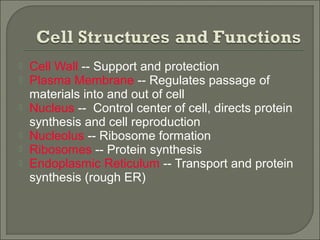
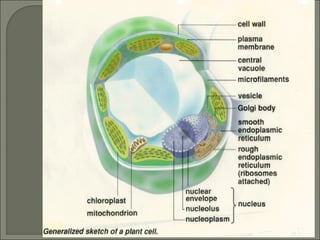
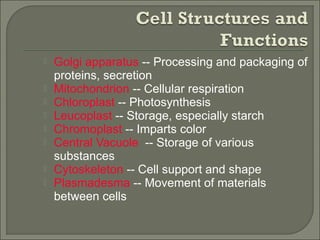
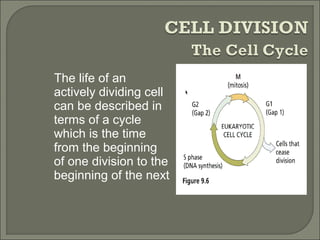
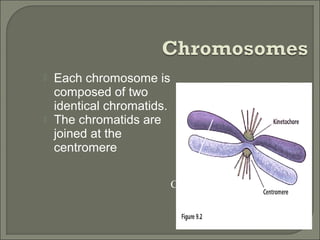
This document provides information about plant cell structure and function. It describes the various organelles found in plant cells, including the cell wall, plasma membrane, nucleus, nucleolus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, leucoplasts, chromoplasts, central vacuole, and cytoskeleton. It also explains how substances move in and out of cells through diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. The process of cell division through mitosis and cytokinesis is summarized.