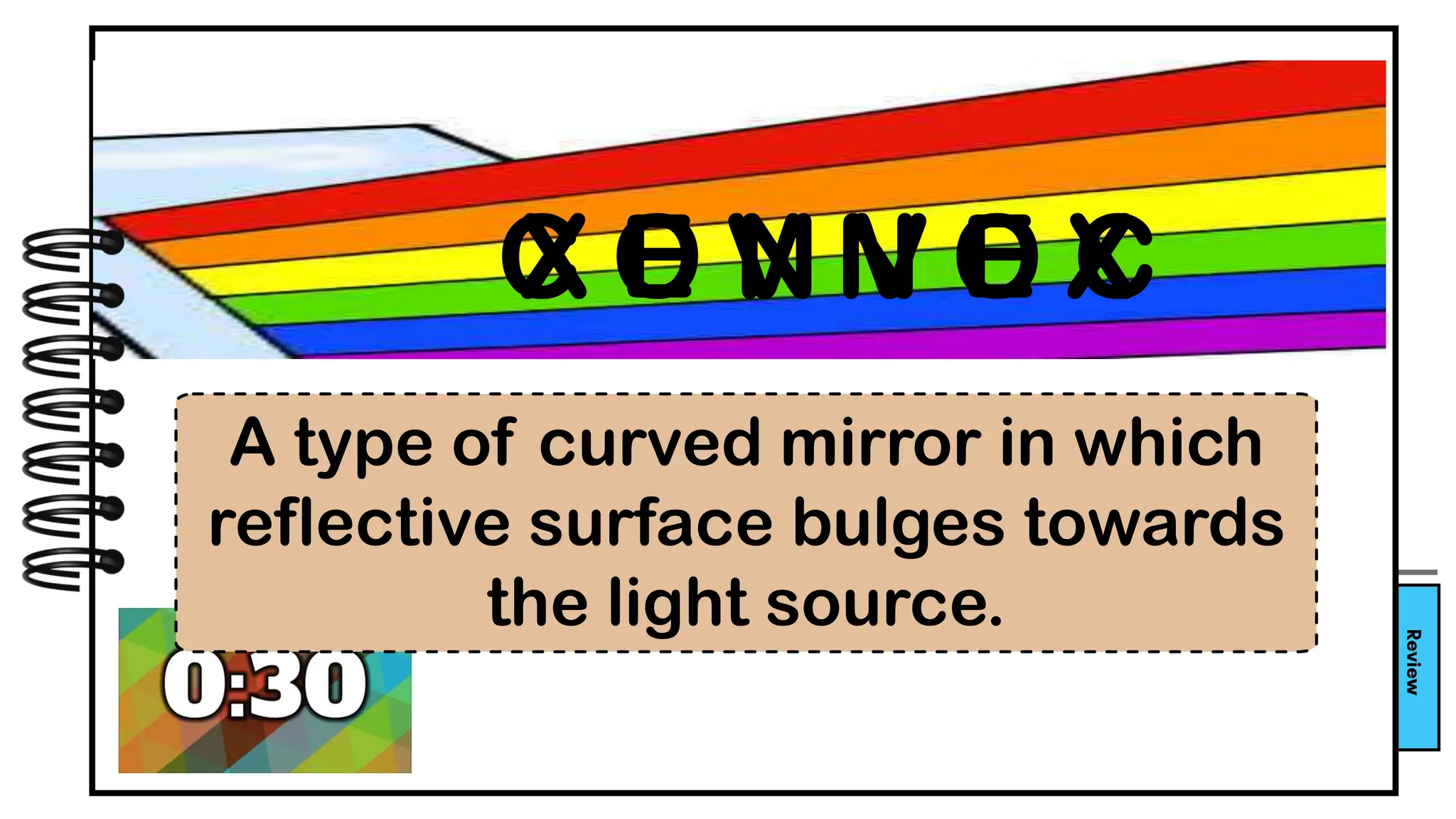
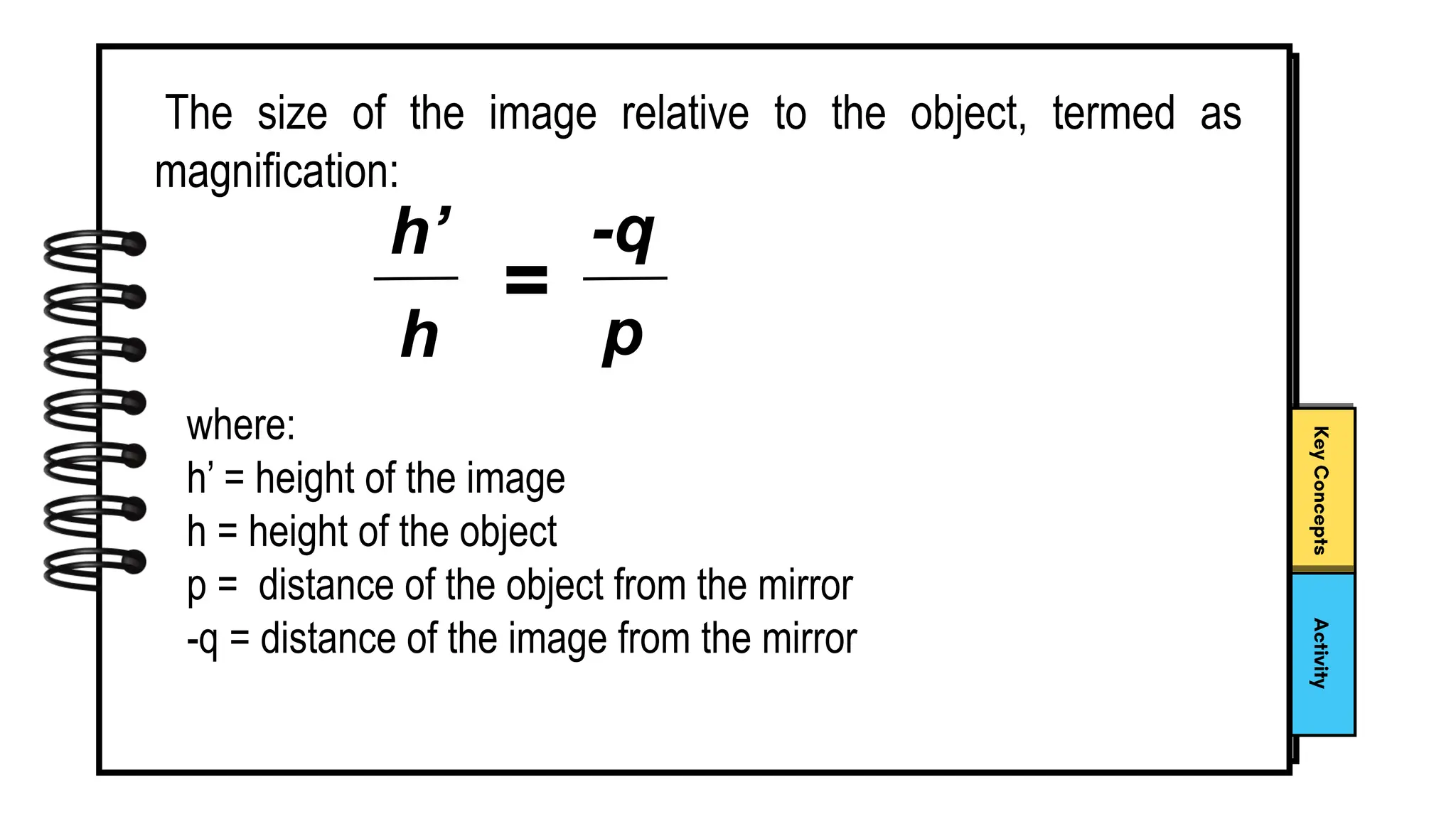
The document describes activities for students to learn about light and mirrors through unscrambling words and acting out gestures related to mirror terminology. Students are introduced to concepts like reflection, convex and concave mirrors. They practice using the mirror equation to calculate image distances and sizes for different object positions relative to curved mirrors.